Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Big Picture: Ii. Gains From International Trade
Uploaded by
adzwinjOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Big Picture: Ii. Gains From International Trade
Uploaded by
adzwinjCopyright:
Available Formats
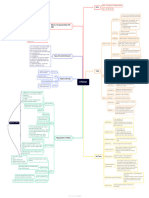
BIG PICTURE
5. International 1. International Trade International Economics
economics 1.1 Gains from trade
1.2 Barriers on free trade i. International Trade
1.3 Arguments for protectionism
ii. Gains from international trade
2. Balance of Payment - Benefits of specialization
2.1 Structure of balance of payment - Benefits of economies of scale
2.2 Corrections of Balance of Payment Deficit - Larger market
- Increased competition
- More and improved choices
- Transfer of technology and economic growth
- Promote beneficial relationship among countries
iii. Barrier/Restrictions to free trade
- Tariffs
- Import quotas
- Embargoes
- Voluntary Export Restrictions (VERs)
- Foreign Exchange (FOREX) controls
iv. Arguments for protection
- Infant-industry argument
- Employment argument
- National security argument
- Cheap foreign labour argument
- Antidumping argument
v. Balance of payments
vi. Structure of balance of payments
- Current account
vii. Capital and financial account
- Capital account
- Financial account
viii. Effects of balance of payment deficit
- Lower economic growth
- Increased indebtedness
- Depletion of official reserves
- Contractionary effects
- Devaluation of domestic currency
ix. Methods to reduce balance of payments deficit
- Stimulate exports and reuce imports
- Reduce aggregate demand
- Attract short-term capital inflows
- Reduce inflation
- Exchange rates
- Demand for foreign currency
- Foreign exchange market equilibrium
- Types of exchange rates
- Fixed (pegged) exchange rates
- advantages of fixed exchange rates
- disadvantages of flexible exchange rates
- Flexible/floating exchange rates
- advantages of fixed exchange rates
- disadvantages of flexible exchange rates
- Managed float
NOTES FROM STUDY GUIDE
Gains from trade 1. Theory of comparative advantage TRIEITMT
This explains that by specializing in goods where countries have a lower opportunity cost, there can
be an increase in economic welfare for all countries TERASA
INDAH
2. Reducing tariff barriers leads to trade creations ENAK
Trade creation occurs when consumption switches from high cost producers to low cost producers. IKHLAS
TANPA
3. Increased exports MAKANAN
As well as benefit for consumers importing goods, firms exporting gods where the UK has a TAMBAHAN
comparative advantage will also see a big improvement in economic welfare. Lower tariffs on UK
exports will enable a higher quantity of exports boosting UK jobs and economic growth.
4. Economies of scale
If countries can specialize in certain goods, they can benefit from economies of scale and lower
average costs, this is especially true in industries with high fixed costs or that require high levels of
investment. The benefits of economies of scale will ultimately lead to lower prices for consumers.
5. Increased competition
With more trade, domestic firms will face more competition from abroad. Therefore there will be
more incentives to cut costs and increase efficiency. It may prevent domestic monopolies from
charging too high prices.
6. Trade is an engine for growth
World trade has increased by an average of 7 % since the 1945, causing this to be one of the big
contributors to economic growth.
7. Make use of surplus raw materials
Middle Eastern countries such as Qatar are very rich in reserves of oil but without trade there would
be not much benefit in having so much oil. Japan, on the other hand, has very few raw material.
Without trade, it would be very poor.
8. Tariffs may encourage inefficiency
If an economy protects its domestic industry by increasing tariffs, industries may not have any
incentives to cut costs.
Barriers on free trade Despite the advantages of free trade, countries may wish to restrict import for various reasons.
This can be done through different methods:
1. Tariffs
This is a tax on imports
2. Quotas
This is a physical limits on the quantity of imports
3. Embargoes
This is a total ban on goods. It may be done to stop dangerous substances.
4. Subsidies common
If a government subsidises production, this gives them an unfair advantage over competitors. This is
quite common.
5. Administrative barriers
Arguments for 1. Infant industry argument
protectionism If developing countries have industries that are relatively new, then at that moment these industry’s
would struggle against international competition.
However, if they invested in the future, (wait for the industry to mature) they may be able to gain
comparative advantage
This shows that comparative advantage can change over time.
Therefore protection would allow them to progress and gain experience to enable them to compete
in the future.
2. The senile industry argument
If industries are declining and inefficient, they may require large investment to make them efficient
again.
Protection for these industries would act as an incentive for firms to invest and reinvent themselves.
However, protectionism could also be an excuse for protecting inefficient firm.
3. To diversify the economy
Many developing countries rely on producing primary products in which they currently have a
comparative advantage.
However, relying on agricultural products has several disadvantages:
- Prices can fluctuate due to environmental factors
- Goods have a low income elasticity of demand. Therefore with economic growth,
demand will only increase a little.
4. Raise revenue for the government
Import taxes can be used to raise money for the government. However, this will only be a small
amount of money.
5. Help the balance of payments
Reducing imports can help the current account.
However, in the long term, this is likely to lead to retaliation. So in order to avoid retaliation, imports
must be allowed to continue.
6. Cultural identity
This is not really an economic argument but more political and cultural..
Many countries with to protect their countries from what they see as an Americanisation or
commercialization of their countries.
(WHAAAATTT?????P APA KAITAAAAAAN????)
7. PROTECTION AGAINST DUMPING
The EU sold a lot of its food surplus from the CAP at very low prices on the world market.
This caused problems for world farmers because they saw a big fall in their market prices.
8. Environmental
It is argued that free trade can harm the environment because LDC may use up natural reserves of
raw materials to export.
Also, countries with strict pollution controls mayfind consumers import the gods from other countries
where legislation is lax and pollution is allowed.
However, supporters of free trade would argue that it is up to individual countries to create
environmental legislation.
You might also like
- Pension Fund RiskDocument2 pagesPension Fund RiskSOPHIA-VNo ratings yet
- Business Sector Household Sector: Foreign Sector Government Sector Capital MarketDocument1 pageBusiness Sector Household Sector: Foreign Sector Government Sector Capital Marketkayla watanabeNo ratings yet
- wtr21 PresentationDocument22 pageswtr21 PresentationG.S.Malarmannan G.S.MalarmannanNo ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument110 pagesInternational Marketingbittu.abhishek99No ratings yet
- Final Accounts: Formats Business Name Statement of Financial Position As On - Assets: Non-Current AssetsDocument35 pagesFinal Accounts: Formats Business Name Statement of Financial Position As On - Assets: Non-Current AssetsHammad KhalidNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Concepts: Usman Shaukat - Revision Resources - 03364468467Document22 pagesMacroeconomics Concepts: Usman Shaukat - Revision Resources - 03364468467Usman Shaukat - 70642/TCHR/BGJTNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument3 pagesConcept MapblankNo ratings yet
- Inflation NotesDocument1 pageInflation Notestxwvwjn2vhNo ratings yet
- B. FIG Analyst Training - Partie IDocument186 pagesB. FIG Analyst Training - Partie IFabrizio100% (1)
- IBM - 5 UnitsDocument87 pagesIBM - 5 UnitsJ. KNo ratings yet
- Books Library - Online 06221845Hp3Q4Document16 pagesBooks Library - Online 06221845Hp3Q4ayoub sanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Matriks Prayogi Gunawan - 0311902001Document5 pagesTugas Matriks Prayogi Gunawan - 0311902001Prayogi GunawanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid 19 On The Banking Sector PDFDocument25 pagesImpact of Covid 19 On The Banking Sector PDFbhagyaNo ratings yet
- Instruments of Trade PolicyDocument8 pagesInstruments of Trade PolicyBhupendra SengarNo ratings yet
- 02-CatbaloganCity2018 AppendicesDocument107 pages02-CatbaloganCity2018 AppendicesRoldz LariosNo ratings yet
- Projected - Suman KharelDocument41 pagesProjected - Suman KharelSuman kharelNo ratings yet
- I N D I A, 2 0 0 7: TelecommunicationsDocument41 pagesI N D I A, 2 0 0 7: Telecommunicationsreba_sNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in AccountingDocument4 pagesReviewer in AccountingJIYAN BERACISNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Second Quarter NotesDocument7 pagesFabm 2 Second Quarter NotesBIGTING, DANIANA MEURNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Businessstudy Notes Chapter 9 Studyguide360Document22 pagesClass 12 Businessstudy Notes Chapter 9 Studyguide360Aaditi VNo ratings yet
- SOC ENG Jan Jun 2021 PDFDocument19 pagesSOC ENG Jan Jun 2021 PDFJunaid Iqbal MastoiNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Theories ReviewerDocument19 pagesPart 1 Theories ReviewerNey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Edgereport Abslamc Iponotes 28-09-2021 285Document20 pagesEdgereport Abslamc Iponotes 28-09-2021 285sudhansumail102No ratings yet
- Ifrs Vs Ifrs For SmesDocument11 pagesIfrs Vs Ifrs For SmesKelvin Yu100% (1)
- Calculation SheetDocument9 pagesCalculation SheetPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Theories ReviewerDocument18 pagesPart 1 Theories ReviewerNey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows - How To Construct Statement of Cash FlowsDocument5 pagesIAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows - How To Construct Statement of Cash FlowsReenestus DumeniNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting NotesDocument7 pagesFinancial Accounting NotesGan JessieNo ratings yet
- PFRS of SME and SE - Concept MapDocument1 pagePFRS of SME and SE - Concept MapRey OñateNo ratings yet
- Money, Banking, and Monetary Policy Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesMoney, Banking, and Monetary Policy Cheat Sheet: by ViaAli Aqeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Money, Banking, and Monetary Policy Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesMoney, Banking, and Monetary Policy Cheat Sheet: by ViaAli Aqeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Introduction PDFDocument12 pagesINTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Introduction PDFIla GuptaNo ratings yet
- 上海CMA新P2 5Document67 pages上海CMA新P2 5geng chenNo ratings yet
- Processes of Financial ManagementDocument7 pagesProcesses of Financial ManagementHarryNo ratings yet
- Batch 2024 - Intermediate Accounting 1Document115 pagesBatch 2024 - Intermediate Accounting 1Zia NuestroNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Economic and Technological GlobalizationDocument2 pagesContemporary World - Economic and Technological GlobalizationRika MiyazakiNo ratings yet
- 2023 L3 Section3Document122 pages2023 L3 Section3PrarthanaRavikumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1. Multinational Finance Management OverviewDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1. Multinational Finance Management OverviewKim NgânNo ratings yet
- Sme VS PFRSDocument17 pagesSme VS PFRSDesai SarvidaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-PostDocument45 pagesLecture 3-PostcoolirlbbNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundDocument43 pagesMutual FundSachi LunechiyaNo ratings yet
- Windham Capital Diversified StrategiesDocument2 pagesWindham Capital Diversified StrategiesdimtharsNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Prelims: Chapter 1Document18 pagesAccounting: Prelims: Chapter 1Noah OfelNo ratings yet
- Presentation Financial Risk ManagementDocument33 pagesPresentation Financial Risk ManagementDeniz OnalNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - FAR 6804 NotesDocument1 pageWeek 1 - FAR 6804 NotesKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Pas 1 PDFDocument1 pagePas 1 PDFJohn Paul BeloyNo ratings yet
- Micro Essays 2021 Only GR 12Document42 pagesMicro Essays 2021 Only GR 12wisanimarksNo ratings yet
- 2019 Revision Notes 8 - Chapter 8 6Document9 pages2019 Revision Notes 8 - Chapter 8 6Sarah RetzNo ratings yet
- A Case For Sustainable FinancingDocument15 pagesA Case For Sustainable FinancingammendNo ratings yet
- AS Economics Chapter 9Document4 pagesAS Economics Chapter 9Rao AliNo ratings yet
- SOC ENG Jan Jun 2024Document22 pagesSOC ENG Jan Jun 2024yasir2020.iqbalNo ratings yet
- 6Document1 page6Laskar REAZNo ratings yet
- CMA Inter FM Past Paper Question Trend+ Chapter Analysis XLSX GoogleDocument1 pageCMA Inter FM Past Paper Question Trend+ Chapter Analysis XLSX GoogleNARAYANNo ratings yet
- Security: DiscoveryDocument39 pagesSecurity: DiscoverySayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Lecture ONE Accounting For ManagerDocument30 pagesLecture ONE Accounting For Managermohamed elsabahiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Islamic Financial Instruments and Contracts For Impact InvestingDocument60 pagesModule 4 Islamic Financial Instruments and Contracts For Impact InvestingMayolla Suci EksaNo ratings yet
- Solution Financial Accounting FundamentalsDocument9 pagesSolution Financial Accounting FundamentalsbillNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesFinancial StatementsGhillian Mae GuiangNo ratings yet
- Managing Global Financial and Foreign Exchange Rate RiskFrom EverandManaging Global Financial and Foreign Exchange Rate RiskNo ratings yet
- Sequence of Listening and Learning DomainsDocument1 pageSequence of Listening and Learning DomainsadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Prep For TradeDocument1 pageTest 1 Prep For TradeadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Eco Test 1 Prep NotesDocument3 pagesEco Test 1 Prep NotesadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech TextDocument2 pagesInformative Speech TextadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Monroe's Motivated Sequence AttentionDocument4 pagesMonroe's Motivated Sequence AttentionadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Exporter Guide Canberra Australia 11-7-2018Document13 pagesExporter Guide Canberra Australia 11-7-2018adzwinjNo ratings yet
- Part B Past Year Questions Ibm537Document10 pagesPart B Past Year Questions Ibm537adzwinj100% (1)
- Writing A Resume PDFDocument4 pagesWriting A Resume PDFadzwinjNo ratings yet
- IBM537 Chapter 1 PowerPoint LectureDocument14 pagesIBM537 Chapter 1 PowerPoint LectureadzwinjNo ratings yet
- F S S M T W T F S S: Semester 1 Mid-Sem Break Catch Up + Sharpen Up Basics + Advance!! Perform!!Document1 pageF S S M T W T F S S: Semester 1 Mid-Sem Break Catch Up + Sharpen Up Basics + Advance!! Perform!!adzwinjNo ratings yet
- ECO Muet MGT420 ACC406 LAW416 Kemas Kemas: 1. Malaysian Legal System - Sources - Courts - How To MakeDocument3 pagesECO Muet MGT420 ACC406 LAW416 Kemas Kemas: 1. Malaysian Legal System - Sources - Courts - How To MakeadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Economics PDFDocument44 pagesEconomics PDFyesuNo ratings yet
- Gr11 - Worksheet - Demand & SupplyDocument2 pagesGr11 - Worksheet - Demand & Supplysnsmiddleschool2020No ratings yet
- Relationship Manager 0Document1 pageRelationship Manager 0Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Beverages BotswanaDocument8 pagesCoca Cola Beverages BotswanaTshepiso RankoNo ratings yet
- Chap016 Managerial ControlDocument40 pagesChap016 Managerial ControlHussain Ali Y AlqaroosNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1: Conceptual Framework: Intermediate Accounting I Spring 2017Document38 pagesCh. 1: Conceptual Framework: Intermediate Accounting I Spring 2017Dyana AlkarmiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To ReinsuranceDocument188 pagesAn Introduction To Reinsurancecruzer11290No ratings yet
- IELTS Task 1Document12 pagesIELTS Task 1saidur183No ratings yet
- Leins - 2020 - Responsible Investment' ESG and The Post-CrisisDocument22 pagesLeins - 2020 - Responsible Investment' ESG and The Post-Crisisjuliette.geisingerNo ratings yet
- Thesis AbstractDocument7 pagesThesis AbstractJianneDanaoNo ratings yet
- Term Report - Mahmood Iqbal-05157Document5 pagesTerm Report - Mahmood Iqbal-05157Mahmood IqbalNo ratings yet
- Teachers ATM Cards As Loan Collateral: The In-Depth Look Into ATM "Sangla" SchemeDocument17 pagesTeachers ATM Cards As Loan Collateral: The In-Depth Look Into ATM "Sangla" SchemeJan Reindonn MabanagNo ratings yet
- Employees' State Insurance General Regulations 1950Document102 pagesEmployees' State Insurance General Regulations 1950P VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Accrual Accounting PDFDocument118 pagesIntroduction Accrual Accounting PDFHi nice to meet you100% (1)
- Administering Subsidiary Accounts and Ledgers PDFDocument33 pagesAdministering Subsidiary Accounts and Ledgers PDFnigus78% (9)
- Prelims Finals InvestmentDocument45 pagesPrelims Finals InvestmentGelo AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Public: Alliances Transform AidDocument7 pagesPublic: Alliances Transform AidVanesa JuarezNo ratings yet
- Principle - DISCIPLINE - Management DiaryDocument8 pagesPrinciple - DISCIPLINE - Management Diaryharsh inaniNo ratings yet
- Coal India Limited ProjectDocument61 pagesCoal India Limited ProjectShubham KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Jensen-1991-Corporate Control and The Politics of FinanceDocument23 pagesJensen-1991-Corporate Control and The Politics of Financeebrahimnejad64No ratings yet
- Item Master TemplateDocument6 pagesItem Master TemplatenrupenvarthyNo ratings yet
- Appraisal of Bank Verification Number (BVN) in Nigeria Banking SystemDocument37 pagesAppraisal of Bank Verification Number (BVN) in Nigeria Banking SystemABDULRAZAQNo ratings yet
- Indiana Free MoneyDocument226 pagesIndiana Free Moneyjohnadams8814100% (1)
- ACC 201 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageACC 201 Cheat Sheet: by ViaAnaze_hNo ratings yet
- BAB 3 - Marketing For Financial InstitutionsDocument47 pagesBAB 3 - Marketing For Financial InstitutionsSyai GenjNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis Case Study 2009: Jarryd Phillips, Jermaine West, Spencer Jacoby, Othniel Hyliger, Steven PelletierDocument47 pagesStrategic Analysis Case Study 2009: Jarryd Phillips, Jermaine West, Spencer Jacoby, Othniel Hyliger, Steven PelletierDiksha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FinTechDocument34 pagesIntroduction To FinTechvarun022084100% (4)
- Nike Pestle AnalysisDocument11 pagesNike Pestle AnalysisdarshininambiarNo ratings yet
- Uob - Fintech in AseanDocument49 pagesUob - Fintech in AseanTrader CatNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 English Agricultural-MarketDocument29 pagesChapter-4 English Agricultural-MarketThach Nguyen Thi ThienNo ratings yet