Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Docking Experiment of Potential Inhibitors of The Human Y
Docking Experiment of Potential Inhibitors of The Human Y
Uploaded by
Kaka TsaiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Docking Experiment of Potential Inhibitors of The Human Y
Docking Experiment of Potential Inhibitors of The Human Y
Uploaded by
Kaka TsaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Kaelin Wilby Tsai November 9, 2018
Docking of Potential Inhibitors of the Human Y-family DNA Polymerase POLK
Introduction
Objectives
The objective of this study is to perform a local docking experiment with potential inhibitors
as the ligands and Pol kappa as the protein using AutoDock4 and AutoDock Vina. To measure
the effectivity of the drug binding, the dissociation constant is determined, along with the
binding energy. The docking score and location of the binding pocket with its corresponding
receptor residues are also shown. The results obtained from the two methods shall be evaluated
through RMSD values and both will be compared to the given literature as well.
Methodology
Given the 2D structures of the inhibitor molecules, their minimized 3D structures were
rendered using Maestro. Next, AutoDockTools was used to prepare the protein and ligands for
docking. Polar hydrogens were added to PolK while the 4 ligands were subjected to the
automatic addition of Gasteiger charges, rotatable bonds and number of torsional degrees of
freedom, and number of non-polar hydrogens merged. The protein was then set to be a rigid
macromolecule while several map files for the inhibitors were produced. The search space was
set afterwards wherein the number of points in each dimension was 60 and centered at the known
ligand-binding residues (47.65, 19.46, 70.18). Once the rigid receptor, search space, and flexible
molecules were set, AutoGrid was run to generate a log file output. The search method used in
AutoDock4 was genetic algorithm and default parameters, wherein the output was a docking
parameter file with instructions for a Lamarckian GA docking. The results were then determined
and visualized with AutoDockTools again. For AutoDock Vina, the same input files were used
and the program was run in the terminal. The results were presented in the log output file.
Results and Discussion
The binding affinities from AutoDock Vina
Possible Sources of Deviations:
1. Minimization: Only the default minimization function was used in Maestro
2. Grid center may have been different, despite having known the residues surrounding the
binding pocket; number of points of the grid box may have also been different
3. Only Polar hydrogens were added to the molecule/protein
4. Torsions/number of torsions of the ligands may have been modified after the automatic
designations
5. Flexible residues may have been added in the receptor
6. Different settings for the search parameter, docking parameter, and type of genetic
algorithm used
7. AutoDock Vina and AutoDock4 both report vastly different values.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 4th Edition Christopher K Mathews Kensal e Van Holde Dean R ApplingDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 4th Edition Christopher K Mathews Kensal e Van Holde Dean R ApplingGeorgeAndersonikwq100% (35)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Che 142 - Final Exam Reviewer 01 Intro Hse in Design: HealthDocument8 pagesChe 142 - Final Exam Reviewer 01 Intro Hse in Design: HealthKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- PI 100 Report On Cultural ISADocument36 pagesPI 100 Report On Cultural ISAKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- Notes For NMT & EF ReadingsDocument3 pagesNotes For NMT & EF ReadingsKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- PI 100 Report On Educational ISADocument37 pagesPI 100 Report On Educational ISAKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- 2 Vs - 1 Plot: 650 700 F (X) 104.1041490596x - 702.4391748891 R 0.9410704028Document2 pages2 Vs - 1 Plot: 650 700 F (X) 104.1041490596x - 702.4391748891 R 0.9410704028Kaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- GROMACS Installation and Simulation GuideDocument10 pagesGROMACS Installation and Simulation GuideKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
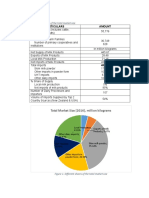
- Total Market Size (2016), Million KilogramsDocument6 pagesTotal Market Size (2016), Million KilogramsKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Overview of The Total Market Size: Particulars AmountDocument1 pageTable 1. Overview of The Total Market Size: Particulars AmountKaka TsaiNo ratings yet
- Ecology + Bio NotesDocument9 pagesEcology + Bio Notesashra rNo ratings yet
- Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis IIDocument36 pagesSodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis IIYUEALVIN17No ratings yet
- 3 Carbohydrates' StructureDocument33 pages3 Carbohydrates' StructureDilan TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Phospholipid and Sphingosine SynthesisDocument2 pagesPhospholipid and Sphingosine SynthesisAlliah Mae LumanogNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument6 pagesTopic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationAdeyinka OluyoleNo ratings yet
- Understanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivAntonisNo ratings yet
- Stabilising Forces in Protein Structure: E-Content M.Sc. Zoology (Semester II) CC7-Biochemistry Unit: 3.2Document16 pagesStabilising Forces in Protein Structure: E-Content M.Sc. Zoology (Semester II) CC7-Biochemistry Unit: 3.2paresh kumar sahoo100% (1)
- Enzyme - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesEnzyme - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediachanackchanackNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure: The Peptide BondDocument13 pagesProtein Structure: The Peptide BondanaNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument35 pagesElectron Transport ChainNusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- DPN - Biochem 1-Exam 2 - 2022Document9 pagesDPN - Biochem 1-Exam 2 - 2022chienyu2002No ratings yet
- 02.06.2018 - 5 - M. Vives Santacana - Principles of PharmacodynamicsDocument46 pages02.06.2018 - 5 - M. Vives Santacana - Principles of PharmacodynamicsPhilippe KinnaerNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Lipids and Protein Exam QuestionsDocument13 pages1.5 Lipids and Protein Exam QuestionsAhmad LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Omega Fatty AcidsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Omega Fatty Acidsdrubwang100% (1)
- Alexa Riley - Enzyme Lab ExperimentDocument9 pagesAlexa Riley - Enzyme Lab Experimentapi-553676905No ratings yet
- Aux/IAA Gene Family in Plants: Molecular Structure, Regulation, and FunctionDocument17 pagesAux/IAA Gene Family in Plants: Molecular Structure, Regulation, and FunctionViaNo ratings yet
- 27 - Protein Trafficking - Nuclear TransportDocument12 pages27 - Protein Trafficking - Nuclear TransportHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument339 pagesUntitledJOS� FRANCISCO G�MEZ RODR�GUEZNo ratings yet
- J. Gram, J. Jespersen (Auth.), J. Jespersen, R. M. Bertina, F. Haverkate (Eds.) - Laboratory Techniques in Thrombosis - A Manual-Springer Netherlands (1999)Document307 pagesJ. Gram, J. Jespersen (Auth.), J. Jespersen, R. M. Bertina, F. Haverkate (Eds.) - Laboratory Techniques in Thrombosis - A Manual-Springer Netherlands (1999)BipedalJoeNo ratings yet
- Asupan Gizi Dengan Pengendalian Diabetes Pada Diabetisi Tipe Ii Rawat Jalan Di Blu Prof - Dr.R.D.Kandou ManadoDocument11 pagesAsupan Gizi Dengan Pengendalian Diabetes Pada Diabetisi Tipe Ii Rawat Jalan Di Blu Prof - Dr.R.D.Kandou Manadochafeb febiNo ratings yet
- 2nd - Part 3 - Lipid Structure and MetabolismDocument56 pages2nd - Part 3 - Lipid Structure and MetabolismAkbarWirawanNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 8 Activity 4Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 8 Activity 4andrea gomez herreraNo ratings yet
- Blood RevisedDocument105 pagesBlood RevisedKanelle SisayanNo ratings yet
- Oxidized LDL (Blog Post)Document10 pagesOxidized LDL (Blog Post)simasNo ratings yet
- Signals and ReceptorsDocument28 pagesSignals and ReceptorsEmilio MurciaNo ratings yet
- Ganga Et Al 2011Document10 pagesGanga Et Al 2011Rachid GangaNo ratings yet
- Sankar Et Al., 2013Document6 pagesSankar Et Al., 2013Natasha MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Protein StructuresDocument6 pagesProtein StructuresKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Acute-Phase Protein - WikipediaDocument4 pagesAcute-Phase Protein - WikipediaZACHARIAH MANKIRNo ratings yet