Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STATICS OF RIGID BODIES CHAPTER 2 PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
Neil Anthony Pojas Blanca0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThis document contains 13 sample problems related to statics of rigid bodies and particles. The problems cover a range of concepts including determining the magnitude and direction of resultant forces, resolving forces into component vectors, and solving static equilibrium problems involving cables, pulleys, and inclined planes. Solutions are provided for some of the problems to demonstrate the application of concepts and steps to solve static force problems.
Original Description:
Original Title
STARIG 205 - CHAPTER 2 PROBLEMS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 13 sample problems related to statics of rigid bodies and particles. The problems cover a range of concepts including determining the magnitude and direction of resultant forces, resolving forces into component vectors, and solving static equilibrium problems involving cables, pulleys, and inclined planes. Solutions are provided for some of the problems to demonstrate the application of concepts and steps to solve static force problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesSTATICS OF RIGID BODIES CHAPTER 2 PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
Neil Anthony Pojas BlancaThis document contains 13 sample problems related to statics of rigid bodies and particles. The problems cover a range of concepts including determining the magnitude and direction of resultant forces, resolving forces into component vectors, and solving static equilibrium problems involving cables, pulleys, and inclined planes. Solutions are provided for some of the problems to demonstrate the application of concepts and steps to solve static force problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
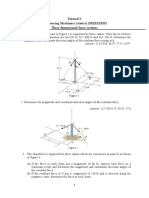
STARIG 205 – STATICS OF RIGID BODIES 1ST SEM 2021-2022
CHAPTER 2 – STATICS OF A PARTICLE PROBLEMS
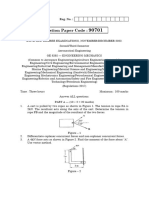
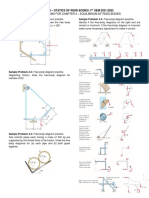
Sample Problem 2.1. Sample Problem 2.5:
Two forces P and Q act on a bolt. Determine the magnitude The forces F1, F2 and F3, all act at point A of the bracket, are
and direction of their resultant. specified in different ways. Determine (a) the x and y
components of each of the three forces and (b) the resultant
of the three forces.
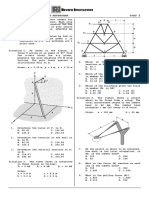
Sample Problem 2.2.
It is required that the resultant force acting on the eyebolt is
to be directed along the positive x-axis and that F2 have a
minimum magnitude. Determine this magnitude, the angle
θ, and the corresponding resultant force.
Sample Problem 2.6:
If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the bracket
is to be 80 lb directed along the u axis, determine the
magnitude of F and its direction.
Sample Problem 2.3.
If the resultant force required is to act along the positive u-
axis and have a magnitude of 5kN, determine the required
magnitude of FB and θ.
Sample Problem 2.7:
For the block shown, (a) determine the required value of α if
the resultant of the three forces shown is to be parallel to
the incline, (b) the corresponding magnitude of the
resultant.
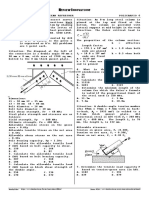
Sample Problem 2.4:
Four forces are acting on the bolt.
(a) Determine the components of the forces.
(b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant Sample Problem 2.8:
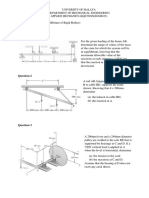
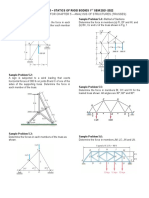
of the four forces. A spike can be removed from the timber by applying a force
of 820 N along the axis of the spike. An obstruction A
prevents direct access so that two forces, one 400 N and
the other P, applied by cables as shown (the cables just
nearly touch the corners of the obstruction). Determine the
magnitude of the force P to ensure a resultant necessary to
remove the spike
Sample Problem 2.9:
A 1200-kg car is being lowered slowly onto the dock using Sample Problem 2.12.
A load of weight 400 N is suspended from a spring and two
the hoist A and winch C. Determine the forces in cable BA
chords are attached to blocks of weights 3W and W as
and BC for the position shown.
shown. Knowing that the constant of the spring is 800 N/m,
determine (a) the value of W, (b) the unstretched length of
the spring.
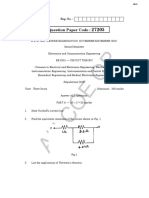
Sample Problem 2.10.
Determine the magnitude and direction θ of the equilibrium
force FAB exerted along link AB by the tractive apparatus
shown. The suspended mass is 10 kg. Neglect the size of
the pulley at A.
Sample Problem 2.13.
Cylinders E weighs 60 N and cylinder F weighs 120 N.
These cylinders are suspended through the support cables
shown. Determine the value of angle θ for equilibrium.
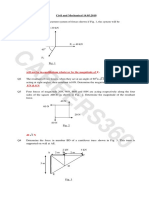
Sample Problem 2.11.
In a circus act, an aerialist performs a handstand on a
wheel while being pulled across a high wire ABC of length 8
m by another performer as shown. Knowing that the tension Answers:
in the rope DE is 35 N when the aerialist is held at a = 2.5
m, determine (a) the weight of the aerialist, (b) the tension 2.3. ;
in the wire.
2.4. (b)
2.5. (b)
2.6.
2.7. (a) α =56.30993 °, (b) R=1021.11026 N
2.8. P=542.66011 N
2.9.
2.10. ;
2.11. (a) W =785.92407 N ; (b) T =3254.74327 N
2.12. (a) W =62.8406 N ; (b) Lu=757.831 mm
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid Bodies Tutorial QuestionsZulfadzli RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (For Week 2 Tutorials)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (For Week 2 Tutorials)2200851No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document6 pagesTutorial 2A SкNo ratings yet
- DAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsDocument20 pagesDAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsJM De Guzman TuzonNo ratings yet
- Civil and Mechnical Finalkey PDFDocument15 pagesCivil and Mechnical Finalkey PDFNAVEEN BUDDARAPUNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS2Document2 pagesSec - PS2Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1,2,3Document8 pagesTutorial 1,2,3RameshNo ratings yet
- STATICS OF RIGID BODIES problemsDocument11 pagesSTATICS OF RIGID BODIES problemsLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS EXAMDocument3 pagesF.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS EXAMAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ge8251 Engineering Mechanics EnglishDocument4 pagesGe8251 Engineering Mechanics EnglishNAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Ge8292 ND22Document8 pagesGe8292 ND22pocolokesh2005No ratings yet
- 3.1. ProblemsDocument20 pages3.1. Problemssaumya irugalbandaraNo ratings yet
- Civil and MechnicalDocument15 pagesCivil and MechnicalLokeshNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter2 3552Document5 pagesExercise Chapter2 3552Khuon RatanaNo ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedDocument20 pagesApplied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedYoukesh GautamNo ratings yet
- SBVLDocument5 pagesSBVLvuong100% (1)
- Preboard Problems FinalDocument5 pagesPreboard Problems FinalAngel MarkNo ratings yet
- Assignment in MechanicsDocument4 pagesAssignment in MechanicsMarvin Bryant MedinaNo ratings yet
- Structural Question/P.1 - Hong Kong Advanced Level Exam 1984 Physics Question on Steel Wire PropertiesDocument8 pagesStructural Question/P.1 - Hong Kong Advanced Level Exam 1984 Physics Question on Steel Wire PropertiescheongjiajunNo ratings yet
- f6cb57702022 Endsem MOSDocument2 pagesf6cb57702022 Endsem MOSshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- Mom Ssignment Final 2016Document3 pagesMom Ssignment Final 2016das2No ratings yet
- Calculate fundamental frequency of original tubeDocument7 pagesCalculate fundamental frequency of original tubeMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics (Statics)Document4 pagesApplied Mechanics (Statics)sushilNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu Forces and Equilibrium ReviewDocument6 pagesUniversity of Cebu Forces and Equilibrium Reviewjovar jumao-asNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS PROBLEMSDocument3 pagesF.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS PROBLEMSRosette de AsisNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 2Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity 2nrg8619No ratings yet
- PSAD 1 - Part 1Document3 pagesPSAD 1 - Part 1John Gavin CarmenNo ratings yet
- 1 Problem Set 1Document13 pages1 Problem Set 1ziraziziNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium SystemsDocument12 pagesEquilibrium SystemsEmilio Joaquin FloresNo ratings yet
- P1 TH Problems StaticsDocument35 pagesP1 TH Problems StaticsNguyenNo ratings yet
- Refresher Modules DesignDocument11 pagesRefresher Modules Designyajnad_10No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 10, 2024Document7 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 10, 2024rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- CE 102 Engineering Mechanics 2019 PDFDocument34 pagesCE 102 Engineering Mechanics 2019 PDFManish MeenaNo ratings yet
- Keieiie TQMCorrelation DesignDocument5 pagesKeieiie TQMCorrelation DesignJeth Verdejo RiveroNo ratings yet
- Classify The Structure On The Basis of Determinacy and Indeterminacy and Also On The Stability and InstabilityDocument4 pagesClassify The Structure On The Basis of Determinacy and Indeterminacy and Also On The Stability and InstabilitykamalnitrrNo ratings yet
- Ge 6253Document23 pagesGe 6253athishankaranNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument5 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesUwu WehNo ratings yet
- IITB MechanicsDocument49 pagesIITB Mechanicskeshavkrishna20007No ratings yet
- Problems: Fig. P2.1Document3 pagesProblems: Fig. P2.1hector cabalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - Week 9Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet - Week 9bananaNo ratings yet
- QB AnsDocument29 pagesQB Ans18WJ1A03F4 Shashank reddyNo ratings yet
- PS Statics 1Document9 pagesPS Statics 1Kenny SiludNo ratings yet
- April 2024 - PSAD 2Document2 pagesApril 2024 - PSAD 2rando12345No ratings yet
- Fuerzas en 3D y Equilibrio de Una Particula en 3D - Estatica de Beer 9edDocument11 pagesFuerzas en 3D y Equilibrio de Una Particula en 3D - Estatica de Beer 9edSheyla Estefany Salome VilcahuamanNo ratings yet
- Module1 - Set 2aDocument2 pagesModule1 - Set 2aindhubalab200413chNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios ElectricidadDocument6 pagesEjercicios ElectricidadNICOLAS NAVAS SUASNAVASNo ratings yet
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Document8 pagesE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101No ratings yet
- VOL1Document3 pagesVOL1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 1Document1 pageUnit Test 1Pandey 14No ratings yet
- Numerical Sheet 1Document4 pagesNumerical Sheet 1failuretotoppertargetNo ratings yet
- Civil and Mechnical RKDocument2 pagesCivil and Mechnical RKrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 6 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 6 - Refresher SECJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Forces and Structures ProblemsDocument8 pagesForces and Structures ProblemsMarco AlfantaNo ratings yet
- University Question Bank - CTDocument25 pagesUniversity Question Bank - CTSenthil IlangovanNo ratings yet
- ES 333 COE - Statics of Rigid Bodies Midterm Exam SolutionsDocument2 pagesES 333 COE - Statics of Rigid Bodies Midterm Exam SolutionsEngr.PenguinNo ratings yet
- Statics Solved ProblemsDocument4 pagesStatics Solved ProblemsRomeoNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodiesdonald escalanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Sample ProblemsDocument22 pagesChapter 4 - Sample ProblemsNeil Anthony Pojas BlancaNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium Problems Chapter 4Document2 pagesStatic Equilibrium Problems Chapter 4Neil Anthony Pojas BlancaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Sample Problems (Truss Analysis)Document16 pagesChapter 5 - Sample Problems (Truss Analysis)Neil Anthony Pojas BlancaNo ratings yet
- Statics Truss Problems Chapter 5Document2 pagesStatics Truss Problems Chapter 5Neil Anthony Pojas BlancaNo ratings yet
- Vivekananda's Role as Revivalist Reformer and His Ideas of Equality and Spiritual RevolutionDocument2 pagesVivekananda's Role as Revivalist Reformer and His Ideas of Equality and Spiritual RevolutionMartin VanlalhlimpuiaNo ratings yet
- Practical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Document15 pagesPractical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Vaibhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Deutz td2011 l04w Service Manual PDFDocument7 pagesDeutz td2011 l04w Service Manual PDFLuis Carlos RamosNo ratings yet
- Learn Meanings of 96 Difficult WordsDocument400 pagesLearn Meanings of 96 Difficult WordsVaishali Venkatesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Death of Frank LangamanDocument6 pagesDeath of Frank LangamanPaul ToguayNo ratings yet
- The University of QueenslandDocument2 pagesThe University of Queenslandimmanuel nauk elokpereNo ratings yet
- Arduino Mario Bros Tunes With Piezo Buzzer and PWMDocument6 pagesArduino Mario Bros Tunes With Piezo Buzzer and PWMClaudia GrijalvaNo ratings yet
- 286129Document23 pages286129Cristian WalkerNo ratings yet
- Midcheek Lift Using Facial Soft-Tissue Spaces of The MidcheekDocument11 pagesMidcheek Lift Using Facial Soft-Tissue Spaces of The MidcheekЩербакова ЛенаNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter OverviewDocument21 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter OverviewKar KuanNo ratings yet
- World After CovidDocument18 pagesWorld After CovidVidhisha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Group L2 Nitish at Solutions UnlimitedDocument10 pagesGroup L2 Nitish at Solutions UnlimitedMani ThomasNo ratings yet
- Inergen Order Data SheetDocument31 pagesInergen Order Data Sheetkarim3samirNo ratings yet
- FaucifilesDocument302 pagesFaucifilesLady WellingtonNo ratings yet
- 4 A CompiledDocument167 pages4 A CompiledArjun MiddhaNo ratings yet
- Questions Scope PDFDocument10 pagesQuestions Scope PDFabdou madjidNo ratings yet
- Transcricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingaleDocument62 pagesTranscricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingalepauloalaraNo ratings yet
- State-of-Charge Estimation On Lithium Ion Batteries - Mori W YatsuiDocument5 pagesState-of-Charge Estimation On Lithium Ion Batteries - Mori W Yatsuit3hgoneNo ratings yet
- Types of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesDocument77 pagesTypes of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesJyothish VijayNo ratings yet
- Gabriel MarcelDocument6 pagesGabriel MarcelCeciBohoNo ratings yet
- Installing Juniper Router OS JunOS 10 1 in Qemu VM For GNS3Document4 pagesInstalling Juniper Router OS JunOS 10 1 in Qemu VM For GNS3Adrian Ionut NituNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 1: (Traditions and Locations: The Filipino Poem (A Long History of Poetry)Document31 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 1: (Traditions and Locations: The Filipino Poem (A Long History of Poetry)Sicnarf Rolag0% (1)
- Resume Masroor 3Document3 pagesResume Masroor 3mohammad masroor zahid ullahNo ratings yet
- Vedic Healing Through Gems4Document3 pagesVedic Healing Through Gems4gesNo ratings yet
- RTR - Nonmetallic Pipng ProcedureDocument16 pagesRTR - Nonmetallic Pipng Proceduremoytabura96100% (1)
- Maruti Institute of Nursing, Itarsi: Maternal Nursing Child Health Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing FoundationDocument4 pagesMaruti Institute of Nursing, Itarsi: Maternal Nursing Child Health Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing FoundationHarshaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure & Functiongundogan21100% (1)
- Pharmacist Licensing Requirements by StateDocument21 pagesPharmacist Licensing Requirements by StateBio DataNo ratings yet
- Listado 2 4ghzDocument4 pagesListado 2 4ghzRogerNo ratings yet
- a9ff9ISM - Business DefinitionDocument7 pagesa9ff9ISM - Business DefinitionVikram Kumar100% (1)