Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ancient
Uploaded by
Laura MiftodeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ancient
Uploaded by
Laura MiftodeCopyright:
Available Formats
Ancient
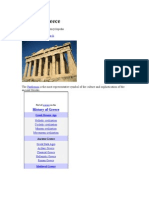
Ancient Greece was a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history from the Greek Dark
Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of antiquity (c. 600 AD). Immediately following this
period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era.[1] Roughly three
centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to
form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the period of Archaic Greece and colonization of the
Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the period of Classical Greece, an era that began
with the Greco-Persian Wars, lasting from the 5th to 4th centuries BC. Due to the conquests
by Alexander the Great of Macedonia, Hellenistic civilization flourished from Central Asia to the
western end of the Mediterranean Sea. The Hellenistic period came to an end with
the conquests and annexations of the eastern Mediterranean world by the Roman Republic,
which established the Roman province of Macedonia in Roman Greece, and later the province
of Achaea during the Roman Empire.
Classical Greek culture, especially philosophy, had a powerful influence on ancient Rome, which
carried a version of it to many parts of the Mediterranean Basin and Europe. For this reason
Classical Greece is generally considered to be the seminal culture which provided the foundation
of modern Western culture and is considered the cradle of Western civilization.
You might also like
- Timeline of Ancient History: (Common Era Years in Astronomical Year Numbering)Document10 pagesTimeline of Ancient History: (Common Era Years in Astronomical Year Numbering)deepakNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesAncient Greece: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaanku5108100% (1)
- About Ancient GreeceDocument25 pagesAbout Ancient GreeceGost hunterNo ratings yet
- A Short History of the Middle East: From Ancient Empires to Islamic StateFrom EverandA Short History of the Middle East: From Ancient Empires to Islamic StateRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Ancient Greeks at War: Warfare in the Classical World from Agamemnon to AlexanderFrom EverandAncient Greeks at War: Warfare in the Classical World from Agamemnon to AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Anatolian Pontian GenocideDocument45 pagesAnatolian Pontian GenocideAnonymous Pu2x9KV100% (1)
- Background of LiteratureDocument25 pagesBackground of LiteratureMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- (Cultural Politics) Constance Penley, Andrew Ross (Editors) - Technoculture-University of Minnesota Press (1991) PDFDocument346 pages(Cultural Politics) Constance Penley, Andrew Ross (Editors) - Technoculture-University of Minnesota Press (1991) PDFLaura Miftode100% (1)
- A Overview of Greek HistoryDocument19 pagesA Overview of Greek Historynetname1100% (1)
- Chronology: Ancient Greece (Document2 pagesChronology: Ancient Greece (Azreen Anis azmiNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece Was A: CitationDocument1 pageAncient Greece Was A: CitationIoana PuriceNo ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument1 pageAncient GreeceMary Ann Pastolero BalatongleNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece Was A: Citation NeededDocument1 pageAncient Greece Was A: Citation NeededamninemoranNo ratings yet
- AntiquityDocument2 pagesAntiquityslyothersNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece (: Hellás) Was ADocument2 pagesAncient Greece (: Hellás) Was AJack SwaggerNo ratings yet
- Epoca Pietrei:: Neolithic Greece Covering A Period Beginning With TheDocument2 pagesEpoca Pietrei:: Neolithic Greece Covering A Period Beginning With Theadelita radulescuNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece (GreekDocument22 pagesAncient Greece (GreekAndreGuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument17 pagesAncient Greece - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediasandra072353No ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument23 pagesAncient GreeceASDNo ratings yet
- Sts AssignmentDocument3 pagesSts AssignmentMaxene DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece Was ADocument17 pagesAncient Greece Was AFernán GaillardouNo ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument15 pagesAncient Greeceaquel1983No ratings yet
- Classical Antiquity: (Note 1)Document11 pagesClassical Antiquity: (Note 1)SashimiTourloublancNo ratings yet
- World CivilizationsDocument3 pagesWorld CivilizationsJaya ShankarNo ratings yet
- Classical Antiquity 54Document12 pagesClassical Antiquity 54Ryan HoganNo ratings yet
- How Can You Realize The Classical Age of Mediterranean CivilizationDocument2 pagesHow Can You Realize The Classical Age of Mediterranean CivilizationMNo ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument21 pagesAncient GreeceTamer BhuiyannNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Ancient HistoryDocument2 pagesTimeline of Ancient HistoryFace BananeNo ratings yet
- Ancient History As A Term Refers To The Aggregate of Past EventsDocument2 pagesAncient History As A Term Refers To The Aggregate of Past EventsOstonal, Marco O.No ratings yet
- Ancient Greece (GreekDocument22 pagesAncient Greece (GreekSashimiTourloublancNo ratings yet
- A Very Brief Outline of Greek History (To A.D. 1453) : The Prehistoric PeriodsDocument4 pagesA Very Brief Outline of Greek History (To A.D. 1453) : The Prehistoric PeriodsPrincess kc DocotNo ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument25 pagesAncient GreeceAdam Bin Mat RofiNo ratings yet
- Prehistory: Recorded History or Written History Is ADocument2 pagesPrehistory: Recorded History or Written History Is Adanish_1985No ratings yet
- From The Earliest Settlements To The 3rd Century B.C.: Main ArticleDocument45 pagesFrom The Earliest Settlements To The 3rd Century B.C.: Main Articleemmanuelosorio0207No ratings yet
- Timeline: Ancient HistoryDocument5 pagesTimeline: Ancient HistoryAngelo Otañes GasatanNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece: The World History (His205)Document16 pagesAncient Greece: The World History (His205)salman kabirNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece: Navigation SearchDocument22 pagesAncient Greece: Navigation SearchashwinisathyaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece - WikipediaDocument55 pagesAncient Greece - Wikipediaalapideeric75No ratings yet
- History of The Mediterranean RegionDocument13 pagesHistory of The Mediterranean Regionhasan jamiNo ratings yet
- Classical AntiquityDocument11 pagesClassical Antiquityahmedzommit394No ratings yet
- HistoryDocument1 pageHistorycarlosachonNo ratings yet
- RD THDocument2 pagesRD THbruhNo ratings yet
- Ancient History As A Term Refers To The Aggregate of Past EventsDocument2 pagesAncient History As A Term Refers To The Aggregate of Past EventsMihaella GrișcoNo ratings yet
- Late AntiquityDocument1 pageLate Antiquity123nicky123No ratings yet
- Fourth Lecture On Orientalism Final 07042022 033206pmDocument34 pagesFourth Lecture On Orientalism Final 07042022 033206pmAbbasi WritesNo ratings yet
- 2nd Millennium BCDocument11 pages2nd Millennium BColympiaNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Ancient Literature: The Age of Antiquity Early in This Time PeriodDocument2 pagesAncient History Ancient Literature: The Age of Antiquity Early in This Time PeriodRoza PuspitaNo ratings yet
- History of Entire WorldDocument8 pagesHistory of Entire WorldkhadijatulkobrarimshaNo ratings yet
- History of Egypt - WikipediaDocument10 pagesHistory of Egypt - WikipediaMonicaNo ratings yet
- Classical Antiquity - WikipediaDocument7 pagesClassical Antiquity - Wikipediavedprakashabhay500No ratings yet
- Neolithic To Bronze Age (7000-1100 BC)Document2 pagesNeolithic To Bronze Age (7000-1100 BC)Azreen Anis azmiNo ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument12 pagesAncient GreeceAngela PageNo ratings yet
- PrehistoryDocument2 pagesPrehistoryJolly Ducoy PuertosNo ratings yet
- Iron Age CivilizationDocument48 pagesIron Age CivilizationThulla SupriyaNo ratings yet
- HistoryTopics in Chronological Order 2.0Document6 pagesHistoryTopics in Chronological Order 2.0aishamajeed129No ratings yet
- Ancient GreeceDocument12 pagesAncient GreeceSWAPNILNo ratings yet
- Hoa1 - RSW01 - Roman Architecture (Group 6)Document14 pagesHoa1 - RSW01 - Roman Architecture (Group 6)Sheena MaiquezNo ratings yet
- What Are Time Periods in History - Time Periods For KidsDocument6 pagesWhat Are Time Periods in History - Time Periods For Kidszarniaung.gpsNo ratings yet
- Classical GreeceDocument1 pageClassical GreeceCallithya BentleaNo ratings yet
- Ancient India (Pre-Historic To AD 700)Document6 pagesAncient India (Pre-Historic To AD 700)GoPika GiRiNo ratings yet
- GreeceDocument1 pageGreeceDiana LujzaNo ratings yet
- Identity Transformation in Real and Virtual Worlds: The Overlapping World ViewDocument5 pagesIdentity Transformation in Real and Virtual Worlds: The Overlapping World ViewLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- In The News: Salvador Sobral Portugal Amar Pelos Dois RansomwareDocument1 pageIn The News: Salvador Sobral Portugal Amar Pelos Dois RansomwareLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Temples: Pharaohs Their Religion Offerings Gods Rituals Divine Presence Divine OrderDocument1 pageEgyptian Temples: Pharaohs Their Religion Offerings Gods Rituals Divine Presence Divine OrderLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Ray Charles Invites You To Listen Hot 100 Chart: Here We Go AgainDocument1 pageRay Charles Invites You To Listen Hot 100 Chart: Here We Go AgainLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- SouthDocument1 pageSouthLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- The USNDocument1 pageThe USNLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Subjects and Symbols in ArtDocument2 pagesDictionary of Subjects and Symbols in ArtLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- SouthDocument1 pageSouthLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- USS Ranger (CV-4) Was The First Ship of The: United States Navy Keel Aircraft Carrier SuperstructureDocument1 pageUSS Ranger (CV-4) Was The First Ship of The: United States Navy Keel Aircraft Carrier SuperstructureLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Pluto (: New HorizonsDocument1 pagePluto (: New HorizonsLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Past Simple Present Perfect Simple Past Perfect Simple Future SimpleDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Past Simple Present Perfect Simple Past Perfect Simple Future SimpleLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 - 8 February 1587), Also Known As Mary Stuart I of Scotland, WasDocument1 pageMary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 - 8 February 1587), Also Known As Mary Stuart I of Scotland, WasLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Simple Past Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesInfinitive Simple Past Past ParticipleLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet
- TasmaniaDocument1 pageTasmaniaLaura MiftodeNo ratings yet