Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(A) Skeletal Muscle Tissue (B) Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
Uploaded by
fafafa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
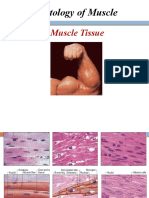
9 views2 pagesSkeletal muscle tissue contains bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains repeating contractile units called sarcomeres composed of actin and myosin filaments. The sarcomere, bounded by Z-lines, is the basic contractile machinery where overlapping actin and myosin filaments interact to generate force and cause muscle contraction.
Original Description:
affa
Original Title
Documentf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSkeletal muscle tissue contains bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains repeating contractile units called sarcomeres composed of actin and myosin filaments. The sarcomere, bounded by Z-lines, is the basic contractile machinery where overlapping actin and myosin filaments interact to generate force and cause muscle contraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pages(A) Skeletal Muscle Tissue (B) Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
Uploaded by
fafafaSkeletal muscle tissue contains bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains repeating contractile units called sarcomeres composed of actin and myosin filaments. The sarcomere, bounded by Z-lines, is the basic contractile machinery where overlapping actin and myosin filaments interact to generate force and cause muscle contraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
(A)Skeletal muscle tissue
(B)Mechanism of muscle contraction
1. Skeletal muscle tissue is covered by a connective tissue called epimysium.
2. Inside the skeletal muscle tissue are fascicles(bundles) containing skeletal muscle
cells/fibres.
3. Fascicles are covered by a layer of connective tissue called perimysiun
4. Skeletal muscles fibres found inside these fascicles are covered by a thin layer of
connective tissue called endomysium.
5. There are numberous skeletal muscle cells in a muscle tissue
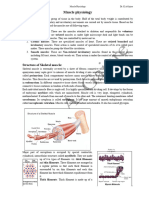
6. Skeletal muscle fibres are cylindrical, long and unbranched
7. Each fibre contains many nuclei located peripherally
8. The plasma membrane of muscle fibres is termed sarcolemma
9. The cytoplasm is termed sarcoplasm
10. There are numerous mitochondria in each sarcomere
11. Skeletal muscle fibres contain smaller units called myofibrils
12. Myofibrils contain two types of filaments
13. Thin actin filaments
14. Thick myosin filaments
15. The arrangement of these filaments in a repeated pattern gives a striated appearence to
muscle cells
16. The region between two Z lines is termed the sarcomere.
17. It is the contractile unit of muscle cell.
18. Z lines are thin membranes made of actin protein
19. Actin filaments are attached to Z lines
20. The region containing only actin filaments is termed I band( light band )
21. The region which contains both actin and myosin filaments is termed A band and it
appears dark in colour
22. The thin membrane that marks the midline of the sarcomere is the M line
23. Myosin filaments are attached to it.
24. Regions containing only myosin filaments are H zones
25. They are the regions between two actin filaments
26. Each myosin filament is surrounded by 6 actin filaments
27. Actin filaments are stacked between myosin filaments
afa
faa
af
af
You might also like
- Chap-20 - Locomotion & MovementDocument52 pagesChap-20 - Locomotion & MovementMittal SavaniNo ratings yet
- Histology, Lecture 5, Muscular Tissue (Slides)Document17 pagesHistology, Lecture 5, Muscular Tissue (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (3)
- Histology of MuscleDocument49 pagesHistology of MuscleTewachew Dessie100% (1)
- Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryDocument13 pagesChapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Célula Muscular, Macro y MicrobiologicoDocument11 pagesCélula Muscular, Macro y MicrobiologicoimanolNo ratings yet
- Muscular TDocument18 pagesMuscular TSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument88 pagesMuscle PhysiologyAftab MughalNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI - Contraction of The Skeletal Muscle: Filamentous Bands Light Bands Dark BandsDocument13 pagesChapter VI - Contraction of The Skeletal Muscle: Filamentous Bands Light Bands Dark BandsLorenz L. Llamas IIINo ratings yet
- 3D. Muscle TissueDocument47 pages3D. Muscle Tissuejaf123xyNo ratings yet
- Classification of MusclesDocument50 pagesClassification of MusclesNoor HaleemNo ratings yet
- Histo MuscleDocument11 pagesHisto MuscleaikaNo ratings yet
- Excitable Tissues 1Document8 pagesExcitable Tissues 1gojaisaiah787No ratings yet
- 589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyDocument3 pages589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyMalti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of Skeletal MuscleDocument6 pagesUltra Structure of Skeletal MuscleRehna FathimaNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle TissueDocument11 pagesTypes of Muscle TissueAndrea Louise ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument65 pagesMuscular TissueMitzel SapaloNo ratings yet
- Stevens & Lowe's Human Histology 4 EdDocument13 pagesStevens & Lowe's Human Histology 4 EdsheldonboyNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton MADocument22 pagesCytoskeleton MAsema raraNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument11 pagesMuscle TissueAlexNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Muscular System: Movement: PSYN 103: Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument67 pagesChapter 7: Muscular System: Movement: PSYN 103: Human Anatomy and PhysiologyWindy LavarientosNo ratings yet
- Wa0038Document10 pagesWa0038Shehzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue Slides C 20152016Document39 pagesMuscle Tissue Slides C 20152016brennan12345No ratings yet
- Microscopic Anatomy of Muscle - 746056Document7 pagesMicroscopic Anatomy of Muscle - 746056Abhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Contraction and The Motor UnitsDocument4 pagesSkeletal Muscle Contraction and The Motor UnitsAnonymous vnv6QFNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissuesDocument46 pagesMuscular TissuesDAVE CANALETANo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy - ContentDocument14 pagesFunctional Anatomy - ContentxanaduNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesTopic 7 Muscular SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument11 pagesMuscleJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Medicine: Practical Work No. 9Document3 pagesFaculty of Medicine: Practical Work No. 9Andrei TimofteNo ratings yet
- Human Histology (Laboratory) Lesson 5: Muscle Tissue: Pre-Lab DiscussionDocument2 pagesHuman Histology (Laboratory) Lesson 5: Muscle Tissue: Pre-Lab DiscussionAJ MERCADONo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissues: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarDocument65 pagesMuscle Tissues: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarYulius SamuelNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 PDFDocument6 pagesLec 6 PDFАбу ДжудNo ratings yet
- Muscles Lecture For AnatomyDocument56 pagesMuscles Lecture For AnatomyJennifer FirestoneNo ratings yet
- 04muscle TissueDocument39 pages04muscle Tissueapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Fungsi Sistem OtotDocument8 pagesFungsi Sistem OtotMahesha RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleDocument73 pagesHistology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleShehryar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleDocument73 pagesHistology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleShehryar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Development of Vertebrate Skeletal MuscleDocument11 pagesDevelopment of Vertebrate Skeletal Muscletesfaye mekonnenNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument3 pagesSkeletal Musclekrystal1994No ratings yet
- Microscopic Anatomy of A Skeletal Muscle FiberDocument33 pagesMicroscopic Anatomy of A Skeletal Muscle FiberKumar MSNo ratings yet
- Tejido MuscularDocument2 pagesTejido MuscularLourdes Tatyana Ramirez CubasNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue SummaryDocument2 pagesMuscle Tissue SummaryLindenScholesNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyDocument6 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)Document21 pagesAnatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)HumrazNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue-Wl06.11Document54 pagesMuscle Tissue-Wl06.11api-19641337No ratings yet
- LPT 321Document103 pagesLPT 321rahul roshanNo ratings yet
- ST - of Myofilaments..Document10 pagesST - of Myofilaments..Mohammed HamadaNo ratings yet
- Muscle CellsDocument45 pagesMuscle CellsAkaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesHistology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue 2012Document13 pagesMuscle Tissue 2012ST. Fatimah KadirNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument24 pagesMuscle PhysiologyArmando AlehandroNo ratings yet
- Muscle ContractionDocument44 pagesMuscle ContractionIshani ManivannanNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesMuscular SystemTricia Mae LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesReviewer - Muscular SystemIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument12 pagesMuscle PhysiologyAyres EvangNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument9 pagesLocomotion and Movementpoojari.dedeepyaNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument81 pagesMuscular TissueimmmiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue OutlineDocument4 pagesMuscle Tissue OutlinePeachy PieNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Imp Ch7 2Document6 pages11 Biology Imp Ch7 2th1nv2rNo ratings yet