Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mapset 2
Uploaded by
api-3668043630 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesOriginal Title
mapset 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesMapset 2
Uploaded by
api-366804363Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Flood in Yangtze River
Caption: The Yangtze River is a long river in China. It is the
third longest river in the world.The main stream flows through
11 provinces of Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing,
Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Jiangsu and Shanghai. It is
injected into the East China Sea east of Chongming Island in
Shanghai, with a total length of 6397km. In 1998, the Yangtze
River experienced another full-scale flood since 1954. Since
mid-June, the Yangtze River flow has increased rapidly due to
heavy rains and heavy rains in Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake.
Affected by upstream water and tides, the tide level along the
Yangtze River in Jiangsu Province has exceeded the warning
level since June 25.
Flood in South-eastern China
Caption: In South-eastern China, rain season usually starts
from June to October. Because of it, the rain will cause flood
high prossibly. The annual precipitation in the South-eastern
China is mostly above 1000 mm. But every month precipitation
is different. Mainly concentrated in the summer half year, the
rainy season is shortened from south to north. Most floods in
China will occur in this area. Flooding in the Yangtze River is a
result of water and soil loss caused by deforestation in the
Yangtze River basin, and the direct consequences of land
reclamation and rivers in the middle and lower reaches of the
river. There are 400 million people living on both sides of the
Yangtze River. In the mid-1950s, the forest coverage rate in the
upper reaches of the Yangtze River was 22%. Due to the
continuous development of agricultural land, construction and
urbanization, 80% of the forests on both sides of the river were
cut down.
Rain in China
Caption: The monsoon affecting China's annual precipitation
is mainly the southeast monsoon from the Pacific Ocean in the
summer and the southwest monsoon from the Indian Ocean.
With the influence of the summer monsoon, the annual
precipitation decreases from the southeast coast to the northwest
inland. Generally, from Daxinganling to Yinshan to Helanshan
to Bayankala to Gangdese, China is divided into monsoon and
non-monsoon regions, which are consistent with precipitation
lines such as 400 mm. The southern part of China and the north
are bounded by the Qinling to the Huaihe River, and the
Qinling-Huaihe line is also a precipitation line of 800 mm. The
southeast coastal frontal rain brought early, retired late, and the
annual precipitation was more than 800 mm.
You might also like
- Project Report On Water ResourcesDocument20 pagesProject Report On Water Resourcessymphonic8260% (15)
- Map Set 2Document4 pagesMap Set 2api-365899741No ratings yet
- The Main Characteristics of China's GeographyDocument9 pagesThe Main Characteristics of China's GeographyGraciela BarrantesNo ratings yet
- Yangtze River 4-10-07Document3 pagesYangtze River 4-10-07api-3708558No ratings yet
- Rain in Jiangxi CaptionDocument3 pagesRain in Jiangxi Captionapi-366804363No ratings yet
- Flood Affection in Pakistan Presentation by AbdDocument7 pagesFlood Affection in Pakistan Presentation by AbdicouldntthinkofausernameNo ratings yet
- NATURAL DISASTER DoneDocument24 pagesNATURAL DISASTER Donedm58wywgfyNo ratings yet
- Canton-Hong Kong Report (1945)Document80 pagesCanton-Hong Kong Report (1945)CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- 1931 China Floods - IntternationalDocument3 pages1931 China Floods - Intternationalpatrecia0% (1)
- Drainage Basin: Mekong River South of - The Mekong FromDocument4 pagesDrainage Basin: Mekong River South of - The Mekong FromHendrix900No ratings yet
- PM's Special Cabinet (Crisis Committee) - North India Floods 2023Document9 pagesPM's Special Cabinet (Crisis Committee) - North India Floods 2023Dhruv AgarwalNo ratings yet
- M 6 L 02Document28 pagesM 6 L 02neha161857697No ratings yet
- An Analytical Study of Flood Management in BangladeshDocument6 pagesAn Analytical Study of Flood Management in BangladeshIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Geography of ChinaDocument15 pagesGeography of ChinaakyatwinejoshuaNo ratings yet
- Data On BangaloreDocument6 pagesData On BangaloreDiana DavisNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Management in PakistanDocument7 pagesWater Resource Management in PakistanNaeem MehboobNo ratings yet
- Vol7No3-4 2 Water Resources Situation MAkramKahlown PDFDocument13 pagesVol7No3-4 2 Water Resources Situation MAkramKahlown PDFPerwez21No ratings yet
- Geography of China: Rivers and LakesDocument2 pagesGeography of China: Rivers and LakesAlwin Glen PapaNo ratings yet
- China GeographyDocument1 pageChina Geographykamala 123No ratings yet
- Drainage Issue in The Terai Region of NepalDocument5 pagesDrainage Issue in The Terai Region of NepalBhuwan ShahNo ratings yet
- Ujjani Reservoir-A World Lake Vision Candidate-Waiting For RestorationDocument16 pagesUjjani Reservoir-A World Lake Vision Candidate-Waiting For RestorationsandycrackjackNo ratings yet
- Significant Points On Bundelkhand Drought.Document4 pagesSignificant Points On Bundelkhand Drought.Rohit TrivediNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Char (Ganga Indian River)Document1 pageHydrological Char (Ganga Indian River)Sayan MondalNo ratings yet
- M-Three Gorges Concern OncreteDocument6 pagesM-Three Gorges Concern OncreteSivaganesan SNo ratings yet
- Yangtze R.: 32 Legacies and SettingDocument4 pagesYangtze R.: 32 Legacies and SettingJacqieNo ratings yet
- Geographical SettingDocument2 pagesGeographical SettingSantania syebaNo ratings yet
- Ancient China Word ListDocument2 pagesAncient China Word Listapi-208349712No ratings yet
- GeographyDocument6 pagesGeographysavita sharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Surface Water Made Up of Rivers, Streams, Lakes, Beels and Ponds. in Other WordsDocument5 pagesIntroduction: Surface Water Made Up of Rivers, Streams, Lakes, Beels and Ponds. in Other WordsAl-Rafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- IWFM BUET PreparationDocument3 pagesIWFM BUET PreparationZahid Hasan ZituNo ratings yet
- Deadliest Floods in WorldDocument3 pagesDeadliest Floods in WorldFaraz HussainiNo ratings yet
- FloodDocument4 pagesFlood756 MazinNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Genreal: Chapter - 1Document17 pages1.1 Genreal: Chapter - 1Sivan RajNo ratings yet
- Pricing of Irrigation Water in China: Zhou Yaozhou and Wei BingcaiDocument26 pagesPricing of Irrigation Water in China: Zhou Yaozhou and Wei Bingcaiibrahim3318No ratings yet
- Glacial Lake Outflow DisasterDocument19 pagesGlacial Lake Outflow DisasterAmandeep GargNo ratings yet
- Irans Dam Policy and The Case of The LakDocument6 pagesIrans Dam Policy and The Case of The LakAhmet DicleNo ratings yet
- Tsunami of Mud, Rocks, and Water.Document4 pagesTsunami of Mud, Rocks, and Water.M.E.RezaNo ratings yet
- Types of Floods in PakistanDocument3 pagesTypes of Floods in PakistanOvaid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Songea Water AuthorityDocument1 pageSongea Water AuthorityDavid SabaiNo ratings yet
- Yellow River黃河 Hs PresentationDocument12 pagesYellow River黃河 Hs Presentationsky animal girlNo ratings yet
- LEVELnews 11 2015 eDocument2 pagesLEVELnews 11 2015 eInternational Joint CommissionNo ratings yet
- China's Water1Document11 pagesChina's Water1Hindol SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Floods in Uttarakhan1Document3 pagesFloods in Uttarakhan1Kosygin LeishangthemNo ratings yet
- Moot Problem NehuDocument5 pagesMoot Problem NehuSaba MirzaNo ratings yet
- Run Off and Sediment LoadDocument10 pagesRun Off and Sediment LoadSuntoyo SuntoyoNo ratings yet
- Indus Waters Treaty-Future Prospects: (Evening Programme)Document13 pagesIndus Waters Treaty-Future Prospects: (Evening Programme)Azhar AhmadNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument6 pagesChinayazeen firusNo ratings yet
- 14 Fun Facts About the Yangtze: A 15-Minute BookFrom Everand14 Fun Facts About the Yangtze: A 15-Minute BookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Climate Change PuneDocument10 pagesClimate Change PuneSHRIYA YOGESHNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Study BhagirathiDocument134 pagesHydrological Study BhagirathiSkshukla ShuklaNo ratings yet
- China, Mongolia, and TaiwanDocument40 pagesChina, Mongolia, and TaiwanRichard CNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering, Vol.7, No.3A, 2018 - Odysseas KopsidasDocument51 pagesJournal of Environmental Science and Engineering, Vol.7, No.3A, 2018 - Odysseas KopsidasAnonymous kqqWjuCG9No ratings yet
- China 2Document77 pagesChina 2Feri Rahmat Chandra PiliangNo ratings yet
- Water Transboundary Policy of Kazakhstan and China 2018Document15 pagesWater Transboundary Policy of Kazakhstan and China 2018陈チン 垚ヨウ旭クNo ratings yet
- Essay: TOPIC:-Water Resource Utilisation and Irrigation Development in IndiaDocument9 pagesEssay: TOPIC:-Water Resource Utilisation and Irrigation Development in IndiaSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Rivers of Vietnam: Peter Sokov (41a9n)Document9 pagesRivers of Vietnam: Peter Sokov (41a9n)YawnNo ratings yet
- Rivers of Uttarakhand Himalaya Impact of Floods in The Pindar and Saryu ValleysDocument7 pagesRivers of Uttarakhand Himalaya Impact of Floods in The Pindar and Saryu ValleysAlok Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Landforms and Waterways: A Regional OverviewDocument4 pagesLandforms and Waterways: A Regional OverviewRichard ShiauNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument9 pagesChinashimeyonmelkiasNo ratings yet
- 14 Fun Facts About the Yangtze: Educational VersionFrom Everand14 Fun Facts About the Yangtze: Educational VersionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Mapset 3Document4 pagesMapset 3api-366804363No ratings yet
- Individual Hazard Atmosphere Map SetDocument2 pagesIndividual Hazard Atmosphere Map Setapi-366804363No ratings yet
- Hazard Field Trip Project Part 1 InstructionsDocument3 pagesHazard Field Trip Project Part 1 Instructionsapi-366804363No ratings yet
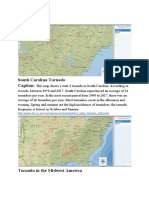
- South Carolina Tornado Caption:: Xushuai ShaoDocument2 pagesSouth Carolina Tornado Caption:: Xushuai Shaoapi-366804363No ratings yet