Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ict Course Outline
Uploaded by
api-451242734Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ict Course Outline
Uploaded by
api-451242734Copyright:
Available Formats
COURSE OUTLINE: EDUC2632X08, 2019, Semester One
ASSESSMENT RUBRICS
The overall grade awarded for each assignment cannot be greater than that awarded for the Academic Literacy
component.
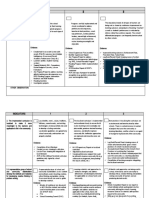
Criteria F P C D HD
Students are expected to Insufficient evidence of ability Adequate level of ability High level of ability Very high level of ability Extremely high level of ability
demonstrate a high displayed. There are substantial displayed. There are several displayed. There are few displayed. There are incidental displayed. There are no errors
standard of academic errors in: errors in: errors in: errors in: in:
writing. To score a high • the structure and coherence of the• the structure and coherence of the • the structure and coherence• the structure and coherence of the the structure and coherence of
grade, standard Australian written work; written work; of the written work; written work; the written work;
English should be used to
• the appropriate use of expression • the appropriate use of expression • the appropriate use of • the appropriate use of expression the appropriate use of
communicate key ideas
and grammar; and grammar; expression and grammar; and grammar; expression and grammar.
clearly and concisely.
• the accuracy of spelling and • the accuracy of spelling and • the accuracy of spelling • the accuracy of spelling and the accuracy of spelling and
punctuation. punctuation. and punctuation. punctuation. punctuation.
The reference
list/bibliography is correct.
Electronic resource identifiers
are consistently used (DOIs -
Digital Object Identifiers
and/or URLs - Universal
Resource Locators)
Assessment 1: Planning Rubric (25%)
Criteria Aspect Assessed Marks
Sequence • Planning document describes three sequential lessons 15
• Referenced to selected Year and Standard from WA/SCASA curriculum.
• Exhibits ICT innovation in curriculum design to motivate and stimulate learners to
achieve their goals.
• The overall design of the learning sequence is significant to students’ lives and is
stimulating for the target audience.
• Overall design elicits thinking that goes beyond rote comprehension.
• The learning design promotes communication amongst students.
Learning • Strong elements of learning theory have influenced the design of the curriculum and 5
Theory they have been drawn on in the implementation.
• Draws upon wider reading, learning theories or models.
ICT • ICT is carefully embedded into the curriculum as a tool to support thinking and 5
statement learning. Detailed explanation provided. Draws upon wider reading.
Assessment 2: Group Presentation Rubric (Group mark 20%)
Group members must demonstrate their ICT competence in terms of both the component of the lesson that they are directly
responsible for, as well as being technically able to help their team members in the class activity. Individual marks may vary.
Criteria Aspect Assessed Marks
Organisation • Learning objectives clearly stated, used and reviewed. 2.5
of session • Prior knowledge checked and acted upon.
• Successfully/innovatively gains group’s attention.
• Group members support each other throughout and ensure smooth transitions between
activities
Active • ICT activity engages audience creatively by using ICT thoughtfully. 9.5
engagement • Challenges audience to consider the ICT within the context, and reflect.
• Audience encouraged to consider how ICT contributed to learning. 4
Post activity • Discussion considered possible ICT implementation issues.
• Focussed on key concepts encountered in readings and lectures.
Lesson • Clear directions and scaffolding processes are provided. 4
online/shared • Checks are in place to assess student understanding.
environment • Provision of supporting material, e.g., guides, templates, and examples.
The University of Notre Dame Australia Date of Publication to Students: 1 February 2019 Page 9 of 11
You might also like
- Foster+Partners Manigua Fee Proposal 171109Document11 pagesFoster+Partners Manigua Fee Proposal 171109Ricardo Sarmiento Chaves100% (3)
- Algebra Syllabus 2020-2021Document2 pagesAlgebra Syllabus 2020-2021api-327138530No ratings yet
- Understanding Informational Text Features, Grades 6 - 8From EverandUnderstanding Informational Text Features, Grades 6 - 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Landscape Design WorkbookDocument26 pagesLandscape Design WorkbookEdit Makai100% (1)
- Engineering ManagementDocument213 pagesEngineering ManagementDarnell H. de Luna93% (15)
- Soc Methodology TrainingDocument202 pagesSoc Methodology TrainingAhmed HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Obe Framework - ChedDocument31 pagesObe Framework - ChedJose Marie Anoos100% (1)
- Game Design PatternsDocument31 pagesGame Design PatternsChu Quang ViênNo ratings yet
- Developing and Using RubricsDocument33 pagesDeveloping and Using RubricsYudha Nawa Anggara100% (1)
- Schedule MEPDocument36 pagesSchedule MEPReysa Hermanda SariNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process Automation Special Edition PDFDocument48 pagesRobotic Process Automation Special Edition PDFSanjay100% (1)
- Urban Greening Policy, A ProposalDocument12 pagesUrban Greening Policy, A ProposalRonald Gomeseria y Valledor100% (1)
- Emr408 A2 KL MarkedDocument21 pagesEmr408 A2 KL Markedapi-547396509No ratings yet
- Instructional Materials Evaluation Criteria - MathematicsDocument5 pagesInstructional Materials Evaluation Criteria - MathematicsVillanueva Ameera MaeNo ratings yet
- BMP4001 As1 Sep'23Document6 pagesBMP4001 As1 Sep'23Rokonuzzaman RekonNo ratings yet
- Letter Writing: AssignmentDocument8 pagesLetter Writing: AssignmentMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- 2022 Digital Portfolio RubricDocument2 pages2022 Digital Portfolio Rubricapi-609667270No ratings yet
- BMP3004+WW As1+Brief Sep+2022+CohortDocument5 pagesBMP3004+WW As1+Brief Sep+2022+CohortSwarnali Dutta ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1: ITECH 7400 IT Service Management & Professional Culture Name Purpose Timelines and ExpectationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Task 1: ITECH 7400 IT Service Management & Professional Culture Name Purpose Timelines and ExpectationsJodd EzNo ratings yet
- ST Johns Lutheran Primary School Unit Title Year 1 B-J Anderson Duration of UnitDocument13 pagesST Johns Lutheran Primary School Unit Title Year 1 B-J Anderson Duration of UnitBJMAndersonNo ratings yet
- AssesmentRubrics FinalDocument8 pagesAssesmentRubrics FinalASHOKKUMAR ARJANBHAI PARMARNo ratings yet
- Rubric Workshop: Learning OutcomesDocument22 pagesRubric Workshop: Learning OutcomesgorkitorcazaNo ratings yet
- Assessment BookletDocument83 pagesAssessment Bookletberatmete26No ratings yet
- Principle 2: Curriculum and Instruction Indicators 1 2 3Document12 pagesPrinciple 2: Curriculum and Instruction Indicators 1 2 3Livy PadriqueNo ratings yet
- PPD Assignment 2-CCCU LSC BABS With FoundationDocument18 pagesPPD Assignment 2-CCCU LSC BABS With FoundationSimona AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development Assignment 8 NovDocument6 pagesCurriculum Development Assignment 8 NovNony GovenNo ratings yet
- BMP3002 BP - As1 Brief - Sept 2022 CohortDocument4 pagesBMP3002 BP - As1 Brief - Sept 2022 Cohortmilka traykovNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ArtsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan ArtsElectona Kai SairNo ratings yet
- E Portfolio RubricDocument3 pagesE Portfolio RubricKyle Hamilton-LeckyNo ratings yet
- 7097MAA OctJan 1920 Coursework 2Document5 pages7097MAA OctJan 1920 Coursework 2RikNo ratings yet
- Unit 41 42 - Assignment Brief 1Document8 pagesUnit 41 42 - Assignment Brief 1Psychotic FaceNo ratings yet
- 5d11c85256e5e2265938x Blackboard S3 Bucket Learn Eu CDocument7 pages5d11c85256e5e2265938x Blackboard S3 Bucket Learn Eu Cr48gyxwc4fNo ratings yet
- Creation of A Portfolio David Rodrigo Mora LealDocument7 pagesCreation of A Portfolio David Rodrigo Mora Lealdavid english teacherNo ratings yet
- Scoring Rubrics ReferenceDocument26 pagesScoring Rubrics Referencereeyu lalalalaNo ratings yet
- SLRP Make Meaning Grade 9 BiologyDocument34 pagesSLRP Make Meaning Grade 9 BiologyjasonNo ratings yet
- Education Portfolio Self-Assessment MatrixDocument2 pagesEducation Portfolio Self-Assessment Matrixapi-511104676No ratings yet
- Unit Plan: Criteria HD A B C FDocument2 pagesUnit Plan: Criteria HD A B C FDebNo ratings yet
- PSPA8112-Presentation Rubric-2023Document4 pagesPSPA8112-Presentation Rubric-2023mirdedutreNo ratings yet
- Business CaseDocument5 pagesBusiness CaseSarah NoorNo ratings yet
- EN221 CMapDocument64 pagesEN221 CMapRyan EstonioNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Senior High School Quantitative Research: January 2021Document49 pagesLearning Module: Senior High School Quantitative Research: January 2021DYLANNo ratings yet
- Digital Portfolio Rubric 2020Document2 pagesDigital Portfolio Rubric 2020api-533818816No ratings yet
- In Semester (Individual) AssignmentDocument12 pagesIn Semester (Individual) Assignmentsaeed khanNo ratings yet
- Adapting The VALUE Rubrics To ABET ETAC Outcomes A-KDocument21 pagesAdapting The VALUE Rubrics To ABET ETAC Outcomes A-KCarolina LenisNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessments CriteriaDocument2 pagesSummative Assessments CriteriaAmbOladimejiMosesOkunribidoNo ratings yet
- Individual Report QuestionDocument7 pagesIndividual Report QuestionFang May YeohNo ratings yet
- Training For Master Teacher On The Philippine Professional Standards For TeachersDocument48 pagesTraining For Master Teacher On The Philippine Professional Standards For TeachersAngelica Fojas RañolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 ED305Document4 pagesLesson 4 ED305Maria Jhessa Mae Magdasoc, R.No ratings yet
- Assignment Handout OB HRMDocument6 pagesAssignment Handout OB HRMAr Arunima RaneNo ratings yet
- Sep5-9 EAPPDocument4 pagesSep5-9 EAPPRoxette Marie TuzonNo ratings yet
- Undergrad U WagDocument5 pagesUndergrad U WagPhiliplukaNo ratings yet
- !!! E-Portfolio Assessment RubricDocument2 pages!!! E-Portfolio Assessment RubrickamaNo ratings yet
- Assignment HandoutDocument10 pagesAssignment HandoutAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Written Essay RubricDocument2 pagesWritten Essay RubricomarszNo ratings yet
- Assignment StudentDocument8 pagesAssignment StudentAshley Ooi Shi QiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Output Day 2 Pedro C. Nepomuceno Jr.-Batangas ProvinceDocument6 pagesWorkshop Output Day 2 Pedro C. Nepomuceno Jr.-Batangas ProvinceJessica Marie FosNo ratings yet
- Pepsico AssignmentDocument28 pagesPepsico AssignmentNicK OnGNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH-I Secondary Education Curriculum 2010Document38 pagesENGLISH-I Secondary Education Curriculum 2010Hari Ng Sablay100% (10)
- BITS F437 Course HandoutDocument3 pagesBITS F437 Course HandoutVaibhav KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Rubric CSTUDY Jul23 MBAN MEC901 Final 20230508101055Document2 pagesRubric CSTUDY Jul23 MBAN MEC901 Final 20230508101055UrvasheeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Sem MARCH - AUGUST 2023Document4 pagesAssignment 1 - Sem MARCH - AUGUST 2023nurainizanori99No ratings yet
- PortDocument2 pagesPortapi-302641614No ratings yet
- Principle 2: Curriculum and Instruction Indicators 1 2 3Document5 pagesPrinciple 2: Curriculum and Instruction Indicators 1 2 3ruel gervacioNo ratings yet
- Ib Wit RubricDocument1 pageIb Wit RubricNiki LiNo ratings yet
- A607156092 - 27361 - 2 - 2022 - Assignment 1 SOC102Document3 pagesA607156092 - 27361 - 2 - 2022 - Assignment 1 SOC102Pankaj MahantaNo ratings yet
- QRMB Section A Assignment 1Document6 pagesQRMB Section A Assignment 1aysha banuNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Rating of Learning Outcomes Under The K To 12 Basic Education CurriculumDocument63 pagesAssessment and Rating of Learning Outcomes Under The K To 12 Basic Education CurriculumJude Vincent MacalosNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in ENGLISH8Document4 pagesCurriculum Map in ENGLISH8Aira MoresNo ratings yet
- Scheduling-Breaks-Creating-A-Quiet-Space 1Document3 pagesScheduling-Breaks-Creating-A-Quiet-Space 1api-451242734No ratings yet
- What Is AutismDocument2 pagesWhat Is Autismapi-451242734No ratings yet
- First Steps For Autism Planning MatrixDocument1 pageFirst Steps For Autism Planning Matrixapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Example Individual Education PlanDocument4 pagesExample Individual Education Planapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Along Side Me: WalkingDocument32 pagesAlong Side Me: Walkingapi-451242734No ratings yet
- RequestDocument5 pagesRequestapi-451242734No ratings yet
- My Child's StorybookDocument20 pagesMy Child's Storybookapi-451242734No ratings yet
- T-C-124-Visual-Timetable-Sen-Using-The-Toilet Ver 2Document4 pagesT-C-124-Visual-Timetable-Sen-Using-The-Toilet Ver 2api-451242734No ratings yet
- Curriculum Links - Ict Assignment 3Document1 pageCurriculum Links - Ict Assignment 3api-451242734No ratings yet
- Nappy Changing RoutineDocument1 pageNappy Changing Routineapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Dietary GuidelinesDocument3 pagesDietary Guidelinesapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Ict ReferencesDocument1 pageIct Referencesapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Ict Tools Thingamabobby 1Document12 pagesIct Tools Thingamabobby 1api-451242734No ratings yet
- Marking Rubric Lesson 2Document2 pagesMarking Rubric Lesson 2api-451242734No ratings yet
- Groups For Hypothetical ClassDocument1 pageGroups For Hypothetical Classapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Social Constructivism ParagraphDocument1 pageSocial Constructivism Paragraphapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Storyboard TemplateDocument1 pageStoryboard Templateapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Marking Rubric 3Document1 pageMarking Rubric 3api-451242734No ratings yet
- ICT Forward Planning Document: Final ProductDocument13 pagesICT Forward Planning Document: Final Productapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Ict Tools UsedDocument3 pagesIct Tools Usedapi-451242734No ratings yet
- Peo MechDocument4 pagesPeo Mechmailsk123No ratings yet
- Imark CompetitionDocument3 pagesImark CompetitionDisha KaushalNo ratings yet
- O8516004 TM111 Tma01Document6 pagesO8516004 TM111 Tma01sandy zipNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Architecture - Búsqueda de Google PDFDocument5 pagesPortfolio Architecture - Búsqueda de Google PDFabenorthNo ratings yet
- 282 - Ux Journey 1.3Document95 pages282 - Ux Journey 1.3Dimas FahrulNo ratings yet
- 11050002G4 Biplane ConfigurationDocument20 pages11050002G4 Biplane Configurationtha_ansNo ratings yet
- Applications of Affordance and Semantics in Product DesignDocument6 pagesApplications of Affordance and Semantics in Product DesignVivekanand KhatuaNo ratings yet
- Pablo - The Innovative Design of Adjustable Coffee TableDocument3 pagesPablo - The Innovative Design of Adjustable Coffee TableAzizan NordinNo ratings yet
- Planning Grid Junior Cert GraphicsDocument5 pagesPlanning Grid Junior Cert Graphicsapi-545610225No ratings yet
- Block Chain PowerPoint TemplatesDocument36 pagesBlock Chain PowerPoint TemplatesRafi DwiatmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Repair and MaintenanceDocument12 pagesAssignment On Repair and MaintenanceMuhammad AyyazNo ratings yet
- Standard Furniture Specifications: Palo Alto Downtown LibraryDocument9 pagesStandard Furniture Specifications: Palo Alto Downtown LibraryAnusha IvaturiNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan KTVDocument1 pageFloor Plan KTVBrylle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Professional Resume v2Document1 pageProfessional Resume v2Wayan GedeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningHazel MosotNo ratings yet
- 10 54 45ASME ç×ÓÊéÊéDocument6 pages10 54 45ASME ç×ÓÊéÊéipla_mecanicoNo ratings yet
- BMM 4623 Mechanical System Design - Rev01 July 31, 2013Document6 pagesBMM 4623 Mechanical System Design - Rev01 July 31, 2013huszsNo ratings yet
- Jigs&Fixture For Aircraft IndustriesDocument21 pagesJigs&Fixture For Aircraft Industriessaravananpg7911100% (3)
- Riset Harga Kompetitor, Sabtu 23 Desember 2023Document16 pagesRiset Harga Kompetitor, Sabtu 23 Desember 2023RaisNo ratings yet
- Annex L Thesis Book OutlineDocument3 pagesAnnex L Thesis Book OutlineJonel Andrew FranciscoNo ratings yet
- CV - Intern - Kartika Dwi Arianti - 2019Document1 pageCV - Intern - Kartika Dwi Arianti - 2019Eugenia KartikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ملخصDocument3 pagesChapter 1 ملخصalhomidiatheer48No ratings yet