Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The World of Triangles and Circles: Alyanna Jozeah G. Ambalong
Uploaded by
Alyanna JozeahOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe World of Triangles and Circles: Alyanna Jozeah G. Ambalong
Uploaded by
Alyanna JozeahTHE WORLD OF TRIANGLES AND CIRCLES
Alyanna Jozeah G. Ambalong
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between the sides and
angles of triangles. In other words, Trigonometry is basically the mathematics of triangle measurement.
Technically, it came from three Greek words, “tri” which means three, “gono” which means side, and
“metron” which means measure.
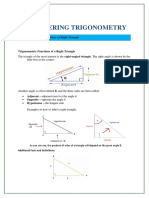
In Trigonometry, the triangle of most interest is the right triangle—a triangle with a 90-degree
angle. The right angle is commonly shown by a little box on the corner of the angle itself. The triangle
consists of three sides referred to as adjacent (next to the angle), opposite (opposite the angle), and
hypotenuse (the longest side of the triangle).
The main functions in trigonometry are the sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan). In triangles,
the sine is always equal to the opposite side divided by the hypotenuse; the cosine is equal to the adjacent
side divided by the hypotenuse; the tangent is equal to opposite side divided by the adjacent side. The
other functions are the cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot).
While Trigonometry is useful in triangle measurements, its usefulness is not limited to triangles.
It can also be used to the application of circular functions.
The real numbers in Trigonometry are numbers which should be located on a unit circle. A unit
circle is a circle with a radius of one unit and center at the origin of the coordinate plane. All the points on
the unit circle are called trigonometric points.
There are six circular functions of a real number 𝜃 (theta). Sin 𝜃 is equal to the ordinate divided
by the radius; cosine 𝜃 is equal to the abscissa divided by the radius; tangent 𝜃 is equal to the ordinate
divided by abscissa. The remaining three are just the reciprocals of the first three: cosecant 𝜃 is equal to
the radius divided by the ordinate; secant 𝜃 is equal to the radius divided the abscissa; cotangent 𝜃 is
equal to the abscissa divided by the ordinate.
The applications of Trigonometry can be found in engineering, surveying, and navigation aside
from astronomy.
You might also like
- Trigonometry WorksheetDocument4 pagesTrigonometry Worksheetapi-143521979No ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Document6 pagesMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometrydummkopfworkNo ratings yet
- Maths Trigonometry IntroductionDocument4 pagesMaths Trigonometry IntroductionDivyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDocument15 pagesBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Encyclipedia of Trignometry - Andrew BarnesDocument140 pagesEncyclipedia of Trignometry - Andrew Barnessaka1977No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument7 pagesTrigonometryRagav VijayNo ratings yet
- What Is TrigonometryDocument4 pagesWhat Is Trigonometryapi-150536296No ratings yet
- Random LecturesDocument30 pagesRandom LecturesTrisha KayeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry - Ashnaf - FINALDocument8 pagesTrigonometry - Ashnaf - FINALKazi RafsanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Came From Three Greek Words, Tri Which Means Three, Gono Which MeansDocument1 pageTrigonometry Came From Three Greek Words, Tri Which Means Three, Gono Which MeansRoberto C. DiscutidoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry WorksheetsDocument4 pagesTrigonometry Worksheetsapi-150536296No ratings yet
- Circumcircle of A Triangle - Math Open ReferenceDocument3 pagesCircumcircle of A Triangle - Math Open ReferenceSomen SahaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About TrigonometryDocument10 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Trigonometryjohn sinnyNo ratings yet
- Triang LEDocument10 pagesTriang LEJezrael NacionNo ratings yet
- Incircle and Excircles of A Triangle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesIncircle and Excircles of A Triangle - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedianeiljain421No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions 2Document34 pagesTrigonometric Functions 2Sahil JindalNo ratings yet
- Algebra (From: Sin A Opposite/Hypotenus A/cDocument1 pageAlgebra (From: Sin A Opposite/Hypotenus A/cRai GastaNo ratings yet
- Types of Triangles: by Relative Lengths of SidesDocument16 pagesTypes of Triangles: by Relative Lengths of SidesSaran Vijai100% (2)
- Topic 3 ''Trian-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesTopic 3 ''Trian-WPS OfficeMatias ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Properties of TriangleDocument10 pagesProperties of Triangleapi-3709966No ratings yet
- Trig Ratios of SpecialDocument3 pagesTrig Ratios of SpecialJillianne PadilloNo ratings yet
- Triangles: June 7, 2021 Via ZoomDocument49 pagesTriangles: June 7, 2021 Via ZoomEunice MirandaNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument36 pagesTrigonometryYoshika GNo ratings yet
- Triangle - WikipediaDocument107 pagesTriangle - Wikipediamathiazhahan24No ratings yet
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Trigonometrymishel veronicaNo ratings yet
- Math 122 Module 3Document54 pagesMath 122 Module 3phoebe lhou gadgad catao-anNo ratings yet
- SOHCAHTOADocument17 pagesSOHCAHTOAYsa BurguillosNo ratings yet
- Triangle TheoremDocument3 pagesTriangle TheoremDipti GargNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry EssayDocument1 pageTrigonometry EssayLaura BarthaNo ratings yet
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument30 pagesThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument15 pagesTrigonometryMa Grace Ramisarez AballaNo ratings yet
- By Relative Lengths of Sides: Regular PolygonDocument13 pagesBy Relative Lengths of Sides: Regular Polygonjunior_bassgNo ratings yet
- Mastering The Basics of TrigonometryDocument8 pagesMastering The Basics of TrigonometryKarthik RNo ratings yet
- 3 Diocton Edward ADocument46 pages3 Diocton Edward AgdhehhhdbdbdnhwNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry - WikiDocument46 pagesTrigonometry - WikiNikhil RajNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument14 pagesTrigonometryaditya9463178650173100% (4)
- Trigonometric RatiosDocument2 pagesTrigonometric RatiosHarshad GurumoorthyNo ratings yet
- Trig Ratios of SpecialDocument3 pagesTrig Ratios of SpecialJillianne PadilloNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument31 pagesTrigonometryHamza Javed100% (1)
- Week 4Document15 pagesWeek 4lexmaster0224No ratings yet
- Application of TrigonometryDocument6 pagesApplication of TrigonometryLim Yan Hong100% (1)
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument30 pagesThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNo ratings yet
- Geometry in The Real World3Document3 pagesGeometry in The Real World3api-295629565No ratings yet
- What Is Oblique Triangle: Triangulation Numerical ErrorDocument3 pagesWhat Is Oblique Triangle: Triangulation Numerical Errorcloud_fantasyNo ratings yet
- Notable Great Thinkers in TrigonometryDocument3 pagesNotable Great Thinkers in TrigonometryihatesmokersNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To TrigonometryYayerad Mekonnen (MrRad Productions)No ratings yet
- Types of TriangleDocument78 pagesTypes of TriangleammuNo ratings yet
- Shapes Geometry Polygon Vertices Line SegmentsDocument5 pagesShapes Geometry Polygon Vertices Line SegmentsJitendra TiwariNo ratings yet
- Triangle: (Classifying Triangles)Document15 pagesTriangle: (Classifying Triangles)Nezir M AliNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry in Modern ApplicationsDocument12 pagesPlane Trigonometry in Modern ApplicationsJOVANIE CLAVERONo ratings yet
- B2 Module 1 Lesson 2Document11 pagesB2 Module 1 Lesson 2Kate RellitaNo ratings yet
- Project On Basic Trigonometry: Presented byDocument14 pagesProject On Basic Trigonometry: Presented byRajesh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Maths 6Document19 pagesMaths 6rNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument1 pageTrigonometryrukovishnikovaNo ratings yet
- God StealerDocument29 pagesGod StealerAlyanna Jozeah100% (2)
- Horticultural SocietyDocument7 pagesHorticultural SocietyAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument5 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldAlyanna Jozeah100% (1)
- Timog Aprika: Malala YousafzaiDocument2 pagesTimog Aprika: Malala YousafzaiAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument4 pagesGender EqualityAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- BTS AlbumDocument1 pageBTS AlbumAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- Strange MagicDocument2 pagesStrange MagicAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- Bts StickersDocument3 pagesBts StickersAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic ConceptsDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Basic ConceptsAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- The Legalization of Marijuana in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesThe Legalization of Marijuana in The PhilippinesAlyanna JozeahNo ratings yet
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenFrom EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)