Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Work Performance Data
Work Performance Data
Uploaded by
phoneme790 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pagedata on work perforamcne
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdata on work perforamcne
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageWork Performance Data
Work Performance Data
Uploaded by
phoneme79data on work perforamcne
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
5 - PROJECT SCOPE MANAGEMENT
5.6.1.4 Work Performance Data
Described in Section 4.3.3.2. Work performance data can include the number of change requests received, the
number of requests accepted or the number of deliverables completed, etc.
5.6.1.5 Organizational Process Assets
Described in Section 2.1.4. The organizational process assets that can influence the Control Scope process
include, but are not limited to: 5
s� Existing formal and informal scope, control-related policies, procedures, guidelines; and
s� Monitoring and reporting methods and templates to be used.
5.6.2 Control Scope: Tools and Techniques
5.6.2.1 Variance Analysis
Variance analysis is a technique for determining the cause and degree of difference between the baseline and
actual performance. Project performance measurements are used to assess the magnitude of variation from the
original scope baseline. Important aspects of project scope control include determining the cause and degree of
variance relative to the scope baseline (Section 5.4.3.1) and deciding whether corrective or preventive action is
required.
5.6.3 Control Scope: Outputs
5.6.3.1 Work Performance Information
Work performance information produced includes correlated and contextualized information on how the project
scope is performing compared to the scope baseline. It can include the categories of the changes received, the
identified scope variances and their causes, how they impact schedule or cost, and the forecast of the future scope
performance. This information provides a foundation for making scope decisions.
©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition 139
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Noise MeasurementDocument1 pageNoise Measurementphoneme79No ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument1 pageWork Breakdown Structurephoneme79No ratings yet
- Network DiagramDocument1 pageNetwork Diagramphoneme79No ratings yet
- Backlash DefinitonDocument1 pageBacklash Definitonphoneme79No ratings yet
- Schedule Management PlanDocument1 pageSchedule Management Planphoneme79No ratings yet
- Cage Defect Frequency: Modulation, Frequency Modulation, and ModulationDocument1 pageCage Defect Frequency: Modulation, Frequency Modulation, and Modulationphoneme79No ratings yet
- 1.2 Stakeholder Register: 8 Initiating FormsDocument1 page1.2 Stakeholder Register: 8 Initiating Formsphoneme79No ratings yet
- Requirements Management PanDocument1 pageRequirements Management Panphoneme79No ratings yet
- Machinery Health Sensors: White PaperDocument1 pageMachinery Health Sensors: White Paperphoneme79No ratings yet
- Number of AveragesDocument1 pageNumber of Averagesphoneme79No ratings yet
- Beating DefinitionDocument1 pageBeating Definitionphoneme79No ratings yet
- Spectram LinesDocument1 pageSpectram Linesphoneme79No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Charts For WaterDocument1 pageHydraulic Charts For Waterphoneme79No ratings yet
- Design of Water Pipe FlowsDocument1 pageDesign of Water Pipe Flowsphoneme79No ratings yet
- Predict CorrosionDocument1 pagePredict Corrosionphoneme79No ratings yet
- Data Display SpectrumDocument1 pageData Display Spectrumphoneme79No ratings yet
- Max Ferequrency Seleti9onDocument1 pageMax Ferequrency Seleti9onphoneme79No ratings yet
- Important Note: Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI) Can Often Be VeryDocument1 pageImportant Note: Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI) Can Often Be Veryphoneme79No ratings yet
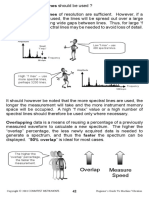
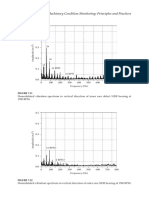
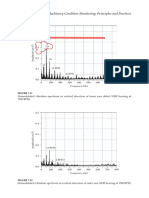
- Vibration Monitoring: Demodulated Vibration Spectrum in Vertical Direction of Normal NDE Bearing at 1740 RPMDocument1 pageVibration Monitoring: Demodulated Vibration Spectrum in Vertical Direction of Normal NDE Bearing at 1740 RPMphoneme79No ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Pipe Standards 1Document1 pageCarbon Steel Pipe Standards 1phoneme79No ratings yet
- Sintakote JointDocument1 pageSintakote Jointphoneme79No ratings yet
- Dignostic Mode VibrationDocument1 pageDignostic Mode Vibrationphoneme79No ratings yet
- Straub Flex CouplingDocument1 pageStraub Flex Couplingphoneme79No ratings yet
- Static Dynamic MeasurementDocument1 pageStatic Dynamic Measurementphoneme79No ratings yet
- Rotational VibrometerDocument1 pageRotational Vibrometerphoneme79No ratings yet
- Machinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and PracticesDocument1 pageMachinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and Practicesphoneme79No ratings yet
- 6.10 Force Measurements: Machinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and PracticesDocument1 page6.10 Force Measurements: Machinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and Practicesphoneme79No ratings yet
- Machinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and PracticesDocument1 pageMachinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and Practicesphoneme79No ratings yet
- 6.3 Measurement Errors: Machinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and PracticesDocument1 page6.3 Measurement Errors: Machinery Condition Monitoring: Principles and Practicesphoneme79No ratings yet