Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MyNotes Column BreslerEquation
Uploaded by
Gladies Mhay Binay SandovalCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMyNotes Column BreslerEquation
Uploaded by
Gladies Mhay Binay SandovalBRESLER EQUATION
A method published by Professor Boris Bresler in 1960 relates the desired value of ØPn under
biaxial loading (ex and ey) to three other Pu values.
1 1 1 1
= + −
𝑃𝑛 𝑃𝑛𝑥 𝑃𝑛𝑦 𝑃𝑛𝑜
Where
Pnx = axial load capacity of the column for eccentricity ex with ey = 0
Pny = axial load capacity of the column for eccentricity ey with ex = 0
Pno = pure axial capacity of the column
The Bresler equation works well as long as Pn is at least as large as 0.1Pno. Should Pn be less than
0.1Pno, it is satisfactory to neglect the axial force completely and design as a member subject to
biaxial bending only.
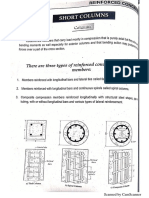
Procedure to determine the load capacity of column for a given eccentricity:
1. Calculate ρg
2. Determine the ratio γ
ℎ−2𝑑′
γ=
ℎ
3. Determine e/h
4. Select the appropriate interaction diagram.
5. From the interaction diagram, draw the line e/h.
6. Locate the intersection of line e/h and ρg. Draw a horizontal line and read the value on
vertical axis
7. Determine the Pn.
Example: Using the attached Interaction Diagrams, calculate the axial load that can be carried by the column
shown below at the given eccentricities. Assume f’c = 27.6 MPa (4 ksi) and fy = 414 MPa (60 ksi)
CEP 544D2 Concrete Design 1/5
CEP 544D2 Concrete Design 2/5
CEP 544D2 Concrete Design 3/5
CEP 544D2 Concrete Design 4/5
CEP 544D2 Concrete Design 5/5
You might also like
- Design of Purlins: With Engr. Mark Lehi P. Palmes Faculty-RMMC Civil Engineering Program Review LecturerDocument5 pagesDesign of Purlins: With Engr. Mark Lehi P. Palmes Faculty-RMMC Civil Engineering Program Review LecturerMohammad Taha PumbayaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Beam Design ProblemsDocument4 pagesReinforced Concrete Beam Design ProblemsRaine ZaficoNo ratings yet
- Co78 QuizDocument3 pagesCo78 QuizEjitNo ratings yet
- Members in CompressionDocument28 pagesMembers in CompressionNemanja RandelovicNo ratings yet
- LOCAL BUCKLING2 VisualBeeDocument24 pagesLOCAL BUCKLING2 VisualBeeMart Brevin BitonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction - Minimum Design Loads (Part 2)Document5 pagesLesson 1 Introduction - Minimum Design Loads (Part 2)Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document12 pagesLesson 5MIKE ARTHUR DAVID100% (1)
- Earthqauke Load Analysis (NSCP 2015) Static Force ProcedureDocument4 pagesEarthqauke Load Analysis (NSCP 2015) Static Force ProcedureMuayad AlzbediNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Home-Eval 1Document9 pagesModule-1 Home-Eval 1Michael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNDocument7 pagesEnhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNChristian VillenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Flexural Design - (Part 3)Document37 pagesChapter 4 Flexural Design - (Part 3)Adil ImtiazNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument12 pagesHydraulicsMugiwara Sparrow0% (1)
- Ot Online Quiz Ce181Document8 pagesOt Online Quiz Ce181Chrispin BarnigoNo ratings yet
- Plate 1Document2 pagesPlate 1Dawnald Fortin PepitoNo ratings yet
- Design of Beams Columns Base PlateDocument67 pagesDesign of Beams Columns Base PlateRommel Dave TejanoNo ratings yet
- RCD Quiz CompilationDocument12 pagesRCD Quiz CompilationApril Lyn LimbocNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Compression MembersDocument21 pagesAnalysis and Design of Compression MembersSilendrina Misha100% (1)
- CE Correl 4Document90 pagesCE Correl 4Marbel PerezNo ratings yet
- Seismic Forces - Simplified Static Force Method and Static Force MethodDocument13 pagesSeismic Forces - Simplified Static Force Method and Static Force MethodJaid HedrianaNo ratings yet
- Steps in Vertical Stirrup DesignDocument7 pagesSteps in Vertical Stirrup DesignJayvee EcayNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Compression Members Lec #1Document5 pagesModule 3 Compression Members Lec #1k. NotujNo ratings yet
- 4.) RCD - Midterm Library Work Quiz - Concept and Solutions (1-Way Slab)Document8 pages4.) RCD - Midterm Library Work Quiz - Concept and Solutions (1-Way Slab)Penuel G. Bantog100% (1)
- Design of Combined FootingsDocument45 pagesDesign of Combined FootingsAnkit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Seatwork 4: Calculating Uniform Flow in Various Channel GeometriesDocument11 pagesModule 2 Seatwork 4: Calculating Uniform Flow in Various Channel GeometrieshgfhfghfghgNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 3 April 2024Document3 pagesSteel Design 3 April 2024Craeven AranillaNo ratings yet
- Cap 8 Bending Strength of Compact and Noncompact ShapesDocument13 pagesCap 8 Bending Strength of Compact and Noncompact Shapescarlomonsalve1No ratings yet
- Review Module - Steel Design - Compression Members (ASD/LRFD)Document3 pagesReview Module - Steel Design - Compression Members (ASD/LRFD)Vergel SabanalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Axially Loaded Compression MembersDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Axially Loaded Compression MembersBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of DRBDocument13 pagesAnalysis and Design of DRBACES JEEL CENDA�ANo ratings yet
- Soil Profile Analysis of Barangay Datu Usman Mampen, Bagua 2, Cotabato CityDocument72 pagesSoil Profile Analysis of Barangay Datu Usman Mampen, Bagua 2, Cotabato CityNoraima EdrisNo ratings yet
- What Upward Force (KN) Is To Be Applied at The Free End To Prevent The Beam From Deflecting?Document15 pagesWhat Upward Force (KN) Is To Be Applied at The Free End To Prevent The Beam From Deflecting?Jhoriz QuilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersDocument56 pagesChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiNo ratings yet
- FLOWCHARTDocument13 pagesFLOWCHARTPaulo BurceNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap DesignDocument12 pagesPile Cap DesignRey Dominique VillarNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Board Exam Bridge ProblemsDocument7 pagesCivil Engineering Board Exam Bridge ProblemsRyan CagsawaNo ratings yet
- Structural Beam ComputationsDocument12 pagesStructural Beam ComputationsJustine LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Sas 1 - 7Document50 pagesSas 1 - 7jaira.masuangatNo ratings yet
- Wall FootingDocument4 pagesWall FootingMunthir NumanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Concrete With Coconut Husk and Dried Banana Leaffibers As Aggregate ReplacementintroductionrationaleDocument3 pagesProperties of Concrete With Coconut Husk and Dried Banana Leaffibers As Aggregate Replacementintroductionrationalejohn philip s garciaNo ratings yet
- ENCI 461 Influence Lines Practice Problems Set 4Document4 pagesENCI 461 Influence Lines Practice Problems Set 4ColdWinterKidNo ratings yet
- Beams and Other Flexural Members PDFDocument52 pagesBeams and Other Flexural Members PDFJeyjay BarnuevoNo ratings yet
- CO1 HaysDocument4 pagesCO1 Hayso100% (1)
- 4-Storey Building DesignDocument2 pages4-Storey Building DesignarielicawatNo ratings yet
- A. Read The Following Book Chapters and Other Readings For ReferenceDocument4 pagesA. Read The Following Book Chapters and Other Readings For ReferenceJomar LampitokNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing DesignDocument4 pagesCombined Footing DesignAJNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Liability of The Civil Engineer and The Client: Breach of Duty of Care Break of Client's DutyDocument2 pages3.5. Liability of The Civil Engineer and The Client: Breach of Duty of Care Break of Client's DutyCharlie OnlyNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design Exam ScoresDocument16 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Exam ScoresMarcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- RCD 2 - Two Way SlabDocument12 pagesRCD 2 - Two Way Slabcharles guetaNo ratings yet
- 2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFDocument10 pages2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFLester Khiets RoaNo ratings yet
- Welding ConnectionDocument46 pagesWelding ConnectionSabih Hashim AlzuhairyNo ratings yet
- Long Exam 1: E.S. 13 - Mechanics of Deformable Bodies 1 Semester, A.Y. 2010-2011Document1 pageLong Exam 1: E.S. 13 - Mechanics of Deformable Bodies 1 Semester, A.Y. 2010-2011Junhong BapNo ratings yet
- Design of Doubly Reinf and - T-BeamsDocument13 pagesDesign of Doubly Reinf and - T-BeamsGrace Ann CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Beam MethodDocument12 pagesConjugate Beam MethodKobina BondzieNo ratings yet
- Design of Beams Miscellaneous Topics (Shear, Deflection, Etc.)Document37 pagesDesign of Beams Miscellaneous Topics (Shear, Deflection, Etc.)Morad AJNo ratings yet
- RCD 2Document4 pagesRCD 2John Joshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Bicol University CE 420C Flowchart Analysis and Design of RC StructuresDocument23 pagesBicol University CE 420C Flowchart Analysis and Design of RC StructuresSam Barotilla100% (1)
- 2 RCD 2 Besavilla ColumnDocument56 pages2 RCD 2 Besavilla ColumnJay LoyaoNo ratings yet
- P3 AxialloadDocument47 pagesP3 AxialloadBagas PinandikaNo ratings yet
- Handout SewerDocument2 pagesHandout SewerGladies Mhay Binay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures Vol. 1Document2 pagesTheory of Structures Vol. 1Gladies Mhay Binay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Engineers: My Notes StructuralDocument14 pagesEngineers: My Notes StructuralGladies Mhay Binay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Waste Water EngineeringDocument3 pagesWaste Water EngineeringGladies Mhay Binay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank DesignDocument5 pagesSeptic Tank DesignGladies Mhay Binay SandovalNo ratings yet
- CE 507-Water Resources-Rule Curve-HandoutsDocument3 pagesCE 507-Water Resources-Rule Curve-HandoutsGladies Mhay Binay SandovalNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindFrom EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet