Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supervisory Responsibilities Checklist Ps
Uploaded by
venkat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesSupervisory responsibilities
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSupervisory responsibilities
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesSupervisory Responsibilities Checklist Ps
Uploaded by
venkatSupervisory responsibilities
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Confined Space – Supervisory Responsibilities Checklist
SUPERVISORY RESPONSIBILITIES YES/NO
1. Supervisors shall identify and report all job areas and locations that are or may be
confined spaces.
2. Maintain and provide a list of confined spaces that are identified which shall be submitted
to the Safety Organization.
3. In addition, the designated supervisors hall carry out the following tasks:
4. Classify confined spaces as "permit required," “Alternate Procedure” or "non-permit
required.”
5. Identify personnel who will enter confined spaces.
6. Identify the personnel under their supervision required to wear respirators.
7. Advise personnel on routine measurement of respiratory hazards in confined spaces.
8. Provide detailed instruction and training on confined space hazards and entry procedures
to those who may enter confined spaces.
9. Provide instruction to personnel on the proper use of equipment required for confined
space entry.
10. Maintain equipment that is used to enter confined spaces.
11. Conduct work site inspections to review unit compliance with confined space entry
procedures.
12. Maintain records of equipment maintenance and employee training.
13. Inform employees who may enter the permit confined space by posting danger signs or by
training.
14. Issuance and cancellation of entry permits.
15. Establishment of a lockout program for their department.
16. Identify and evaluate the hazards of permit spaces before employees enter them.
17. Conduct a pre-entry briefing to inform entrants of possible hazards that may be
encountered.
18. Identify the people who will enter the confined spaces.
19. Take the necessary measures to prevent entrance into prohibited permit spaces.
DUTIES OF THE “LEAD WORKER” (ENTRY SUPERVISOR): YES/NO
20. Know the potential hazards during entry and work.
21. Determine if acceptable entry conditions are present at a permit space where entry is
planned.
22. Terminate entry as required by the standard.
23. Verify that rescue services are readily available and the means for summoning them are
operable.
24. Remove unauthorized individuals who enter or try to enter the permit space during entry
and work.
25. Determine that entry and work operations remain consistent with entry permit terms and
that acceptable entry conditions are maintained.
26. Determine if entry into confined space is necessary to perform work.
Note: The person authorizing the entry may also serve as the entrant or attendant for the
entry
The following minimum required equipment should be on hand: YES/NO
27. Ventilation,
28. Barrier and warning signs,
29. Gas monitor capable of measuring concentrations of oxygen, flammable gases, hydrogen
sulfide and carbon monoxide.
30. Eliminate any unsafe conditions before the access door or cover is opened.
Conduct hazard assessment YES/NO
31. Test the real or potential atmospheric hazards
32. Oxygen content less than 19.5% or greater than 23.5%
33. Flammable gases and vapors greater than 10% of the LEL (Lower Explosive Limit)
34. Hydrogen Sulfide concentrations greater than 10 ppm (Parts per million)
35. Carbon Monoxide concentrations greater than 35 ppm
Review the space for other observable serious safety and health hazards: YES/NO
36. mechanical,
37. electrical,
38. burn,
39. heat stress,
40. engulfment, or
41. entrapment hazards, etc.
If any hazardous atmosphere exists, do the following: YES/NO
42. If possible, determine and eliminate the source of the atmospheric hazards (for example:
carbon monoxide from nearby truck or gas-powered generator).
43. When the atmosphere contains toxins or flammables, ventilate the space by drawing air
out until the air has been changed over several times.
44. When oxygen deficient, ventilate by pushing air into the space until the air has been
changed over several times.
45. Verify the hazardous atmosphere has been eliminated by testing the air.
2
Determine from information gathered above which of the following entry procedures is YES/NO
appropriate:
46. Non-Permit Space - If there are neither real nor potential atmospheric hazards and no
observable serious safety and health hazards, this should be certified in writing.
47. Alternative Entry Procedures – If no observable serious safety and health hazards exist
and atmospheric hazards are controlled with continuous ventilation; this should be
certified in writing.
48. Permit-Required Space - If there are any observable serious safety/health hazards in
addition to potential or real atmospheric hazards, all procedure here must be followed.
Authorize permit with signature.
49. Non-Respirable Atmospheres - If hazardous atmosphere cannot be eliminated by
continuous ventilation, contact the Safety Organization before continuing.
Follow pre-entry precautions: YES/NO
50. Notify affected departments of service interruption.
51. Lock-out/tag-out all sources of energy (e.g. steam, electric, mechanical) posing a risk to
workers.
52. Install blank in affected pipes where valves are not secure or seated.
53. Clean and/or purge any chemical storage vessel.
54. Wear appropriate personal protective and respiratory protection.
55. Have lights and or ladder available.
56. If coordination is needed with contractors, see Contractor Checklist.
57. Have appropriate MSDS's (Material Safety Data Sheet).
58. Determine how often air monitoring will be conducted.
Additional precautions necessary for Permit-Required Spaces: YES/NO
59. Determine start and end times for authorized entry.
60. Assign roles and responsibilities as entrant(s), attendant(s), leadworker(s)
61. Set up non-entry rescue equipment (tri-pod, harness).
62. Identify rescue service.
63. Determine communication method between entrant/attendant.
64. Conduct pre-entry briefing: review hazards, procedures, and precautions.
65. Sign and post the Permit/Certification at the site.
66. Continually ventilate the space by pushing air so that a positive pressure changes the air
over several times every hour. Direct the clean air toward the worker.
67. Test the air periodically while personnel are in the confined space to ensure the ventilation
is preventing any accumulation of a hazardous atmosphere.
68. Under the following conditions, personnel must exit the confined space, re-evaluate
3
hazards, and modify entry procedures:
If any hazardous atmosphere is detected after entry.
If any health or safety hazard develops which was not anticipated.
If Attendant (on Permit-Required Confined Space Entry) cannot effectively perform
duties.
If personnel in confined space are experiencing symptoms from heat stress or over-
exposure to atmospheric hazards.
69. When work is completed, return the space to original condition. Close out the
permit/certification and submit the completed paperwork to your supervisor.
You might also like
- Confined Space Entry ProcedureDocument13 pagesConfined Space Entry ProcedureToma Adriana100% (1)
- Lead Compliance PlanDocument12 pagesLead Compliance PlanArsalan Ahmed SheikhNo ratings yet
- Seaweeds Infofolder WebDocument2 pagesSeaweeds Infofolder Webmaiara melo malinowskiNo ratings yet
- 7 Respiratory Protection July2014Document1 page7 Respiratory Protection July2014joker batmanNo ratings yet
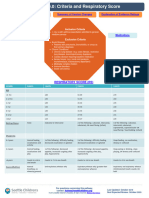
- 2019 SEATTLE CHILDREN'S Hospital. Healthcare-Professionals:clinical-Standard-Work-Asthma - PathwayDocument41 pages2019 SEATTLE CHILDREN'S Hospital. Healthcare-Professionals:clinical-Standard-Work-Asthma - PathwayVladimir Basurto100% (1)
- Coraline: by Neil GaimanDocument5 pagesCoraline: by Neil Gaimanfeliz juevesNo ratings yet
- Tribology and Dynamics of Engine and Powertrain Fundamentals Applications and Future TrendsDocument13 pagesTribology and Dynamics of Engine and Powertrain Fundamentals Applications and Future Trendskumar_yogesh2238810% (2)
- Service Manual For Preventive Maintenance 6SE483 0303Document55 pagesService Manual For Preventive Maintenance 6SE483 0303Antony MorenoNo ratings yet
- Technical Standards for Luxury HotelsDocument173 pagesTechnical Standards for Luxury HotelsHoangDung LeNo ratings yet
- HSE Docs - Confined Space Entry Procedure For Mechanical ActivitiesDocument27 pagesHSE Docs - Confined Space Entry Procedure For Mechanical ActivitiesKhuda BukshNo ratings yet
- Confined-Space Entry ProgramDocument16 pagesConfined-Space Entry Programamjadkhan6573833No ratings yet
- Hot Work Permit details safety precautionsDocument1 pageHot Work Permit details safety precautionsAhmed BahgatNo ratings yet
- MSL946001A Implement and Monitor OHS and Environmental Management SystemsDocument35 pagesMSL946001A Implement and Monitor OHS and Environmental Management Systemschaerul.anwar554No ratings yet
- Woodlands N5C23 - FPP-TPWDocument29 pagesWoodlands N5C23 - FPP-TPWSuresh ThevanNo ratings yet
- Blinding Deblinding Best Practices Lessons From of Adnoc Gas ProcessingDocument26 pagesBlinding Deblinding Best Practices Lessons From of Adnoc Gas ProcessingUnique OfficerNo ratings yet
- 13.2.9 RA SWP For Cable Installation Glanding Terminating Testing at DCL PDFDocument15 pages13.2.9 RA SWP For Cable Installation Glanding Terminating Testing at DCL PDFamalNo ratings yet
- 6.basic Workshop Practice-I PDFDocument13 pages6.basic Workshop Practice-I PDFPreethamgowda PreciousNo ratings yet
- Arma LOTO Presentation 2.2019Document35 pagesArma LOTO Presentation 2.2019Rio Dianto PraditamaNo ratings yet
- Tagging and Lockout ProcedureDocument4 pagesTagging and Lockout ProcedureibrahimkhansahilNo ratings yet
- EOHSMS-02-F06 Hot Work PermitDocument2 pagesEOHSMS-02-F06 Hot Work PermitHassan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- RFA FormDocument2 pagesRFA FormRitche Lim BragaisNo ratings yet
- Amazon Dupont Citation and Notice, May 2021Document9 pagesAmazon Dupont Citation and Notice, May 2021GeekWireNo ratings yet
- Doug Ingram: General ManagerDocument14 pagesDoug Ingram: General ManagerArshad Rashid ShahNo ratings yet
- Engineer Department: Scope Identifying Hazards, Assessing and Controlling Risks Worker Safety Series Hazards & SolutionsDocument30 pagesEngineer Department: Scope Identifying Hazards, Assessing and Controlling Risks Worker Safety Series Hazards & Solutionsubi_gadongNo ratings yet
- Be Accountable For Your Safety at Work by Dr. Anuar SuunDocument27 pagesBe Accountable For Your Safety at Work by Dr. Anuar SuunakubestlahNo ratings yet
- Welding With Arc Wedling EquipmentDocument4 pagesWelding With Arc Wedling EquipmentKuber Jawaharpur EHSNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety Test - Answer Qcon HSE Format - 52Document1 pageScaffolding Safety Test - Answer Qcon HSE Format - 52Novheed TakNo ratings yet
- EOHSMS 02 F03 Excavation PermitDocument1 pageEOHSMS 02 F03 Excavation PermitHassan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 3221 ConcreteDocument15 pages3221 Concretesada44No ratings yet
- Road To I PT Final PosterDocument1 pageRoad To I PT Final PosterChristian Trésor KandoNo ratings yet
- Safe Audit Checklist TemplateDocument7 pagesSafe Audit Checklist Templatemugabo bertinNo ratings yet
- Portable Fire Extinguishers ChecklistDocument3 pagesPortable Fire Extinguishers ChecklisteastNo ratings yet
- Lockout/Tagout: It'S A Mater of Life and DeathDocument12 pagesLockout/Tagout: It'S A Mater of Life and Deathhany mohamedNo ratings yet
- Item P-152 Excavation and Embankment: UnclassifiedDocument16 pagesItem P-152 Excavation and Embankment: UnclassifiedebherlinNo ratings yet
- Wildfire Aide Memoire: Primary Secondary FloaterDocument3 pagesWildfire Aide Memoire: Primary Secondary Floatersimon_pilkingto3222No ratings yet
- Northern Ohio ASSE Kirk Key Presentation 10 22 15 PDFDocument47 pagesNorthern Ohio ASSE Kirk Key Presentation 10 22 15 PDFJUAN ATALAYANo ratings yet
- Isolation Work Instruction TemplateDocument5 pagesIsolation Work Instruction TemplateppnNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Test Plan - Site ClearanceDocument1 pageInspection & Test Plan - Site ClearanceJohan BurgerNo ratings yet
- Contractor ConstructionDocument6 pagesContractor ConstructionAshwinSiddaramaiahNo ratings yet
- Seaweed and Plants: Multicellular Primary ProducersDocument32 pagesSeaweed and Plants: Multicellular Primary ProducersAurora ÇizmjaNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Permit 2Document3 pagesHot Work Permit 2prabu lingamNo ratings yet
- Diversified Fall Protection Guide OSHA Updates Slips Trips FallsDocument159 pagesDiversified Fall Protection Guide OSHA Updates Slips Trips FallsHomer SilvaNo ratings yet
- Improving Supervisory Leadership: How To Become ExemplaryDocument2 pagesImproving Supervisory Leadership: How To Become ExemplaryFuzail AyazNo ratings yet
- Safety Health & Environment: ManagementDocument14 pagesSafety Health & Environment: Management56fredfred100% (1)
- Industrial Training PresentationDocument14 pagesIndustrial Training PresentationNik AmirNo ratings yet
- RA082-C Grinding - ThornliebankDocument2 pagesRA082-C Grinding - Thornliebankloveson709No ratings yet
- Excavation Risk Assessment and PermitDocument3 pagesExcavation Risk Assessment and Permituditha_ranatungeNo ratings yet
- KRA 1.4 Plant and EquipmentDocument13 pagesKRA 1.4 Plant and EquipmentSubburajMechNo ratings yet
- Astm F2959-16Document9 pagesAstm F2959-16ReliantNo ratings yet
- Construction Safety Project Pre-Work Meeting ChecklistDocument1 pageConstruction Safety Project Pre-Work Meeting ChecklistBrianna SawyerNo ratings yet
- Machinery and Equipment Safety - An Introduction: 1st EditionDocument22 pagesMachinery and Equipment Safety - An Introduction: 1st EditionAdel SukerNo ratings yet
- 032 CI Process - Functional Deployment Map v4.2Document2 pages032 CI Process - Functional Deployment Map v4.2enjoythedocsNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Permit For Confined SpaceDocument3 pagesHot Work Permit For Confined SpaceDarus IshakNo ratings yet
- Jacks and Hoists: Self Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesJacks and Hoists: Self Inspection ChecklistSajeewa LakmalNo ratings yet
- Using This Template: Lockout/Tagout ProgramDocument14 pagesUsing This Template: Lockout/Tagout ProgramAhmad KharisNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument9 pagesRisk Management PlanLinus100% (1)
- CUA 2011 Hot Work TagDocument1 pageCUA 2011 Hot Work Tagjhslabber123No ratings yet
- Lifting Permit PermitDocument1 pageLifting Permit PermitHSE Health Safety EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- AIG Hot Work Permit Only Rev 120618Document6 pagesAIG Hot Work Permit Only Rev 120618Herik renaldoNo ratings yet
- Hot & Cold Work PermitDocument10 pagesHot & Cold Work PermitSubratNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: Nicole A. Clarke Manager, Eastern Region Tank Industry ConsultantsDocument72 pagesConfined Spaces: Nicole A. Clarke Manager, Eastern Region Tank Industry Consultantsnermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument5 pagesConfined Space EntryMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument3 pagesConfined Space Entrygeo_hazreq100% (1)
- Confined Space TrainingDocument20 pagesConfined Space TrainingAnonymous y1pIqcNo ratings yet
- Hassan Jannah, Computer Operations SpecialistDocument6 pagesHassan Jannah, Computer Operations SpecialistvenkatNo ratings yet
- Welding Basic VocationalDocument42 pagesWelding Basic VocationalvenkatNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument17 pagesWeldingkatfy1No ratings yet
- Welding Defect TWI CSWIP PDFDocument54 pagesWelding Defect TWI CSWIP PDFHaithem100% (2)
- Pressure Relief Valve Engineering HandbookDocument93 pagesPressure Relief Valve Engineering Handbookakrouti92% (12)
- Chap 26 Isometric Drawing PDFDocument22 pagesChap 26 Isometric Drawing PDFvenkatNo ratings yet
- Sumalinog Teodoro Jr. LPDocument5 pagesSumalinog Teodoro Jr. LPDAITO CHRISTIAN DHARELNo ratings yet
- Purifying Water: Study of MethodsDocument21 pagesPurifying Water: Study of MethodsRohit Thirupasur100% (2)
- Economics Examples of Calculus of Multivariable Function in EconomicsDocument6 pagesEconomics Examples of Calculus of Multivariable Function in Economicskayesalingay3No ratings yet
- Quickspecs: HP Z840 WorkstationDocument108 pagesQuickspecs: HP Z840 WorkstationAbraham Leon GuardalesNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Kangaroo Mother CareDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Kangaroo Mother CareafdtuwxrbNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources: Earth ScienceDocument20 pagesMineral Resources: Earth ScienceRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Roland RD-800 Manuale Stage PianoDocument64 pagesRoland RD-800 Manuale Stage PianoAlberto FicheraNo ratings yet
- Grove RT422 22T PDFDocument4 pagesGrove RT422 22T PDFJulio QuilarqueNo ratings yet
- 5S Office OrganizationDocument14 pages5S Office Organizationthuy linh phamNo ratings yet
- Crux v20n04 AprDocument35 pagesCrux v20n04 AprMauricioNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Random-VariablesDocument29 pagesLESSON 1 Random-Variablesnica jane madrigalNo ratings yet
- Cengel FTFS 6e ISM CH 13Document83 pagesCengel FTFS 6e ISM CH 13Duck FernandoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 STRDocument10 pagesChapter 7 STRmedrekNo ratings yet
- KGP HG-3Document2 pagesKGP HG-3Lau VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Morteza MirzaeiDocument3 pagesMorteza MirzaeiUmitNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 & 11: Presented By: Group 4Document55 pagesExperiment 7 & 11: Presented By: Group 4Julliane JuanNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Slab Shoring System - ROYALFRAME50Document6 pagesLightweight Slab Shoring System - ROYALFRAME50Renji Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- 23 Section I GW Glasses Window System and MirrorsDocument58 pages23 Section I GW Glasses Window System and Mirrorsamir8100No ratings yet
- 6-1 Homework Team 7Document3 pages6-1 Homework Team 7Edgar ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Family Nomenclature and Same-Name Divinities in Roman Religion and MythologyDocument17 pagesFamily Nomenclature and Same-Name Divinities in Roman Religion and MythologyhNo ratings yet
- Song of The Ancients Lyrics (English)Document1 pageSong of The Ancients Lyrics (English)Keith-Yves Rayden VonLiktinstine SiroisNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Module: Powerful Software Featuring Intuitive WorkflowDocument4 pagesGeotechnical Module: Powerful Software Featuring Intuitive WorkflowMuhammadAviCennaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Wall FinalDocument8 pagesCoastal Wall Finalapi-508287240No ratings yet
- Calculation of Insulation Thickness For PipesDocument2 pagesCalculation of Insulation Thickness For PipesnarmathaNo ratings yet
- Ensemble Marin OscillantDocument4 pagesEnsemble Marin OscillantRobson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Iberchem - French: Code Item Name Code Item Name 35000 7600Document2 pagesIberchem - French: Code Item Name Code Item Name 35000 7600Noor AshrafiNo ratings yet