0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views3 pagesSoil Permeability Coefficients Overview
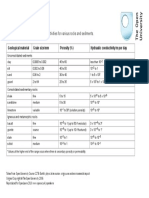
The document presents tables showing the ranges of permeability coefficients and saturated hydraulic conductivity for different types of soils and earth materials. Soil types with higher permeability like soft sand and gravel have coefficients from 102 to 107 m/day and conduct water rapidly from seconds to days. Finer grained soils with lower permeability like clay and tight rock can take years or centuries for water to pass through and have coefficients ranging from 10-6 to 10-7 m/day. Unconsolidated deposits, sandstones and fractured rocks generally have the highest permeability while clays and unfractured igneous rock have the lowest.
Uploaded by
Zahid UmairCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views3 pagesSoil Permeability Coefficients Overview
The document presents tables showing the ranges of permeability coefficients and saturated hydraulic conductivity for different types of soils and earth materials. Soil types with higher permeability like soft sand and gravel have coefficients from 102 to 107 m/day and conduct water rapidly from seconds to days. Finer grained soils with lower permeability like clay and tight rock can take years or centuries for water to pass through and have coefficients ranging from 10-6 to 10-7 m/day. Unconsolidated deposits, sandstones and fractured rocks generally have the highest permeability while clays and unfractured igneous rock have the lowest.
Uploaded by
Zahid UmairCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd