Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 1: IS Foundation
Uploaded by
Ajay Davis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesThe document discusses information systems and business processes. It defines information and data, and explains how information systems are relevant in today's digital age by supporting decision making and business operations. It also outlines different types of business processes like transaction processing systems and supply chain management systems. Finally, it discusses technologies that enable collaboration between organizations, such as email, instant messaging, videoconferencing, and tools from Google, IBM and Microsoft.
Original Description:
Summarized points related to Management Information Systems
Original Title
MIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses information systems and business processes. It defines information and data, and explains how information systems are relevant in today's digital age by supporting decision making and business operations. It also outlines different types of business processes like transaction processing systems and supply chain management systems. Finally, it discusses technologies that enable collaboration between organizations, such as email, instant messaging, videoconferencing, and tools from Google, IBM and Microsoft.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesChap 1: IS Foundation
Uploaded by
Ajay DavisThe document discusses information systems and business processes. It defines information and data, and explains how information systems are relevant in today's digital age by supporting decision making and business operations. It also outlines different types of business processes like transaction processing systems and supply chain management systems. Finally, it discusses technologies that enable collaboration between organizations, such as email, instant messaging, videoconferencing, and tools from Google, IBM and Microsoft.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Chap 1: IS Foundation
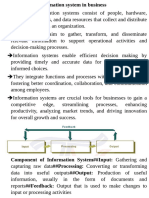
1. What is information and why is it important to businesses?
● Information is a piece of something that will make sense when conveyed to some means.
● Data that have been shaped in a form that is meaningful and useful to human beings.
● Data are streams of raw facts representing events occurring organizations or the physical
environment before they have organized and arranged into a form that people can understand to
make sense.
2. What is information system and how is it relevant in information technology age?
● A set of inter related components that collect and store data process and present data in the form of
information to support decision making, control, analyze problems, visualize complex subjects and create
new products.
3. Strategic Advantages of IS
a. Operational Excellence:
● Improve efficiency of business operations in order to achieve higher profitability, for which IS and
technologies are major tools available to managers, when coupled with changes in business practices &
management behaviors.
b. New products, services and business models:
● IS & technologies enables to create new products and services as well as new business models.
● Business model describes how a company produces, delivers and sells a products & service to create wealth
c. Customer & suppliers intimacy:
To serve and respond to rapidly changing customer demand
d. Improved decision making:
To facilitate improved decisions making at different levels by having right information at right time
e. Competitive advantage:
By operational excellence, better and new products and services, and business models, customer/supplier intimacy
and with improved decision making – help in achieving competitive advantage
f. Survival:
Giving the firm more flexibility to survive in turbulent times
Offering extraordinary opportunities to firms to become global organization
Enable managing key cooperate assets – IP, core competencies, financial & human assets with better efficiency &
security.
4. Dimensions of IS (that contribute to IS development: Management, organization and technology)
● Senior Management: - take long range strategic decisions about product and services as
well as ensures financial performance of the firm
● Middle Management: - carry out programs & plans of senior management
● Operational Management: monitoring daily activities of business
● Knowledge workers: - engineers, scientist, or architects design products or services and
create new knowledge for the firm
● Data Workers: - secretaries or clerks, assist the scheduling and communications at all
levels of firm
● Production & service workers: - produce the product & deliver the service
5. Contemporary approach to IS (Technical, Behavioral):
● Technical Approach: mathematically based models to study information system as
well as physical technology and formal capabilities of
Disciplines contributing to technical approach:
1. Computer science:
● Establish theories of computability
● Methods of computation
● Methods of efficient data storage & access
2. Management science:
● Development of models for decision making and management practices
3. Operational research:
● Mathematical techniques for optimizing parameters of organization – such as
transportation, inventory control, transaction cost
● Behavioral Approach: concerned with behavioral issues arise in the development
and long term maintenance of IS
Discipline contributes to:
1. Sociology - groups, teams, individuals in organization are studied
2. Psychologists – study of IS regarding have decision making are done
3. Economists – influence of IS in cost structures, dynamics of digital markets
etc.
Chap 2: Business Processes, Management Information Systems and
Collaboration
1. What are business processes?
● Business processes refer to the manner in which work is organized, coordinated
and focused to produce a valuable product or service
● Business processes are the collection of activities required to produce a product
or service
● These activities are supported by flows of material, information and knowledge
among the participants in business processes.
2. Different types of business processes
➢ Transaction Processing Systems (TPS):
A transaction processing system is a computerized system that performs and records the daily
routine transactions necessary to conduct business, such as sales order entry, hotel reservations,
payroll, employee record keeping and shipping.
➢ Business Intelligence:
Is a contemporary term for data and software tools for organizing, analyzing and providing
access to data to help managers and other enterprise users make more informed decision.
Marketing Information Systems:
➢ HR Information Systems:
➢ Financial Information Systems:
➢ Decision Support Systems(DSS): -
● Focuses on problems that are unique and rapidly changing for which the procedure for
arriving at a solution may not be fully predefined in advance.
● Although DSS use internal information from TPS and MIS, they often being in information
from external sources such as stock prices or product prices of competition.
➢ Executive Support Systems(ESS): -
Helps senior management make decisions on strategic issues and long term trends
They address non-routine decisions requiring judgment, evaluation and insight because there is
no agreed on procedure for arriving at a solution.
• Systems for linking enterprises:
➢ Supply Chain Management Systems(SCMS): -
● Firms use supply chain management system to help manage relationships with
their supplies.
● These systems help suppliers, purchasing firms, distributors and logistics
companies share information about orders, production, inventory levels, and
delivery of product and services so they can source, produce, and deliver goods
and services efficiently.
➢ Customer Relationship Management Systems (CRMS): -
● Firms use CRM systems to manage their relationships with their customers.
● CRM systems provide information to coordinate all of the business processes that deal
with customers in sales, marketing, and service to optimize revenue, customer
satisfaction, and customer retention
● This information helps firms identify, attract, and retain the most profitable customers,
provide better service to existing customers, and increase sales.
➢ Knowledge Management Systems (KMS): -
● Some firms perform better than others because they have better knowledge about how
to create, produce, and deliver products and services.
● This firm knowledge is unique, is difficult to imitate and can be leveraged into long term
strategic benefits.
● KMS enable organizations to better manage processes for capturing and applying
knowledge and management decisions.
3. Technologies for collaboration:
Collaboration: - collaboration is working with others to achieve shared and explicit goals.
● It focuses on task or mission accomplishment and usually takes place in a business or
other organization and between businesses.
➢ Email & Instant Messaging(IM) : -
Email and instant messaging have been major communication and collaboration tools for
interaction jobs.
● Operates on mobiles, computers and other wireless devices and features like file sharing
● In recent years, email has declined with messaging and social media becoming preferred
channels of communication
➢ Virtual meetings: -
In order to reduce the travel expenses and enable people in different locations to meet and
collaborate, many companies are adopting videoconferencing & web conferencing
Allows two or more individuals to communicate simultaneously through video and audio
transmissions.
Enables sharing documents and presentations with audio conferencing and live video via
webcam
➢ Google tools: -
➢ IBM Notes: -
MS SharePoint
4. IS department in an organization
You might also like
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- Full Value of Data: Maximizing Business Potential through Data-Driven Insights and Decisions. Part 2From EverandFull Value of Data: Maximizing Business Potential through Data-Driven Insights and Decisions. Part 2No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business TodayDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business TodayNam Phuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Ins RevisionDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Ins Revision--No ratings yet
- The Role of Information Systems in An OrganizationDocument27 pagesThe Role of Information Systems in An OrganizationRobert VasquezNo ratings yet
- Mis CTDocument10 pagesMis CTJoy NathNo ratings yet
- BMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020Document8 pagesBMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020sicelo ncubeNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemsDocument62 pagesManagement Information SystemsKartika Bhuvaneswaran NairNo ratings yet
- MIS Module 1Document28 pagesMIS Module 1jsji14No ratings yet
- MIS Research Ch1-4Document10 pagesMIS Research Ch1-4Louis Al BedouinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Nourhan AfifiNo ratings yet
- Information Systems in Global Business Today: Presented By: Maria Luz La Madrid-JimenezDocument26 pagesInformation Systems in Global Business Today: Presented By: Maria Luz La Madrid-JimenezMalu La Madrid JimenezNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document13 pagesWa0002.NitinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and Chapter 2 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 1 and Chapter 2 SummaryGraciella AudreyNo ratings yet
- Impact of IT On BusinessDocument33 pagesImpact of IT On BusinessSamiksha SainiNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems and Business IntelligenceDocument59 pagesDecision Support Systems and Business IntelligencetimmyNo ratings yet
- Book Chapter 2 VivianDocument12 pagesBook Chapter 2 VivianThomasNo ratings yet
- C1H021021 - Almas Delian - Resume MIS Chapter 2Document4 pagesC1H021021 - Almas Delian - Resume MIS Chapter 2Almas DelianNo ratings yet
- Evolution of IS: Management, Decision-Making and Information Systems That Enhance The Value of InformationDocument28 pagesEvolution of IS: Management, Decision-Making and Information Systems That Enhance The Value of InformationKevin SkillzNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument57 pagesManagement Information SystemBHUWNESH AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - GLOBAL E-BUSINESSDocument49 pagesChapter 2 - GLOBAL E-BUSINESSToukyer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument21 pagesUnit IRaghavkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Management Information SystemDocument25 pagesLecture 02 - Management Information SystemThiwanka Tissera100% (1)
- MIS - Lec 1Document22 pagesMIS - Lec 1Abdul Hanan NasirNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Module I - Introduction To Information SystemsDocument30 pagesManagement Information System: Module I - Introduction To Information SystemsNitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument14 pagesClass NotesPema Sonam YangchenNo ratings yet
- Mis Module 1Document24 pagesMis Module 1mohammedansil791No ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document34 pagesChapter 12Herman TusiadiNo ratings yet
- Business Information Systems W2 - IS Building BlocksDocument5 pagesBusiness Information Systems W2 - IS Building BlockslucyNo ratings yet
- Data and InformationDocument30 pagesData and InformationSyed SameerNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Managing The Digital FirmDocument22 pagesCH - 1 Managing The Digital FirmAbhijit_Patkar_2711No ratings yet
- ISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Document48 pagesISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Abhishek PatilNo ratings yet
- U11 Managing Knowledge 2022 Mar July 23Document56 pagesU11 Managing Knowledge 2022 Mar July 23Noppon SETTASATIENNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document39 pagesCH 02YESSICA CECILIA SINAGANo ratings yet
- CHapter 2 MIS SLideDocument38 pagesCHapter 2 MIS SLideRaktimNo ratings yet
- Explain Why Information Systems Are So Essential in Business TodayDocument7 pagesExplain Why Information Systems Are So Essential in Business TodaySmitho UnpluggedNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Management Information SystemDocument41 pagesChapter One: Management Information Systemobsinan dejeneNo ratings yet
- MIS 1sessionalDocument12 pagesMIS 1sessionalAmit Vikram OjhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Information SystemsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Management Information SystemsYus MartianNo ratings yet
- Mis Assignment 2 FinalDocument7 pagesMis Assignment 2 Finaleyob yohannesNo ratings yet
- MD - Mahtabul Islam 192200011Document6 pagesMD - Mahtabul Islam 192200011Mahtab IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignmentno (1) Muhammad Muneeb Ahsan - PDFDocument5 pagesAssignmentno (1) Muhammad Muneeb Ahsan - PDFMuneeb RaajpootNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Global E-BusinessDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Global E-BusinessSyeda Nazneen AzadNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument39 pagesManagement Information SystemYt NoobNo ratings yet
- Mlo5s Is Elmnhg KoloDocument30 pagesMlo5s Is Elmnhg KoloRafeek makramNo ratings yet
- Session - 03 - GLOBAL E-BUSINESS AND COLLABORATIONDocument27 pagesSession - 03 - GLOBAL E-BUSINESS AND COLLABORATIONMohamed Ahmed AbdiNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit 1Document31 pagesMIS Unit 1Rudra ArdurNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Management Information SystemDocument49 pagesModule-1: Management Information SystemJithuHashMiNo ratings yet
- Mis Unit 1Document24 pagesMis Unit 1YoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MIS16Document30 pagesChapter 2 MIS16Nguyễn Thuỳ DungNo ratings yet
- DSS 200 SG1-3Document9 pagesDSS 200 SG1-3Kevin SchusterNo ratings yet
- IT Supports Organizational Performance in Turbulent Business EnvironmentsDocument34 pagesIT Supports Organizational Performance in Turbulent Business EnvironmentsSakshi VermaNo ratings yet
- Managment Information SystemDocument64 pagesManagment Information SystemTech ProffesorNo ratings yet
- Information System Management Meeting 1Document35 pagesInformation System Management Meeting 1Anggraeni TriNo ratings yet
- Assignment For First MidtermDocument7 pagesAssignment For First MidtermJahadul IslamNo ratings yet
- Managing The Digital Firm: This Chapter Will Help You UnderstandDocument33 pagesManaging The Digital Firm: This Chapter Will Help You UnderstandSuman BhandariNo ratings yet
- IMP2Document51 pagesIMP2dhruv mahashayNo ratings yet
- PresentaionDocument15 pagesPresentaionchikonhinetsaitrishNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Supporting Decision Making: Decision Support in BusinessDocument12 pagesUnit 7 - Supporting Decision Making: Decision Support in BusinessBishal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Topic 14: Class A LevelDocument66 pagesTopic 14: Class A LevelzaraNo ratings yet
- Teaching English in The Elementary Grades (Language Arts)Document21 pagesTeaching English in The Elementary Grades (Language Arts)RENIEL PABONITANo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Transport PhenomenaDocument521 pagesFundamental of Transport Phenomenaneloliver100% (2)
- Muscle Building MythsDocument5 pagesMuscle Building MythsKarolNo ratings yet
- Injection Pump Test SpecificationsDocument3 pagesInjection Pump Test Specificationsadmin tigasaudaraNo ratings yet
- SMM Live Project MICA (1) (1)Document8 pagesSMM Live Project MICA (1) (1)Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Venetian Shipping During The CommercialDocument22 pagesVenetian Shipping During The Commercialakansrl100% (1)
- Vistas 1-7 Class - 12 Eng - NotesDocument69 pagesVistas 1-7 Class - 12 Eng - Notesvinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Global Supply Chain Top 25 Report 2021Document19 pagesGlobal Supply Chain Top 25 Report 2021ImportclickNo ratings yet
- GE Money and BankingDocument110 pagesGE Money and BankingBabita DeviNo ratings yet
- MCS 150 Page 1Document2 pagesMCS 150 Page 1Galina NovahovaNo ratings yet
- Decemeber 2020 Examinations: Suggested Answers ToDocument41 pagesDecemeber 2020 Examinations: Suggested Answers ToDipen AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Gprs/Umts: IAB Workshop February 29 - March 2, 2000 Jonne Soininen NokiaDocument34 pagesGprs/Umts: IAB Workshop February 29 - March 2, 2000 Jonne Soininen NokiaSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- SurrealismDocument121 pagesSurrealismLaurence SamonteNo ratings yet
- 12c. Theophile - de Divers ArtibusDocument427 pages12c. Theophile - de Divers Artibuserik7621No ratings yet
- MPLS Fundamentals - Forwardi..Document4 pagesMPLS Fundamentals - Forwardi..Rafael Ricardo Rubiano PavíaNo ratings yet
- A Letter From Sir William R. Hamilton To John T. Graves, EsqDocument7 pagesA Letter From Sir William R. Hamilton To John T. Graves, EsqJoshuaHaimMamouNo ratings yet
- Generator Faults and RemediesDocument7 pagesGenerator Faults and Remediesemmahenge100% (2)
- July 2006 Bar Exam Louisiana Code of Civil ProcedureDocument11 pagesJuly 2006 Bar Exam Louisiana Code of Civil ProcedureDinkle KingNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Steel and AccessoriesDocument4 pagesReinforcing Steel and AccessoriesTheodore TheodoropoulosNo ratings yet
- 9 Electrical Jack HammerDocument3 pages9 Electrical Jack HammersizweNo ratings yet
- Naresh Kadyan: Voice For Animals in Rajya Sabha - Abhishek KadyanDocument28 pagesNaresh Kadyan: Voice For Animals in Rajya Sabha - Abhishek KadyanNaresh KadyanNo ratings yet
- TLE ICT CY9 w4 PDFDocument5 pagesTLE ICT CY9 w4 PDFMichelle DaurogNo ratings yet
- 2007.01 What Does Jesus Think of Science?Document2 pages2007.01 What Does Jesus Think of Science?William T. PelletierNo ratings yet
- NetEco Commissioning Guide (V200R003C01 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument116 pagesNetEco Commissioning Guide (V200R003C01 - 01) (PDF) - enabdo elmozogyNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technology945Document35 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology945Praluki HerliawanNo ratings yet
- The Best John Green QuotesDocument10 pagesThe Best John Green Quotesapi-586467925No ratings yet
- Net 2020Document48 pagesNet 2020Krishan pandeyNo ratings yet
- Class XI Economics 2011Document159 pagesClass XI Economics 2011Ramita Udayashankar0% (1)
- Astm A380 PDFDocument13 pagesAstm A380 PDFaromalara12No ratings yet
- SJK (T) Ladang Renchong, PagohDocument2 pagesSJK (T) Ladang Renchong, PagohAinHazwanNo ratings yet