0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views5 pagesRouter Configuration and Protocol Setup Guide
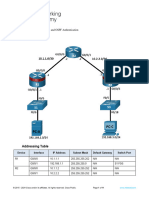
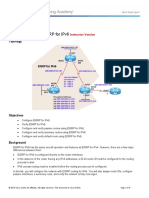
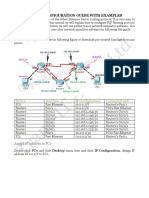
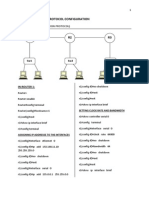
The document provides instructions for basic router configuration including hostname, passwords, banners, aliases, SSH, and routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, EIGRP. It includes configuration of interfaces, static routes, default routes, route redistribution, authentication, and verification commands.
Uploaded by
شيماء عياشيCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views5 pagesRouter Configuration and Protocol Setup Guide
The document provides instructions for basic router configuration including hostname, passwords, banners, aliases, SSH, and routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, EIGRP. It includes configuration of interfaces, static routes, default routes, route redistribution, authentication, and verification commands.
Uploaded by
شيماء عياشيCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd