Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 3 First Grading K-12
Uploaded by
lanie.taneco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesGrade 3 Science First Grading Period
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGrade 3 Science First Grading Period
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesScience 3 First Grading K-12
Uploaded by
lanie.tanecoGrade 3 Science First Grading Period
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
MATTER – has mass, weight and volume
Mass – amount of matter; does not change Volume – space
Weight – pull of gravity
Gravity – force that an object exerts on another object Force – push or pull
Three STATES of Matter
Solid – has definite shape and particles are tightly packed.
Liquid – does not have definite shape and particles move freely
follows the shape of the container
can be poured from one container to another
Gas – does not have shape and particles are spread out to fill the container
cannot be seen or tasted; you can only feel them and smell some of them.
Physical Change of Matter – change in appearance without any change in its
composition.
Cutting, breaking, folding, tearing, slicing, sharpening and crumpling
EVAPORATION – physical change of liquid to gas
Forming of clouds
Water changes to gas when it is heated
Vaporization: Evaporation due to boiling
- smoke from boiling water is STEAM OR WATER VAPOUR
Boiling point: TEMPERATURE when a liquid change to gas.
CONDENSATION – change from gas to liquid
DEW, CLOUD, FOG; Forming of rain
Gas changes to liquid when it is cooled.
Condensation produces water droplets outside a glass of cold water.
When warm air hits the cold surface of the glass, it is cooled and changes to water
droplets.
DEPOSITION- gas immediately turns to solid
- Occurs in winter season
- At low temperatures, water vapour turns into ice crystals or freezes
directly into ice (FERMAFROST)
SUBLIMATION- solid to gas
- No liquid phase
- DRY ICE: keep ice cream frozen; TOILET FRESHENERS, MOTHBALLS
Freezing – process of changing from liquid to solid.
Forming of ice or snow
Melting – change from solid to liquid
Melting of ice cream
Chemical Change of Matter – happens when a material changes in composition
Rusting – metal bar combined with carbon dioxide
Burning – using fire
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Grade 2 - Science: MagnetsDocument2 pagesGrade 2 - Science: Magnetslanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Magnets and Magnetism (Grade 3) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingDocument1 pageMagnets and Magnetism (Grade 3) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachinglanie.taneco86% (7)
- MIMETICSDocument3 pagesMIMETICSlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 Mathematics First Periodical Examination ReviewerDocument3 pagesGrade 2 Mathematics First Periodical Examination Reviewerlanie.taneco71% (14)
- Kasingkahulugan at Kasalungat Set B: Worksheet Made by - All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesKasingkahulugan at Kasalungat Set B: Worksheet Made by - All Rights Reservedlanie.taneco100% (4)
- Parts of A Nose - Science 3Document2 pagesParts of A Nose - Science 3lanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 MTAP Math Challenge Questions and ReviewerDocument3 pagesGrade 1 MTAP Math Challenge Questions and Reviewerlanie.taneco100% (3)
- Jan2019 Devotion 2Document1 pageJan2019 Devotion 2lanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Primary Colors For Pre - KDocument1 pagePrimary Colors For Pre - Klanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Bilang NG Pantig - Interactive WorksheetDocument1 pageBilang NG Pantig - Interactive Worksheetlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Christ Is Enough Lyrics and ChordsDocument1 pageChrist Is Enough Lyrics and Chordslanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
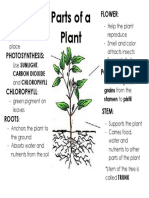
- Parts of A Plant: Leaf (Leaves) FlowerDocument1 pageParts of A Plant: Leaf (Leaves) Flowerlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Skin - Science 3Document6 pagesTongue and Skin - Science 3lanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- When There Is No ComparisonDocument2 pagesWhen There Is No Comparisonlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Fractions VisualDocument1 pageFractions Visuallanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Pluralnouns PDFDocument1 pagePluralnouns PDFlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Name: The Wrong Word in The Sentence and Write The Correct Adjective in The Space ProvidedDocument4 pagesName: The Wrong Word in The Sentence and Write The Correct Adjective in The Space Providedlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Anyong TubigDocument10 pagesAnyong Tubiglanie.tanecoNo ratings yet
- Test Present Progressive enDocument0 pagesTest Present Progressive enRaluca AlexandraNo ratings yet
- AdminDocument1 pageAdminlanie.tanecoNo ratings yet