Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyponatremia Algorithm-1 PDF
Uploaded by
dsaroha1Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hyponatremia Algorithm-1 PDF
Uploaded by
dsaroha1Copyright:
Available Formats
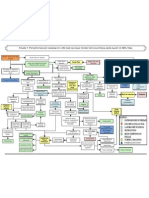
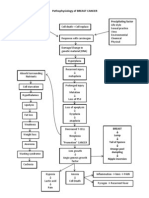
Hyponatremia Algorithm
Measured Serum Osmolality
Normal (~ 280 mOsm) Isotonic Elevated (> 280 mOsm) Hypertonic Low (<280 mOsm) Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Pseudohyponatremia Hyperglycemia
Hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglobulinemia Unmeasured effective osmoles (glycine,
Ion-specific electrodes has alleviated this mannitol, sorbitol, maltose, radiocontrast
lab error dyes)
Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Total body water ↓ Total body water ↑↑ (no edema)
Total body sodium ↓↓ Total body sodium ↑ Total Body Water ↑
Effective arterial blood volume low Total Body Sodium ↔
Uosm > 450 mOsm/kg Uosm > 100 mOsm/kg Uosm > 100 mOsm/kg Uosm < 100 mOsm/kg
Inappropriately High Maximally dilute
Appropriately low
Una < 20 meq/l Una > 20 meq/l UNa < 20 meq/l UNa > 20 meq/l
Maybe > 20 meq/l with diuretic UNa > 20 meq/l UNa < 20 meq/l
Causes: Causes: Causes: Causes Causes: Causes:
Extrarenal Losses Renal Losses CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic Acute or chronic Hypothyroidism (TSH Primary polydipsia
Vomiting, Diarrhea Diuretics, syndrome, renal failure level), Glucocorticoid (psychogenic
Third Spacing (burns, Mineralocorticoid deficiency Low effective arterial deficiency polydipsia),
pancreatitis), Bowel (aldosterone), blood volume (orthostatic (adenocorticotrophin Low solute intake
obstruction, Trauma, Salt losing Nephritis, changes in HR/BP, Treatment: stimulation test); (beer potomania
Sweating, Bicarbonaturia (renal tubular hemoconcentration), Dialysis SIADH, Stress, Drugs, syndrome)
acidiosis, causes release of ADH
metabolic alkalosis), and aldosterone
Cerebral Salt Wasting
Syndrome,
Ketonuria, Osmotic diuresis Treatment: Go to Severe Euvolemic Fluid restrict
Onset Slow (> 48 hours): Fluid Hypotonic Hyponatremia on
restriction Next page
Treatment: Onset Rapid (<48 hours): 3%
Onset Slow (>48 hours): 0.9% NaCl NaCl and loop diuretic
Onset Rapid (<48 hours): May consider
3% NaC l Optimize treatment of underlying
Stop offending medications; restore disease; restrict salt and water
intravascular volume with 0.9% NaCl intake; give loop diuretics
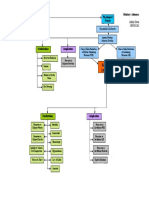
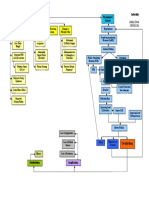
Severe Euvolemic Hyptonic Hyponatremia (Serum Sodium < 125 meq/l)
Symptomatic
Confusion, ataxia, seizures, obtundation, coma, Asymptomatic or mild symptoms
respiratory depression (headache, lethargy, dizziness)
Acute < 48 hours Chronic > 48 hours or
Unknown Duration Chronic
Rarely < 48 hours
Treatment: Treatment
3% Sodium Chloride 1-2 3% Sodium Chloride 1-2
ml/kg/hour until symptoms ml/kg/hour, change to water
resolve, then 0.5 ml/kg/hour restriction after 10% or 10 meq/l No immediate correction
Sodium should not increase any increase in serum sodium or needed
faster than 12 meq/L in first 24 symptoms resolved.
hours, or 20 meq/L in the first Maximum correction of 15
48 hours. Stop 3% Sodium meq/L per day
Chloride as soon as medical
possible. Water restriction, 3% NaCl plus
loop diuretic, stop offending
Water restriction, 3% NaCl plus medications; hormone
loop diuretic, stop offending replacement
medications; hormone Long Term Management
replacement Patients with chronic Identify and treat reversible caused
hyponatremia are at a higher risk Water restriction
If urine mOsm > 300 a loop for severe side effects if serum Furosemide with 2-3 g of sodium chloride
diuretic may be needed to sodium is corrected too rapidly. per day
enhance water excretion Demeclocycline, 1200 mg on day one then
The sum of urinary cations (UNa 300-600 mg bid (avoid if renal or hepatic
The sum of urinary cations + UK) should be less than the insufficiency)
(Una + UK) should be less than concentration of the infused Urea 15-60 g/day
the concentration of the infused sodium to ensure excretion of
sodium to ensure excretion electrolyte-free water.
electrolyte-free water.
There is no consensus about the optimal treatment of symptomatic hyponatremia. Correction should be of a sufficient pace and
magnitude to reverse the manifestations of hypotonicity, but not so rapid and large as to pose a risk for developing osmotic
demyelination.
For mild symptoms of hyponatremia, or asymptomatic patients with serum sodium above 125 meq/l, use a conservative approach.
(Water restriction less than 1-1.25 l/day) If serum sodium continues to decline 0.9% NaCl may be given to clarify diagnosis. If the
patient has SIADH, hyponatremia will worsen and if they are ECF volume contracted serum sodium will improve.
You might also like
- Care Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleDocument3 pagesCare Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleVette Angelikka Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAl RizkyNo ratings yet
- Risk For Falls Aeb Loss of BalanceDocument4 pagesRisk For Falls Aeb Loss of BalanceAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToDocument7 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Case Presenttaion (GRP 1, 3BSN-13) Ra (2NCP)Document22 pagesCase Presenttaion (GRP 1, 3BSN-13) Ra (2NCP)Lorelyn Santos Corpuz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel0% (1)
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocument1 pageZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- CHF Cardiomegaly Volume OverloadDocument1 pageCHF Cardiomegaly Volume Overloadnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367No ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaDhonabelleVanessaFetalinoAdona100% (1)
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseAna Katrina OcanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plansyfi56No ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Case Study Final PortraitDocument11 pagesCase Study Final PortraitZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Module V ActDocument3 pagesModule V ActQueencess hayoNo ratings yet
- Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToDocument8 pagesWhich It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranNo ratings yet
- Gerontologic Health Promotion ActivityDocument3 pagesGerontologic Health Promotion ActivityCorinne50% (2)
- Nursing Priority Problem ListDocument1 pageNursing Priority Problem ListJackyleen Kate BenetuaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument48 pagesDiabetes InsipidusAhmed Fraz MamoonNo ratings yet
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- "Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" AsDocument4 pages"Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" Ashanna caballoNo ratings yet
- NCP EsrfDocument9 pagesNCP EsrfKen RegalaNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchangeruggero07No ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Document20 pagesSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Volume DeficitNecheal BaayNo ratings yet
- NCP Active SeizureDocument4 pagesNCP Active SeizureAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument9 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-606252228No ratings yet
- Chapter 47 Diabetes Mellitus PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 47 Diabetes Mellitus PDFRLLT100% (1)
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDocument9 pagesClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Caso Clinico Electivas 3Document9 pagesCaso Clinico Electivas 3MARIANGEL LAFONTNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentCorinneNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument4 pagesRRLAnnalyn MantillaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultDocument11 pagesSepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultShrests SinhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On MalariaDocument18 pagesCase Study On MalariaRameshKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive NephrosclerosisDocument14 pagesHypertensive Nephrosclerosisreysanne100% (1)
- 3 Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pages3 Nursing Care PlanJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Hypoxia: Lori HolmesDocument5 pagesHypoxia: Lori HolmesDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NDocument41 pagesDisorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NBharath Kumar PamulapatiNo ratings yet
- De Methaq L2 HyponatreamiaDocument11 pagesDe Methaq L2 Hyponatreamiaزين العابدين محمد عويش مشريNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorithm: Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : 3% Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : May Consider 3% Nac LDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorithm: Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : 3% Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : May Consider 3% Nac Lmina000005100% (1)
- Concept Map TemplateDocument1 pageConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocument1 pageDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Concept Map BlankDocument2 pagesConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocument1 pagePathophysiology EmphysemaGil AswiguiNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Concept MapDocument2 pagesMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus PathophsyiologyDocument3 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus Pathophsyiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Physiological ChangesDocument1 pagePhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument2 pagesPATHOmycoclitNo ratings yet
- Hip FractureDocument3 pagesHip Fracturenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocument1 pagePathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroNo ratings yet
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocument1 pageSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Burn InjuryDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Burn InjuryAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocument1 pageBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocument1 pageNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- Critical Care Concept MapDocument1 pageCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocument1 pagePituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocument1 pageDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia MapDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of BREAST CANCERDocument1 pagePathophysiology of BREAST CANCERAlinor Abubacar100% (6)
- Infertility Concept MapDocument1 pageInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocument1 pageOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Robert W. Schrier - Atlas of Diseases of The Kidney Volume 01 PDFDocument316 pagesRobert W. Schrier - Atlas of Diseases of The Kidney Volume 01 PDFAtu Oana100% (3)
- October Sodium DisordersDocument20 pagesOctober Sodium DisordersAngel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chloremia (Hypochloremia) & Acute and Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis (Carbonic Acid Deficit)Document4 pagesChloremia (Hypochloremia) & Acute and Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis (Carbonic Acid Deficit)KQarlo Luis Pestaño Maniaol100% (1)
- Pediatric Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDocument8 pagesPediatric Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyWildan Wisnu WardayaNo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Anti Diuretic HormoneDocument39 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Anti Diuretic Hormonefarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Management of PediatricDocument22 pagesHead Injury Management of PediatricIrma KusumaNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia in Tuberculous MeningitisDocument11 pagesHyponatremia in Tuberculous MeningitisBelinda Putri agustiaNo ratings yet
- Integ 4 Answer PDFDocument12 pagesInteg 4 Answer PDFRhasdie MandiNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Posterior Pituitary-SIADH/Diabetes InsipidusDocument19 pagesDisorders of The Posterior Pituitary-SIADH/Diabetes InsipidusAndy F MonroeNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Hiponatremia, Hiperkalemia, HipomagnesiemiaDocument15 pagesTatalaksana Hiponatremia, Hiperkalemia, HipomagnesiemiaUdyani AgustinaNo ratings yet
- 12 Clinical Pathology of The FoalDocument29 pages12 Clinical Pathology of The FoalKatty ZanabriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Electrolyte Imbalances Part 1Document74 pagesLesson 4 - Electrolyte Imbalances Part 1Clark SavageNo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHDocument14 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHbhatubim100% (1)
- Resident Survival Guide: (Include Ranges of Any Abnormal Vital Signs But Also Include The Current Value For All Vitals.)Document104 pagesResident Survival Guide: (Include Ranges of Any Abnormal Vital Signs But Also Include The Current Value For All Vitals.)scalixto100% (1)
- Hyponatremia in Cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, Clinical Significance, and ManagementDocument48 pagesHyponatremia in Cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, Clinical Significance, and ManagementrlagamNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Physical Adverse ReactionsDocument110 pagesAntidepressant Physical Adverse ReactionsanntjitNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument103 pagesFluids and Electrolyte Disturbancesanreilegarde100% (1)
- The Brigham Renal Board Review CourseDocument2,195 pagesThe Brigham Renal Board Review CourseHydralazine100% (5)
- Hiponatremia Acute ApendicitisDocument13 pagesHiponatremia Acute ApendicitisDeliciousNo ratings yet
- Siadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentDocument1 pageSiadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentVishalNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte General Surgery Review Course.Document97 pagesFluid and Electrolyte General Surgery Review Course.Kamil HannaNo ratings yet
- DehydrationDocument10 pagesDehydrationAbdelrahman M. AlnweiriNo ratings yet
- NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorDocument8 pagesNUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorAmber EssmanNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance 1Document3 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance 1Marius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- Garrahy 2020Document13 pagesGarrahy 2020Ana Elizabeth Gangotena CoralNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument49 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Disorders: Yashi ChauhanDocument22 pagesNutritional Disorders: Yashi ChauhanyashichauhanNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid, Electrolyte FcpsDocument73 pagesBody Fluid, Electrolyte FcpsInzamamul Haque ShihabNo ratings yet
- Physio Multiple Choice Body Fluids and Renal and RespDocument15 pagesPhysio Multiple Choice Body Fluids and Renal and Respsac50900No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes (Acid Base)Document31 pagesFluid and Electrolytes (Acid Base)Diana TahamidNo ratings yet