0% found this document useful (0 votes)
267 views4 pagesGetting Started With Insulin Injections
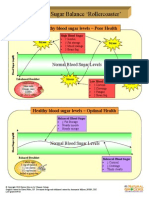
This document provides information about getting started with insulin including how to use insulin pens, mixing insulin, giving injections, insulin types, care and storage, identification for diabetes, treating low blood sugar, checking blood sugars, and proper use of pen tips.
Uploaded by
Jianhua ShiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
267 views4 pagesGetting Started With Insulin Injections
This document provides information about getting started with insulin including how to use insulin pens, mixing insulin, giving injections, insulin types, care and storage, identification for diabetes, treating low blood sugar, checking blood sugars, and proper use of pen tips.
Uploaded by
Jianhua ShiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd