Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Ka
Uploaded by
Mark Manongol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views2 pagesducument
Original Title
physics ka
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentducument
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views2 pagesPhysics Ka
Uploaded by
Mark Manongolducument
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
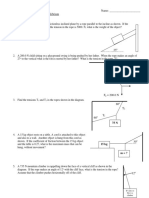
PHYSICS 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM WORKSHEET
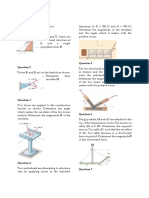
1. For the situation shown to the right, 50°
find the values of T1 and T2 if the T2
weight is 600. N.
T1 600. N
2. Examine the diagram to the left.
40° What force F is required to keep the 60.0 kg
F mass in static equilibrium?
60.0 kg
3. An 11 kg lamp is supported between two vertical
poles by two wires attached as shown to the right. 30° 60°
What is the tension in the right wire? 11 kg
4. Two wires are used to suspend a sign that weighs 500. N. The two wires make an angle
of 100° between each other. If each wire is exerting an equal amount of force, how
much force does each wire exert?
5. What must the tension in each cable be in
the diagram in order to support the cargo in
static equilibrium? Note that pulleys only
50° 30° change the direction of the force, not the
magnitude.
1000 N
2.0 m
fixed
6. What will the unknown angle θ be θ pulley
in order for the pulley system to
the right to be in static equilibrium?
Note that the 80 N weight is
attached to a free-moving pulley, 80 N 400 N
and the cable is fastened to the
wall on the left.
7. In the system to the right, the pulleys
are frictionless and the system hangs in
equilibrium. Determine the values of 50° 35°
each of the unknown weights.
200. N
W1 W2
8. The following forces pull on a ring along the same plane (i.e. coplanar): 200 N at
30° E of N, 500 N at 10° N of E, 300 N at 60° W of S, and an unknown force that keeps the
ring in equilibrium. Find the magnitude and direction of this unknown force.
1. 503 N, 783 N 2. 493 N 3. 54 N 4. 390 N 5. 653 N, 879 N 6. 169° 7. 260 N, 150 N 8. 350 N at 18° S of W
You might also like
- Static Equib WorksheetDocument7 pagesStatic Equib Worksheetsitinasarath100% (1)
- Practice Exercises2Document9 pagesPractice Exercises2Mia ManaloNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Nce 520 Integration Course 2 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Nce 520 Integration Course 2 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Mechanical Engineering: Mec111: Statics Tutorial Chapter 2.2: Equilibrium of ParticleDocument3 pagesFaculty of Mechanical Engineering: Mec111: Statics Tutorial Chapter 2.2: Equilibrium of ParticleFiq KaizoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-CH6-Statics (Class-Watermark) PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial-CH6-Statics (Class-Watermark) PDFJeanette LynnNo ratings yet
- GEAS Refresher (Mechanics)Document2 pagesGEAS Refresher (Mechanics)Eugene Embalzado Jr.No ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 3 Phy210 Static EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial Week 3 Phy210 Static EquilibriumAiman Hariz Bin MohamadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet2 Static EquilibriumI 2010 2011Document2 pagesWorksheet2 Static EquilibriumI 2010 2011Bitcoin PopNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 StaticsDocument10 pagesCh. 4 StaticsJoanne Aga EslavaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - 2 - 3 - 4Document6 pagesTutorial 1 - 2 - 3 - 4Danny MalobaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions-Work, EnergyPowerDocument4 pagesTutorial Questions-Work, EnergyPowerElihle Lihle NyuswaNo ratings yet
- Questions MechanicsDocument2 pagesQuestions Mechanicspravat DashNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- Phy231sp06 Exam3 PracticeDocument8 pagesPhy231sp06 Exam3 PracticeJunsuk AhnNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pagesEngineering MechanicsBVS CollegesNo ratings yet
- Problem Name: Set No. 5 Statics Course & Year: DateDocument3 pagesProblem Name: Set No. 5 Statics Course & Year: DateHeyKyYoureSoFineNo ratings yet
- Sptopics Design Module1Document6 pagesSptopics Design Module1Christian Felix MapilesNo ratings yet
- Faculty Ellen Lewis Equilibrium ProblemsDocument2 pagesFaculty Ellen Lewis Equilibrium ProblemsMacsherwin LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Moments of ForcesDocument8 pagesMoments of ForcestopcatNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsFamia FarazNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1,2,3Document8 pagesTutorial 1,2,3RameshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Unit 1 QuestionsDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit 1 QuestionsShrey SanwariaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion LASDocument2 pagesRotational Motion LASyhaelguan77No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3piyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 12: Equilibrium: AP Physics C Supplementary ProblemsDocument5 pagesProblem Set 12: Equilibrium: AP Physics C Supplementary Problemshakan fizikNo ratings yet
- STATICS OF RIGID BODIES CHAPTER 2 PROBLEMSDocument2 pagesSTATICS OF RIGID BODIES CHAPTER 2 PROBLEMSNeil Anthony Pojas BlancaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial3Document2 pagesTutorial3deetosh22No ratings yet
- Practice Exam 03-1Document7 pagesPractice Exam 03-1Chrislet VaelNo ratings yet
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS NOTESDocument4 pagesSTRENGTH OF MATERIALS NOTESrameshNo ratings yet
- PHYS 201 - Resultant and Equilibrant Forces Formal ReportDocument4 pagesPHYS 201 - Resultant and Equilibrant Forces Formal ReportAudrey CobankiatNo ratings yet
- Forces in EquilibriumDocument7 pagesForces in EquilibriumMUHAMAD ZANDAR BIN ZAKARIA KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- PHY1010 Tut 8 EquilibriumDocument2 pagesPHY1010 Tut 8 EquilibriumKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Torque and Equilibrium (40 charactersDocument2 pagesTorque and Equilibrium (40 charactersEndai DesuNo ratings yet
- EM QBDocument16 pagesEM QBJeganNo ratings yet
- Tute Sheet 1 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument5 pagesTute Sheet 1 - Newton's Laws of MotionAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument22 pagesHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAbdullah ArabiyatNo ratings yet
- Friction problems involving pulleys, wedges, inclined planesDocument2 pagesFriction problems involving pulleys, wedges, inclined planesAbegail Mae PingosNo ratings yet
- 5-Turning Effect of Forces-OrigDocument86 pages5-Turning Effect of Forces-Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiNo ratings yet
- Coulombs LawDocument8 pagesCoulombs LawDaniel Esteban Pinto ChaparroNo ratings yet
- Es1 2ND NotesDocument10 pagesEs1 2ND NotesTristan MuraoNo ratings yet
- Btes103 203 em QBDocument10 pagesBtes103 203 em QBSurajNo ratings yet
- 8 Equilibrium of Force SystemsDocument13 pages8 Equilibrium of Force SystemsRachelle AlquizolaNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium ProblemsDocument19 pagesStatic Equilibrium Problemsshahrul100% (1)
- Experiment 1 Formal Report QuestionsDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 Formal Report QuestionsCharisseNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 16 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture2 16 PDFjeez janiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 01Document6 pagesLecture Note 01Unabia Queeny JaneNo ratings yet
- Equil. #1Document1 pageEquil. #1Nicolas Patrick OntiverosNo ratings yet
- Name: - Worksheet 3.1 - Translational EquilibriumDocument3 pagesName: - Worksheet 3.1 - Translational EquilibriumYehualashet BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual DownloadDocument4 pagesConceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual DownloadSteve Duncan100% (25)
- Mukuba Tut 4 Static Equilibrium and Dynamics 2020Document3 pagesMukuba Tut 4 Static Equilibrium and Dynamics 2020Saviour SichizyaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)Document4 pagesElectromagnetism - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)pragnakrishnan5No ratings yet
- Be Excel For Physics 1Document7 pagesBe Excel For Physics 1naniey1981No ratings yet
- PSAD 1 - Part 1Document3 pagesPSAD 1 - Part 1John Gavin CarmenNo ratings yet
- CH 3b Electromagnetism - Key Examples 2022Document4 pagesCH 3b Electromagnetism - Key Examples 2022andilenbNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Activity SheetDocument18 pagesActivity SheetAnonymous bM3dl8mNo ratings yet
- Belt Aligment Tool TKBA 10 & 20Document2 pagesBelt Aligment Tool TKBA 10 & 20Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Reformer PDFDocument32 pagesReformer PDFEfi TsakalomatiNo ratings yet
- 3.1. ProblemsDocument20 pages3.1. Problemssaumya irugalbandaraNo ratings yet
- Linde T20 /131 ManualDocument63 pagesLinde T20 /131 Manualalan mad100% (2)
- Gilson Test-Master® Testing Screens TM-5 & TM-6: Operating ManualDocument21 pagesGilson Test-Master® Testing Screens TM-5 & TM-6: Operating ManualEduardo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document4 pagesSession 2vijayakumar100% (1)
- CRANK SHAFT OPERATED MULTI BLADE HACKSAWDocument15 pagesCRANK SHAFT OPERATED MULTI BLADE HACKSAWTanvi Khurana100% (2)
- INSP Champs 2022 NLM 1 FinalDocument10 pagesINSP Champs 2022 NLM 1 Finaliitaspirant19No ratings yet
- Statics 13esi Solutions-Manual c03-180898 PDFDocument78 pagesStatics 13esi Solutions-Manual c03-180898 PDFKavinesh Ananthan100% (3)
- Design and Analysis of Alternative Fixed Pitch CVTDocument46 pagesDesign and Analysis of Alternative Fixed Pitch CVTRushabh Rajendra YerunkarNo ratings yet
- Habasync Timing Belts Engineering Guide: Habasit - Solutions in MotionDocument72 pagesHabasync Timing Belts Engineering Guide: Habasit - Solutions in Motionkumar sivaNo ratings yet
- Gearbox Design by ChitaleDocument34 pagesGearbox Design by ChitaleNagu Srirama60% (5)
- SRX-101A Medical Film Processor Service ManualDocument152 pagesSRX-101A Medical Film Processor Service ManualAlexeyNo ratings yet
- Travelling Tripper CalculationDocument5 pagesTravelling Tripper CalculationHarshGuptaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Components MaintenanceDocument25 pagesMechanical Components MaintenanceKroof KayNo ratings yet
- Cable Spring PulleyDocument6 pagesCable Spring PulleyDavid Olorato NgwakoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Mechanics of MachineDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Mechanics of MachineIr Mohammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Inlocuire Dist k4m PDFDocument7 pagesInlocuire Dist k4m PDFMugur AchiteiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science BECE Unit 1 30232Document139 pagesIntegrated Science BECE Unit 1 30232Isaiah BanguraNo ratings yet
- Karcher KM 90 60 R Rider Sweeper Parts ListDocument61 pagesKarcher KM 90 60 R Rider Sweeper Parts ListDavid VaquerizoNo ratings yet
- Screen Operation and Service Manual and Parts Book: Jci Oval Motion Screen 6203-32LP S/N S102431Document42 pagesScreen Operation and Service Manual and Parts Book: Jci Oval Motion Screen 6203-32LP S/N S102431Jorge YaipenNo ratings yet
- ABB - Overhung LoadDocument3 pagesABB - Overhung LoaddrewtwitchNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics NotesDocument25 pagesEngineering Mechanics NotesSameer Sawarkar100% (1)
- When Pulling On A Wireline, Is There More Tension at The Top Sheave Than Is Shown On The Weight Indicator? February 2014Document1 pageWhen Pulling On A Wireline, Is There More Tension at The Top Sheave Than Is Shown On The Weight Indicator? February 2014u2006262918No ratings yet
- Alternator Problem - Charging Problem and or Noisy Operation - 3516HDocument3 pagesAlternator Problem - Charging Problem and or Noisy Operation - 3516Hwagner_guimarães_1No ratings yet
- A Treatise On Milling and Milling MachinesDocument420 pagesA Treatise On Milling and Milling Machineskavadarci14100% (3)
- Heat Sealer Repair and Maintenance Kit IFU 2019-02-06Document27 pagesHeat Sealer Repair and Maintenance Kit IFU 2019-02-06LowayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ElevatorDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ElevatorTun Tun100% (1)
- Catalogo de Partes Canon 3245Document221 pagesCatalogo de Partes Canon 3245Moises MendozaNo ratings yet