Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psych Drugs Cheat Sheet
Psych Drugs Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
nisreen100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
144 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Psych drugs cheat sheet.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
144 views4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat Sheet
Psych Drugs Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
nisreenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
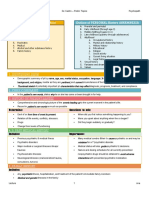
PSYCHIATRIC PHARMACOLOGY
Receptor type Effects of psychiatric drugs Receptor type
Dopamine (D2) Antagonists antipsychotic effect, relief of + symptoms of schizophrenia, Serotonin 3 (5-HT3)
↑extrapyramidal symptoms, increased prolactin levels
Serotonin 1A (5-HT1A) Agonists antidepressant & anxiolytic effects Alpha-1 adrenergic (α-1)
Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) Antagonists improvement in neg symptoms of schizophrenia and Histamine (H1)
improved cognition
Serotonin 2C (5-HT2C) Antagonists weight gain and associated risks Muscarinic (m1)
Class & MOA Generic Agent Brand Info
SSRIs: inhibit Fluoxetine Prozac -Longest half-life = highest risk for serotonin syndrome
reuptake of serotonin -Many drug interactions
as well as slight -Most stimulating SSRI
effects on histamine- -Lowest weight gain = good for eating disorders
R, α1-R, and Citalopram Celexa
muscarinic-R -Low risk of sexual AEs
Escitalopram Lexapro -AEs: GI, CNS, sexual, sedation, fatigue, dry mouth, hypotension,
Fluvoxamine Luvox withdrawal if d/c abruptly, prolonged QT, rash, insomnia, asthenia, seizure,
tremor, somnolence, mania, suicidal ideation, worsened depression
-Risk of serotonin syndrome: shivering, hyperreflexia, myoclonus, ataxia,
Sertraline Zoloft -Few drug interactions n/v/d
-Highest risk of GI problems
Paroxetine Paxil -Shortest half-life = highest risk of d/c symptoms
-Most sedating SSRI and greatest weight gain and
greatest sexual AEs
-Greatest anticholinergic activity
SNRIs: inhibits Venlafaxine (ER Effexor -HTN -Equally effective as SSRIs for treating major depression
reuptake of both avail) -Sedating -May be more effective in the setting of diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia,
serotonin and msk pain, stress incontinence, sedation, fatigue, and patients with comorbid
norepinephrine Duloxetine Cymbalta -Less AEs than venlafaxine anxiety
-Works well for fibromyalgia -AEs: GI, HTN, CNS, permanent sexual?, diaphoresis, dizziness, fatigue,
-Good for sleep and pain insomnia, blurred vision, suicidal ideation, dysuria, worsened depression
Desvenlafaxine Pristiq -Fewer drug interactions
Atypical Bupropion Wellbutrin -May increase sexual function
Antidepressants -Has stimulant effects = good for comorbid ADHD or for helping quit smoking but don’t use if comorbid anxiety or eating disorder
-AEs: lower seizure threshold, insomnia, nervousness, agitation, anxiety, tremor, arrhythmias, HTN, tachycardia, S-J, weight loss, GI,
arthralgia or myalgia, confusion, dizziness, HA, psychosis, suicidal ideation
Mirtazapine Remeron -Less nausea and sexual AEs
-Overdose is generally safe
-AEs: the most sedating antidepressant (= good for insomnia!), weight gain, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, dry mouth
Nefazodone Serzone
Trazodone Oleptro -AEs: arrhythmia, hyper or hypotension, diaphoresis, GI, hemolytic anemia, leukocytosis, dizziness, HA, insomnia, lethargy, memory
impairment, seizure, somnolence, priapism, weight gain
Class & MOA Generic Agent Brand Info Class & MOA
Tricyclic Amitriptyline Elavil -Good for sleep, pain, and depression
Antidepressants:
inhibits reuptake of -AEs: anticholinergic, CV, CNS, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, decreased
both serotonin and Clomipramine Anafranil seizure threshold
norepinephrine Desipramine Norpramin -Least sedating -CV effects: orthostatic hypotension, conduction disturbance, cardiotoxicity
Doxepin Silenor consider EKG prior to initiation
Imipramine Tofranil -Overdose can be lethal
Nortriptyline Pamelor
MAOIs: block Phenelzine Nardil -Irreversible -MAO-A acts on norepinephrine and serotonin
destruction of -MAO-B acts on phenylethylamine and DA
monoamines Tranylcypromine Parnate -Irreversible -AEs: anticholinergic, lower seizure threshold, weight gain, rash, orthostasis,
centrally and sexual dysfunction, insomnia or somnolence, HA, HTN crisis in presence of
peripherally Selegiline Emsam -Reversible monoamines
(transdermal) -Must be on tyramine-free diet = no wine, beer, cheese, aged food, or
smoked meats
-Overdose is lethal
-2 week washout period of other antidepressants needed before starting in
order to prevent serotonin syndrome
Mood Stabilizers Carbamazepine Tegretol -MOA: antiepileptic; inhibits voltage-gated Na channels
-AEs: diplopia, dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, Stevens-Johnson (don’t use in Asians), hypoCa, hypoNa, SIADH, hematologic, hepatitis
monitor CBC, LFTs, mental status, bone density, levels
-Contraindicated with bone marrow depression
-Decreases effectiveness of OCPs and warfarin
-Pregnancy D
Valproate Depakene -MOA: antiepileptic; increases GABA
Depakote -AEs: GI upset, sedation, unsteadiness, tremor, thrombocytopenia, palpitations, immune hypersensitivity, ototoxicity monitor CBC
and LFTs and levels
-Contraindicated with liver disease
-Many drug interactions
-Pregnancy D
Lamotrigine Lamictal -MOA: blocks voltage-gated Na channels and inhibits glutamate release
-AEs: nausea, diplopia, dizziness, unsteadiness, HA, rash, Stevens-Johnson, hematologic, liver failure
-Overdose can be fatal
-Interaction with valproate
-Pregnancy C
Lithium Eskalith -Inhibits adenylate cyclase
Lithobid -AEs: diabetes insipidus, cognitive complaints, tremor, weight gain, sedation, diarrhea, nausea, hypothyroidism
-Many drug interactions
-Requires baseline BMP, TSH, EKG, Ca as well as monitoring of BMP and TSH q 6-12 mo
-Monitoring for signs of toxicity: nausea, tremor, polyuria, thirst, weight gain, diarrhea, cognitive impairment
-Need to monitor levels
-Pregnancy D for neural tube defects
Gabapentin Neurontin -AEs: somnolence, dizziness, ataxia, fatigue, leukopenia, weight gain, Stevens-Johnson
Class & MOA Generic Agent Brand Info
Benzodiazepines: Chlordiazepoxide Librium -Long-acting
GABA-R agonists -Used often during EtOH withdrawal
CNS inhibition Clorazepate Tranxene -Long-acting
Diazepam Valium -Long-acting
Flurazepam Dalmane -Long-acting
Alprazolam Xanax -Intermediate acting
-Approved for panic disorder
Clonazepam Klonopin -Intermediate acting
-Approved for panic disorder
Lorazepam Ativan -Intermediate acting
Temazepam Restoril -Intermediate acting
Oxazepam Serax -Short acting
Triazolam Halcion -Short acting
Other Anxiolytics Buspirone BuSpar -5-HT partial agonist
-Gradual onset in 2 weeks
-Does not potentiate effects of alcohol = useful in alcohols
-Low addiction potential = good for pts who were addicted to benzos or other drugs
-AEs: sexual, dizziness, nausea, HA
-Drug interactions
Typical Haloperidol (inj Haldol -Good for acute agitation as onset is 30 min
Antipsychotics: avail)
nonselective DA-R Fluphenazine Prolixin
antagonists Perphenazine Trilafon
Thioridazine Mellaril -AE: retinitis pigmentosa
-Less risk of EPSEs
Chlorpromazine Thorazine -Less risk of EPSEs
Atypical Aripiprazole Abilify
Antipsychotics: Asenapine (SL Saphris -Costs $$$
block postsynaptic tablet avail)
DA-R, block Olanzapine (inj Zyprexa -High risk of weight gain and metabolic syndrome
serotonin-R, variable avail) Zyprexa -Injectable can cause post-injection delirium must give at healthcare facility and monitor for 3 hours
effect on histaminic Relprevv (inj)
and cholinergic-R Quetiapine Seroquel -Need q 6 month eye exams due to risk of cataracts
Risperidone Risperdal -Least amount of AEs
Consta (inj) -Highest risk of hyperprolactinemia
Ziprasidone Geodon -AE: dose-related QT prolongation
-Less wt gain
Clozapine Clozaril -The only atypical antipsychotic proven effective in treatment of schizophrenia
-Use limited by AEs: high risk of weight gain and metabolic syndrome, seizures, agranulocytosis, myocarditis, lens opacities need
to monitor WBC and ANC frequently
Iloperidone Fanapt -Costs $$$
-Not proven better than other atypical antipsychotics
Lurasidone Latuda -Best choice for reversing metabolic effects
Paliperidone (inj Invega
avail) Invega
Sustenna (inj)
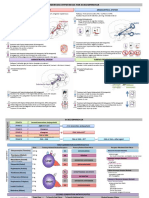
Management of Psychiatric Drug Adverse Effects
Dystonias Parkinsonianism
-Benztropine -Amantadine
-Biperiden -Levodopa
-Diphenhydramine
-Trihexyphenidyl Extrapyramidal Symptoms
-Parkinsonian syndrome, acute dystonias, akathisia
Akathisias = restlessness -Benztropine
-Propranolol -Benadryl
-Benzos
You might also like
- Common Psychiatric MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Psychiatric MedicationsDan Kiarie92% (12)
- Notes For PMHNP CertificationDocument23 pagesNotes For PMHNP CertificationKristine Frost92% (13)
- Johnson and Vanderhoef PMHNP Certification Review ManualDocument451 pagesJohnson and Vanderhoef PMHNP Certification Review ManualSoojung Nam93% (14)
- Aa - LMR Georgette - Final VersionDocument47 pagesAa - LMR Georgette - Final Versionpickles.squad11No ratings yet
- Receptor Binding Profiles of AntipsychoticsDocument1 pageReceptor Binding Profiles of AntipsychoticsM.Dalani100% (3)
- Antidepressant Comparison ChartDocument3 pagesAntidepressant Comparison Chartiggyputtty100% (29)
- 1000 Emergency Medicine QuestionsDocument328 pages1000 Emergency Medicine QuestionsSunel92% (12)
- Mental Health NotesDocument21 pagesMental Health Notesbazahoor97% (33)
- 966baf PDFDocument86 pages966baf PDFkaw gd100% (2)
- Prescribing Psychotropics: From Drug Interactions to PharmacogeneticsFrom EverandPrescribing Psychotropics: From Drug Interactions to PharmacogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Antidepressant ChartDocument7 pagesAntidepressant Chartinher1tance100% (4)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat Sheetfreecouch80% (5)
- Psych CardsDocument10 pagesPsych CardsJennifer Rodriguez96% (24)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetHJ G100% (3)
- Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionFrom EverandMedication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric History and ExaminationDocument14 pagesPsychiatric History and ExaminationPaolo Bonifacio100% (14)
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsDocument7 pagesPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- Psychiatry PharmacologyDocument2 pagesPsychiatry PharmacologyMegatFitriAziz100% (4)
- Second and Third Generation Antipsychotics: A Comprehensive HandbookFrom EverandSecond and Third Generation Antipsychotics: A Comprehensive HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Benzodiazepine Comparison Chart - Commonly Available Sedative Hypnotic Anti Anxiety (Anxiolytic) Anti Epileptic MedicationsDocument2 pagesBenzodiazepine Comparison Chart - Commonly Available Sedative Hypnotic Anti Anxiety (Anxiolytic) Anti Epileptic MedicationsChristopher Chrysostom100% (3)
- Nursing Psych Comprehensive TableDocument13 pagesNursing Psych Comprehensive TableAILENLEIVA100% (19)
- CHT Psyc AntidepressantDocument3 pagesCHT Psyc AntidepressantRicardo Lugon ArantesNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Medications ListDocument1 pagePsychotropic Medications Listapnitickets100% (1)
- PsychiatryDocument52 pagesPsychiatryEma100% (13)
- Psychiatry HX TakingDocument4 pagesPsychiatry HX TakingP KasikrishnarajaNo ratings yet
- (PSYCH) 2.01 The Psychiatric History - Dr. SundiangDocument5 pages(PSYCH) 2.01 The Psychiatric History - Dr. SundiangKeifer Turtle100% (2)
- Psychiatric Assessment ToolDocument53 pagesPsychiatric Assessment ToolLori100% (5)
- The Complete Guide to Psychiatric Drugs: Straight Talk for Best ResultsFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Psychiatric Drugs: Straight Talk for Best ResultsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Psych Meds Review MaterialDocument2 pagesPsych Meds Review MaterialMary Romaine Dela Pasion100% (7)
- "Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry PharamacologyDocument9 pages"Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry Pharamacologytycobb63100% (4)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSuha Abdullah100% (4)
- Psychotropic Medication ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychotropic Medication ReviewAakash Shah100% (1)
- Psychotherapist'S Guide To Psychopharmacology: Second EditionFrom EverandPsychotherapist'S Guide To Psychopharmacology: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Study Psych DrugsDocument14 pagesStudy Psych Drugsapi-369732698% (47)
- Psych Drugs Info SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Info SheetPauline ChanNo ratings yet
- Psych Med ChartsDocument5 pagesPsych Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Psychiatry: Mental State ExaminationDocument3 pagesPsychiatry: Mental State ExaminationSok-Moi Chok100% (4)
- (Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersDocument3 pages(Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersGus AbellaNo ratings yet
- Summary of MH Screening and Assessment Tools For Primary CareDocument20 pagesSummary of MH Screening and Assessment Tools For Primary CareTeresa Meehan100% (1)
- DSM-IV Criteria MnemonicsDocument4 pagesDSM-IV Criteria Mnemonicsleonyap100% (2)
- PMHNP Ancc ReviewDocument4 pagesPMHNP Ancc ReviewEllie Mehr75% (4)
- Norepinephrine Acetylcholine (Ach)Document6 pagesNorepinephrine Acetylcholine (Ach)Jestoni Dulva Maniago100% (3)
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For DepressionDocument2 pagesHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Depressionrowanpurdy100% (4)
- Disorders Duration/Onset Symptoms/Manifestations Treatment: Childhood DDocument7 pagesDisorders Duration/Onset Symptoms/Manifestations Treatment: Childhood DActeen Myoseen100% (2)
- USMLE Mnemonics PsychDocument4 pagesUSMLE Mnemonics Psychzhzizhzi100% (3)
- Examination Notes in PsychiatryDocument367 pagesExamination Notes in Psychiatrysorphy100% (43)
- PSYCHIATRY Course NotesDocument43 pagesPSYCHIATRY Course NotesNisha PillaiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry EvaluationDocument3 pagesPsychiatry Evaluatione-MedTools83% (24)
- Psychiatry High Yield NotesDocument6 pagesPsychiatry High Yield Notesgregry2100% (2)
- Psychotropic Medications: Dale Sanderson, PA-C Physician Assistant Seattle Mental HealthDocument72 pagesPsychotropic Medications: Dale Sanderson, PA-C Physician Assistant Seattle Mental HealthMichael Urrutia100% (2)
- Reviewer On PsychopharmacologyDocument28 pagesReviewer On PsychopharmacologyKristine Ann Hernandez100% (1)
- Commonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDocument2 pagesCommonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDragutin Petrić100% (1)
- ReferenceDocument2 pagesReferenceAaron Shokar100% (2)
- Dopamine HypothesisDocument2 pagesDopamine HypothesisBo123456100% (3)
- 17 (2) PsychiatryDocument4 pages17 (2) PsychiatryIbrahimFikryNo ratings yet
- Study Guide PMHNP Must Know Exam Topics Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesStudy Guide PMHNP Must Know Exam Topics Cheat Sheet: by ViaDodo Eggo100% (4)
- PsychopharmacologyDocument64 pagesPsychopharmacologyGaurav Tandon100% (2)
- The Dsm-5 Survival Guide: a Navigational Tool for Mental Health ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe Dsm-5 Survival Guide: a Navigational Tool for Mental Health ProfessionalsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Box Office & Customer Service SupportDocument1 pageBox Office & Customer Service SupportSunelNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnoses Practical 1Document5 pagesPhysical Diagnoses Practical 1SunelNo ratings yet
- Continuing Juniors Book List - Summer 20Document2 pagesContinuing Juniors Book List - Summer 20SunelNo ratings yet
- CIHE Sunset Park 11-15-10 RevDocument3 pagesCIHE Sunset Park 11-15-10 RevSunelNo ratings yet
- Modern Poetry 2Document2 pagesModern Poetry 2SunelNo ratings yet
- When The Levees Broke Is A Documentary Filmed by Spike Lee, About The Aftermath ofDocument2 pagesWhen The Levees Broke Is A Documentary Filmed by Spike Lee, About The Aftermath ofSunelNo ratings yet
- Med Cu Rulaj LentDocument5 pagesMed Cu Rulaj Lentmarkos simonaNo ratings yet
- Sound Alike Medications: Drug Name Confused Drug NameDocument5 pagesSound Alike Medications: Drug Name Confused Drug NameAhmad TaramsyNo ratings yet
- Consolidated-List-of-VAT-Exempt-Products-with-drugs-and-vaccines-prescribed-and-directly-used-for-Covid-19-treatment As of 9-6-2021Document67 pagesConsolidated-List-of-VAT-Exempt-Products-with-drugs-and-vaccines-prescribed-and-directly-used-for-Covid-19-treatment As of 9-6-2021cayamdas jerryNo ratings yet
- Medicamentos e Insumos 2023Document248 pagesMedicamentos e Insumos 2023Jessi ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Penerimaan Obat Instalasi Farmasi: Rsud CileungsiDocument98 pagesLaporan Penerimaan Obat Instalasi Farmasi: Rsud CileungsidianNo ratings yet
- Price List PT. OGB OTTODocument1 pagePrice List PT. OGB OTTOrsubk sumedangNo ratings yet
- Master ObatDocument77 pagesMaster ObatYoeni IraNo ratings yet
- Ship To Cust Ship-To Customer Name Billing Docu Billing Date SD Document CDocument24 pagesShip To Cust Ship-To Customer Name Billing Docu Billing Date SD Document CRao Arslan RajputNo ratings yet
- Tramadol 50mg IV Q8 PRN For Severe Pain Tramadol 50mg IV NOWDocument2 pagesTramadol 50mg IV Q8 PRN For Severe Pain Tramadol 50mg IV NOWJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Antihistamines 101 Munich 06-05Document15 pagesAntihistamines 101 Munich 06-05pentruNo ratings yet
- Buku Register Obat Apotek PKM BkuDocument5 pagesBuku Register Obat Apotek PKM Bkuyeni fatimahNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument6 pagesFinalOlga CerlatNo ratings yet
- Rekap Penggunaan Obat Per Dokter Peresep: Rsi GondanglegiDocument7 pagesRekap Penggunaan Obat Per Dokter Peresep: Rsi Gondanglegirsi ITNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Neostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDFDocument1 pageNeostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDFpooja lokhandeNo ratings yet
- K11020R111 - Faras Naufal H - Tugas 4 - PKPA PuskesmasDocument8 pagesK11020R111 - Faras Naufal H - Tugas 4 - PKPA PuskesmasKisah CintaNo ratings yet
- Nama Obat Jumlah Order DistributorDocument22 pagesNama Obat Jumlah Order DistributorNdaa NandaNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Laporan Narkotika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFDocument10 pagesRekapitulasi Laporan Narkotika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFMiftah JannahNo ratings yet
- Medication Ticket Case 2.Document4 pagesMedication Ticket Case 2.Juviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Criticalcaredrugs PDFDocument2 pagesCriticalcaredrugs PDFtomywekaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Hold List-MedicineDocument2 pagesAnesthesia Hold List-MedicineYogeswary RamachandranNo ratings yet
- ClopamDocument2 pagesClopammahgadNo ratings yet
- CANAMED 01 03 2022oficialDocument936 pagesCANAMED 01 03 2022oficialStefan IonutNo ratings yet
- Eskag Pharma Pvt. LTD., Haridwar, Unit-I Department: Quality Assurance Product MatrixDocument20 pagesEskag Pharma Pvt. LTD., Haridwar, Unit-I Department: Quality Assurance Product MatrixMohit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Obat Dan Kehamilan, Drugs, Aman Untuk Ibu Hamil, FarmasiDocument13 pagesObat Dan Kehamilan, Drugs, Aman Untuk Ibu Hamil, FarmasifrankysukwendyNo ratings yet
- ANS DrugsDocument2 pagesANS Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Pharmaceutical DrugsDocument31 pagesClassifications of Pharmaceutical DrugsDeepankar Srigyan100% (30)
- Abbreviation of PharmacologyDocument59 pagesAbbreviation of PharmacologyMohamed Abo EmadNo ratings yet
- Controlled Substances ListDocument11 pagesControlled Substances ListNickNo ratings yet
- INJEKSI LDocument21 pagesINJEKSI LSyarif SamNo ratings yet