Professional Documents
Culture Documents
22 Ipv6 Routing Part II
Uploaded by
Amit kumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
22 Ipv6 Routing Part II
Uploaded by
Amit kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
IPv6 Routing
Part II
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Instructor: Joe Rinehart, CCIE #14256
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
In This Lesson:
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
1. BGP for IPv6
2. Redistribution in IPv6
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
BGP for IPv6
• Protocol Mechanics for IPv6 BGP
– Mechanics similar to BGP for IPv4
• Uses TCP port 79 for transport
• Formal neighbor relationships
• eBGP/iBGP neighbor types
• Route selection through path
attributes
• Neighbor/network statements
– Protocol differences
• IPv4 and IPv6 supported
simultaneously in the same device
• Multicast mode supported
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
BGP for IPv6
• Protocol Mechanics for IPv6 BGP
• Configuring IPv6 BGP
– Must enable routing using the ipv6
unicast-routing command
– Process is created using the command
address-family ipv6 under the BGP
routing process
– Neighbors manually configured using
the neighbor <IPv6 address>
remote-as <ASN> command
– Activate command must be used to
bring up neighbor relationship
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
BGP for IPv6
• Configuring IPv6 BGP
– Networks injected into the IPv6 BGP
process using the network or
redistribute commands (as with
IPv4)
– Show commands include:
• show ipv6 protocols
• show ipv6 route bgp
• show ipv6 bgp
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
Redistribution in IPv6
• Protocol Mechanics for IPv6
Redistribution
– Mechanics similar to IPv4
• Redistribution derived from the IP
routing table rather than protocol
databases
• Identical administrative distances
used
• Route-filtering and manipulation is
similar (distribute-lists, route-
maps, etc.)
• Command syntax is similar
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
Redistribution in IPv6
• Protocol Mechanics for IPv6
Redistribution
– Differences from IPv4
• OSPFv3 does not require subnets
keyword to import all routes
• Connected routes not imported
from protocol without the
include-connected
subcommand
• Access-lists and prefix-lists use
IPv6 formats rather than IPv4
formats
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
Redistribution in IPv6
• Configuring IPv6 Redistribution
– Must enable routing using the ipv6
unicast-routing command
– For connected routes, use the
command redistribute connected
[metric <number>] [route-map
<map-name>]
– For BGP and RIP, use the command
redistribute <rip <process> |
bgp <ASN> [metric <number>]
[route-map <map-name>]
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
Redistribution in IPv6
• Configuring IPv6 Redistribution
– For EIGRP, use the command
redistribute eigrp <ASN> [metric
<number>] [route-map <map-
name>] [include-connected]
– For OSPF, use the command
redistribute ospf<process-id>
[match <route-type> [metric
<number>] [route-map <map-
name>] [include-connected]
– Show commands for verification
similar for IPv4 redistribution, using
the IPv6 keyword
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
1. Dual Stack Solutions
2. Tunneling Mechanisms
3. NAT Protocol Translator
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Dual Stack Solutions
• Dual Stack Solutions Deploy both IPv4
and IPv6 side by side
– Applications choose which protocol
– Requires both IPv4 and IPv6
addresses to be configured on the
device
– Typically Cisco recommended
approach
– Microsoft Windows hosts (vista,
Windows 7) will prefer IPv6
– Requires double the configuration on
devices
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Manually Configured Tunnels (MCT)
– Requires use of tunnel interfaces on
both ends of the connection
• Must have valid IPv4 source and
destinations (tunnel source and
tunnel destination)
• Tunnel mode must be specified as
IPv6 over IP (tunnel mode
ipv6ip not GRE)
• verify successful configuration
– Tunnel interface up/up
– Able to ping/reach other side
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Manually Configured Tunnels
– IPv6 parameters also required
• IPv6 address configured using
ipv6 address command (both ends
on the tunnel)
• Add IPv6 routing commands
– Static routes
– Dynamic routing protocols
• verify IPv6 tunnel is operational:
– show ipv6 route connected
– IPv6 ping/traceroute
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– 6to4 Tunnels
• Unique characteristics
– Used to join multiple isolated
IPv6 domains together
– Multipoint in nature rather
than point-to-point
– IPv4 addresses embedded in
IPv6 addresses in hexadecimal
using the 2002::/16 reserved
range
– Also possible to use global
unicast with additional config
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– 6to4 Tunnels
• Configuration
– Tunnel mode must be
specified as IPv6 over IP 6to4
(tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4)
– Tunnel source typically tied to
local IPv4 loopback address
– IPv6 addresses created using
format
2002:AABB:CCDD:Subnet::/64
(AABBCCDD is IPv4 address in
hexadecimal)
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– 6to4 Tunnels
• Configuration
– Static routes must be added
to enable routing between all
spokes of the tunnel, using
the command ipv6 route
2002::/16 Tunnel
<interface#>
• Verify IPv6 tunnel is operational:
– show ipv6 route connected
– IPv6 ping/traceroute
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– IPv4-Compatible Tunnels
• Unique characteristics
– Used to join multiple IPv6
domains together
– Multipoint in nature rather
than point-to-point
– IPv6 global unicast addresses
uses rather than reserved
range
– IPv4 addresses embedded in
in hexadecimal using the
0:0:0:0:0:0:AABBCCDD range
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– IPv4-Compatible Tunnels
• Configuration
– Tunnel mode must be
specified as IPv6 over IP 6to4
(tunnel mode ipv6ip auto-
tunnel)
– Tunnel source typically tied to
local IPv4 loopback address
– IPv6 addresses created using
format ::AA:BB:CC:DD
(AABBCCDD is IPv4 address in
hexadecimal)
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– IPv4-Compatible Tunnels
• Configuration
– BGP used to exchange routing
information for both IPv6 and
IPv6
• Verify IPv6 tunnel is operational:
– show ipv6 route connected
– show ip bgp
– show ip route bgp
– IPv6 ping/traceroute
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– ISATAP Tunnels
• Unique characteristics
– ISATAP stands for Intra-site
Automatic Tunnel Protocol
– Used to join multiple IPv6
domains together
– Multipoint in nature rather
than point-to-point
– Uses IPv6 global unicast
addresses
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– ISATAP Tunnels
• Unique characteristics
– IPv4 addresses embedded in
the last two octets in
hexadecimal using the IPv6-
Prefix:AA:BB:CC:DD range
– Tunnels usually use a single
prefix (i.e., common IPv6
subnet)
– Tunnel interface can optionally
be discovered using modified
EU-164 rules
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– ISATAP Tunnels
• Configuration
– Tunnel mode must be
specified as IPv6 over IP 6to4
(tunnel mode ipv6ip
isatap)
– Tunnel source typically tied to
local IPv4 loopback address
– IPv6 addresses created using
format IPv6-
Prefix:AA:BB:CC:DD (IPv4
address in hexadecimal)
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– ISATAP Tunnels
• Configuration
– Static routes must be added
to enable routing between all
spokes of the tunnel, using
the command ipv6 route
Prefix/Length Tunnel
<interface#>
• Verify IPv6 tunnel is operational:
– show ipv6 route
– IPv6 ping/traceroute
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Tunneling Mechanisms
• Automatic Tunnels
– Other Tunneling Methods
• GRE Tunneling
– Virtually identical to manually
configured tunnel
– Tunnel mode must be
specified as IPv6 over IP 6to4
(tunnel mode gre ip)
– Allows use of dynamic routing
• Teredo Tunneling
– Developed by Microsoft
– Bypasses NAT
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
NAT Protocol Translator
• Unique characteristics
– Similar options to IPv4 NAT
• Static
• Dynamic
• Overload/PAT
– Differences
• Additional option called IPv4-
Mapped NAT (predefined IPv6
prefix defined for use)
• BVI interfaces not supported
• Limited application layer gateway
support (with DNS, ICMP, etc.)
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
NAT Protocol Translator
• Configuration
– Identification of IPv6 addresses to
translate using the ipv6 nat
<prefix>/<length> command
– Specifying the IPv6 and IPv4
interfaces using the ipv6 nat
subcommand
– For mapped NAT, add the v4-
mapped keyword after the prefix
statement
– For static NAT, define translations
using ipv6 nat <v4v6|v6v4>
source commands
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
NAT Protocol Translator
• Configuration
– For PAT, define translations using the
following steps
• Definition of the addresses to be
translated using the ipv6 access-
list command
• Create the mapping on an
interface using the command
ipv6 nat v6v4 source list
<ipv6-acl>interface
<type/number> overload
• Alternatively, a NAT pool can be
defined
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
NAT Protocol Translator
• Verification
– show ipv6 nat translations
– show ipv6 nat statistics
– clear ipv6 nat translation *
– debug ipv6 nat [detailed | port]
• NAT-PT is considered somewhat obsolete
and is not the recommended transition
method
– Dual stack most preferred
– Tunneling mechanisms preferred
when necessary
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
1. Review of IPv6 Configuration Commands
2. Devices Involved in BGP Domain
3. Configuration of IPv6 Devices
4. Verification of IPv6 Operation
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Assignment of IPv6 Addresses
– ipv6 address <prefix>/<length>
– Interfaces to define/use
• Loopback (identify as Loopback 6)
• WAN/vLAN Interfaces
– R1 S0/0.134
– R3/R4 S0
– R1/R3 FA0/0.13
• Tunnel Interfaces
– R5/R9 GRE Tunnel
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Assignment of IPv6 Addresses
– Interfaces to define/use
• Tunnel Interfaces
– R1/R6 IPv4-Compatible Tunnel
– R6/R7 Manually Configured
Tunnel
• Configuration of IPv6 Routing
– Starting process using the ipv6
unicast-routing command in global
configuration mode
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Configuration of IPv6 Routing
– Configuration of RIPng process
• Enabling process using the ipv6
router rip <process-name>
command
• Placing interfaces into the protocol
using the ipv6 rip <process-
name> enable command
– Configuration of IPv6 EIGRP process
• Enabling process using the ipv6
router eigrp <ASN> command
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Configuration of IPv6 Routing
– Configuration of IPv6 EIGRP process
• Enabling process using the ipv6
router eigrp <ASN> command
• Placing interfaces into the protocol
using the ipv6 eigrp <ASN>
enable command
• Include GRE tunnel interfaces in
the routing process
• Do not perform any type of route
filtering
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Configuration of Tunneling
– Configuration of GRE tunnels between
R5 and R6 using the commands:
• interface tunnel 0
• tunnel mode gre ip
• tunnel source <ip-address>
• tunnel destination <ip-
address>
• ipv6 address
<prefix>/<length>
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Configuration of Tunneling
– Configuration of MCT tunnel between
R6 and R7 using the commands:
• interface tunnel 0
• tunnel mode ipv6ip
• tunnel source <ip-address>
• tunnel destination <ip-
address>
• ipv6 address
<prefix>/<length>
• ipv6 route <prefix/length>
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Review of IPv6 Configuration
Commands
• Configuration of Tunneling
– Configuration of IPv4 compatible
tunnel between R1 and R6 using the
commands:
• interface tunnel 0
• tunnel mode ipv6ip auto-
tunnel
• tunnel source <ip-address>
• ipv6 address
<0:0:0:0:0:0:<ipv4-address>
• address-family ipv6 (for BGP)
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Devices Involved in IPv6
• Router 1 (R1)
– VLAN interfaces (VLAN 99, 13)
– S0/0.134 interface
– Loopback 6 interface
– Tunnel interface
• Router 3 (R3)
– VLAN interface (VLAN 13)
– S0/0 interface
– Loopback 6 interface
• Router 4 (R4)
– S0/0 interface
– Loopback 6 interface
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Devices Involved in IPv6
• Router 5 (R5)/Router 9 (R9)
– Loopback 6 interface
– Tunnel interface
• Router 6 (R6)
– VLAN interface (VLAN 99)
– Loopback 6 interface
– Tunnel interfaces
• Router 7 (R7)
– Loopback 6 interface
– Tunnel interface
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Configuration of IPv6 Devices
• Configure all loopback interfaces as
loopback 6 with addresses using the
format (N=router number)
2001:C926:101:NNNN:NNNN:NNNN:NNN
N:N/128
• Configure frame-relay interface addresses
using the format (N=router number)
2001:C926:101:134::N/112
• Configure GRE/MCT tunnels using the
format 2001:C926:101:NY::N/112
(N=router number, Y=neighbor router)
• Configure IPv4 tunnels using the format
<0:0:0:0:0:0:<ipv4-address>
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Configuration of IPv6 Devices
• Configure static routes for the manually
configured tunnel sites
• Configure RIPng on R1/R3/R4 using the
process name IPv6-RIP
• Configure EIGRP on R5 and R6 using the
autonomous system number 100
Verification of IPv6 Operation
• Confirming that IPv6 itself is correct:
– Examine the output of the show
ipv6 interfaces command and verify
expected interfaces are operational
– Examine the output of the show
ipv6 route connected command
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Verification of IPv6 Operation
• Confirming that IPv6 RIP is operating
correctly:
– Examine the output of the show
ipv6 protocols command (see left)
• verify process is running
• verify networks/subnets
– Confirm the presence of expected
networks in the routing table using
the show ipv6 route rip command
– Examine the output of the show ipv6
rip <process name> command and
verify details are correct
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Verification of IPv6 Operation
• Confirming that IPv6 EIGRP is operating
correctly:
– Examine the output of the show
ipv6 protocols command (see left)
• Verify process is running
• Verify networks/subnets
– Confirm the presence of expected
networks in the routing table using
the show ipv6 route eigrp command
– Confirm active neighbor relationships
using the show ipv6 eigrp <ASN>
neighbors command
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Verification of IPv6 Operation
• Confirming that IPv6 EIGRP is operating
correctly:
– Examine the output of show ipv6
eigrp <ASN> interfaces command
• Expected interfaces appear
• Correct ASN is displayed
• Peers are shown in interface
statistics (non-zero)
– Examine the output of the show
ipv6 eigrp <ASN> topology
command
• Successor/feasible successors
present
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
Verification of IPv6 Operation
• Confirming that IPv6 Static Routing (via
tunnels) is operating correctly:
– Examine the output of the show ip
interfaces tunnel <tunnel #>
command
• Interface state is up/up
• Source is correctly identified
• Interface is operational
– Examine the output of the show
ipv6 route static command
• Routes present in the table
• Next-hop correctly identified
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
verification of IPv6 Operation
• Confirming that IPv6 Static Routing (via
tunnels) is operating correctly:
– Test for end-to-end connectivity
• Use the ping ipv6 <ipv6-address>
command to verify reachability
• Use the traceroute ipv6 <ipv6-
address> to review path
• Execute the telnet <ipv6-address>
to fully verify application layer
reachability
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
Key Terms You Should Know
Dual Stack — IPv4 to IPv6 transition mechanism in which both
protocols are actively configured on devices
MCT — Manually Configured Tunnel, an IPv4 to IPv6 transition
mechanism in which a point-to-point tunnel is used to transport
IPv6 traffic across an IPv4 domain
6to4 — Automatically generated tunnel, an IPv4 to IPv6
transition mechanism in which a multipoint tunnel is used to
transport isolated IPv6 domains across an IPv4 domain
(typically uses addressing in the 2002:/16 range)
ISATAP — Intra-site Automatic Tunnel Protocol, an IPv4 to IPv6
transition mechanism in which a multipoint tunnel is used to
transport IPv6 s across an IPv4 domain (uses global addresses)
NAT-PT — NAT Protocol Translator, IPv4 to IPv6 transition
mechanism in which IPv6 addresses are translated to IPv4
IPv6 Routing
Cisco CCNP ROUTE Training
What We Covered
Understanding and Configuring IPv6 Routing
IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence Mechanisms
Configuring IPv6 Lab Exercises
You might also like
- 2 IPv4 IPv6 RickGrazianiDocument32 pages2 IPv4 IPv6 RickGrazianimtcssnspNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Teldat PDFDocument66 pagesPresentacion Teldat PDFJoseNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator GuideDocument1,664 pagesCisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator GuideTu Le ThanhNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik SSTPDocument16 pagesMikrotik SSTPmiraNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Routers and Wireless - SoftwareDocument7 pagesMikroTik Routers and Wireless - Softwareinfra biznetNo ratings yet
- System Package MikrotikDocument4 pagesSystem Package MikrotikFarit Dwi SajiwoNo ratings yet
- Ips MulticastDocument6 pagesIps MulticastsjpfNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI ComandosDocument111 pagesHUAWEI ComandosJuan Carlos RubioNo ratings yet
- Queue Tree - QoS - Using Multiple Interfaces - MikrotikDocument13 pagesQueue Tree - QoS - Using Multiple Interfaces - MikrotikTony Cervantes0% (1)
- Mikrotik Enterprise Wireless Networks and CapsmanDocument51 pagesMikrotik Enterprise Wireless Networks and CapsmanNikos KolosNo ratings yet
- Comandos Esenciales - FORTINETDocument2 pagesComandos Esenciales - FORTINETLuis Gerardo MendozaNo ratings yet
- 7.6.1 Packet Tracer - WAN ConceptsDocument2 pages7.6.1 Packet Tracer - WAN ConceptsAlexisNo ratings yet
- 2V0 622Document88 pages2V0 622Hamza Aqqa100% (1)
- At Tshoot 642-832Document249 pagesAt Tshoot 642-832_asdffgNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.4.4 Implementing Quality of Service With Priority QueuingDocument4 pagesLab 1.4.4 Implementing Quality of Service With Priority QueuingAdamou Daouda MahamadouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic Ripng and Default Gateway ConfigurationDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic Ripng and Default Gateway ConfigurationSebastian Molina FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Exam - Ccnp-Tshoot Sp2016Document9 pagesChapter 10 Exam - Ccnp-Tshoot Sp2016Eddie8375% (16)
- CCNP SWITCH Chapter 1 To 7 TestsDocument38 pagesCCNP SWITCH Chapter 1 To 7 TestsJavier Morales100% (1)
- VOIP - Packet Tracer 6Document2 pagesVOIP - Packet Tracer 6Murash javaidNo ratings yet
- 9 IJAERS-SEP-2016-9-Analysis of Methodologies of Data Networks LAN PDFDocument10 pages9 IJAERS-SEP-2016-9-Analysis of Methodologies of Data Networks LAN PDFMaJosé Contento SegarraNo ratings yet
- HCIE Latest PDFDocument69 pagesHCIE Latest PDFhoussem100% (1)
- B Cisco Cmts SCG PDFDocument2,072 pagesB Cisco Cmts SCG PDFAmina FENo ratings yet
- Adva Netconf CallHomeDocument16 pagesAdva Netconf CallHomehowardchoiNo ratings yet
- Comandos IOS CiscoDocument25 pagesComandos IOS CiscoRodrigo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NAT and PATDocument5 pagesIntroduction To NAT and PATThọ Lương ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Vs IPv6Document19 pagesIPv4 Vs IPv6Sudhakar Ram Nawal MishraNo ratings yet
- 02 Network Reference ModelDocument41 pages02 Network Reference ModelnjimeliabdelNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS-XR - Deploy An IOS-XRv Appliance in GNS3 - Just Lab IT !!!!!Document7 pagesCisco IOS-XR - Deploy An IOS-XRv Appliance in GNS3 - Just Lab IT !!!!!Naz LunNo ratings yet
- Cisco APIC REST API Configuration Guide 42xDocument56 pagesCisco APIC REST API Configuration Guide 42xTrương Văn HuyNo ratings yet
- TR-069 1.4 Estandar Oficial Broadband FORUM PDFDocument276 pagesTR-069 1.4 Estandar Oficial Broadband FORUM PDFManolo Ferreira HerreraNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik - Part1Document154 pagesMikrotik - Part1ebilma2No ratings yet
- Linux QoS (Save)Document18 pagesLinux QoS (Save)JC JCNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik IPSec VPN FailOver ScriptDocument1 pageMikrotik IPSec VPN FailOver ScriptSarwar MurshedNo ratings yet
- LACP and DTDocument60 pagesLACP and DTWK OngNo ratings yet
- 640-802 CCNA Course OutlineDocument4 pages640-802 CCNA Course OutlineDavid LiuNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting - Layer 2 NetworkDocument40 pagesTroubleshooting - Layer 2 NetworkkmadNo ratings yet
- Meraki Datasheet MXDocument7 pagesMeraki Datasheet MXernestogon1983No ratings yet
- Examen 4 MikrtikDocument24 pagesExamen 4 MikrtikjorgeNo ratings yet
- Website: Vce To PDF Converter: Facebook: Twitter:: 300-535.vceplus - Premium.Exam.60QDocument35 pagesWebsite: Vce To PDF Converter: Facebook: Twitter:: 300-535.vceplus - Premium.Exam.60QAla JebnounNo ratings yet
- Configure Ap Aruba ConsoleDocument2 pagesConfigure Ap Aruba ConsoleKule MemphisNo ratings yet
- Lab 9.8.1 Managing Network Performance Using Content-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) and Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)Document7 pagesLab 9.8.1 Managing Network Performance Using Content-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) and Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)Kishore Reddy KandiNo ratings yet
- CCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Practice Final Exam Answers Full PDFDocument28 pagesCCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Practice Final Exam Answers Full PDFJoseph JesusNo ratings yet
- Saca IpDocument5 pagesSaca Ip1110113No ratings yet
- Ccnav7.02: Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Srwe) Release NotesDocument4 pagesCcnav7.02: Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Srwe) Release NotesWalid UmarNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik Ipv6Document6 pagesMikrotik Ipv6AfrilexxNo ratings yet
- Mtcna PDFDocument345 pagesMtcna PDFManit SonyNo ratings yet
- 25-1 HSRP Configuration - Lab ExerciseDocument3 pages25-1 HSRP Configuration - Lab ExerciseJasmoonNo ratings yet
- Fortinet ComandosDocument9 pagesFortinet ComandosJuan Jose Ortiz VegaNo ratings yet
- Aula Final - ExtraDocument2 pagesAula Final - Extracleitomanderson100% (1)
- Chapter2 - VirtualizationDocument12 pagesChapter2 - VirtualizationAfia Kamran100% (1)
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Final WrittenDocument41 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Final WrittenMaria De La O Pequeña58% (31)
- Resumen TR-069 y Diferencias SNMP PDFDocument26 pagesResumen TR-069 y Diferencias SNMP PDFManolo Ferreira HerreraNo ratings yet
- Vyatta - Install and UpgradeDocument21 pagesVyatta - Install and UpgradeLee WiscovitchNo ratings yet
- Cisco: Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSD)Document5 pagesCisco: Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSD)Mohammed AbdElwhab MadaniNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab2-2 EIGRP-Stub-Routing InstructorDocument12 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab2-2 EIGRP-Stub-Routing Instructorcrystian257100% (1)
- l3vpn Asr9000Document80 pagesl3vpn Asr9000kmadNo ratings yet
- VTP Server Configuration On Switch 1Document7 pagesVTP Server Configuration On Switch 1Manish SinghNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Routing Part IDocument14 pagesIpv6 Routing Part IAmit kumarNo ratings yet
- Ixia T DS IxNetwork Routing and SwitchingDocument27 pagesIxia T DS IxNetwork Routing and SwitchingThành Trung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic Ripng and Default Gateway ConfigurationDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic Ripng and Default Gateway ConfigurationLeinner RamirezNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNotes ERouting v4 0 1Document21 pagesReleaseNotes ERouting v4 0 1devilishaloNo ratings yet
- Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesLab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology Diagramchanda_banda272No ratings yet
- Assam MPBN Configuration - PB18-28th-Jan-2014Document497 pagesAssam MPBN Configuration - PB18-28th-Jan-2014Vinod BishtNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 9 6 2 InstructorDocument8 pagesE2 Lab 9 6 2 Instructordiverron100% (1)
- Alda Fitria A.P - P17410181002 - 3A - D3RMIK - Jaringan Komputer - Kelompok 1 - TM 7Document7 pagesAlda Fitria A.P - P17410181002 - 3A - D3RMIK - Jaringan Komputer - Kelompok 1 - TM 7Alda FitriaNo ratings yet
- Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 400-101 Exam Name: CCIE Routing and Switching Written ExamDocument378 pagesVendor: Cisco Exam Code: 400-101 Exam Name: CCIE Routing and Switching Written ExamTuPro Fessional100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Part 1 SRWE - Module - 15 IP Static RoutingDocument45 pagesChapter 1 Part 1 SRWE - Module - 15 IP Static RoutingLAN BIN CHENNo ratings yet
- Casa3200 SNMP ConfigDocument2 pagesCasa3200 SNMP ConfigHardIgenyNo ratings yet
- iS5Com Application Note VRRPDocument8 pagesiS5Com Application Note VRRPFrancisco Antonio Bolaño CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cup ADocument22 pagesCup ASammy CupaNo ratings yet
- RIP Routing FundamentalsDocument3 pagesRIP Routing FundamentalsKarlNo ratings yet
- 06 - HSDPA Call SetupDocument66 pages06 - HSDPA Call Setupneerajj.jainNo ratings yet
- Comp Network Assignment No. 2 Cpes 5523aDocument3 pagesComp Network Assignment No. 2 Cpes 5523aJigz Vasquez100% (1)
- 10.1.1.12 Packet Tracer - Determining The DR and BDR Instructions - ILMDocument3 pages10.1.1.12 Packet Tracer - Determining The DR and BDR Instructions - ILMSergio TejedorNo ratings yet
- CCNP Route-NotesDocument50 pagesCCNP Route-NotesMao BourichaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of DiffServ Based Q PDFDocument9 pagesPerformance Analysis of DiffServ Based Q PDFNiel DariusNo ratings yet
- Workflow Name Title Ticket Id Ticket StatusDocument39 pagesWorkflow Name Title Ticket Id Ticket StatusnazilaNo ratings yet
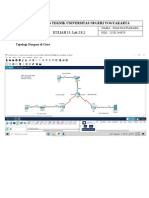
- Fakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta: KULIAH 13: Lab 2.8.2Document10 pagesFakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta: KULIAH 13: Lab 2.8.2029 Dias Djati AbabilNo ratings yet
- Mahmoud Reda Ibrahim - CV-6Document4 pagesMahmoud Reda Ibrahim - CV-6Rafiq MagdyNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocument15 pages2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routesbalvinder singh50% (6)
- Formation ICM: Pause DéjeunerDocument108 pagesFormation ICM: Pause DéjeunerMuhammad ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Scalable IP Lab Guide v2.0 - DownloadableDocument52 pagesAlcatel-Lucent Scalable IP Lab Guide v2.0 - DownloadableSavaşFurkanAkılevi100% (2)
- Chapter 6: EIGRP: Instructor MaterialsDocument71 pagesChapter 6: EIGRP: Instructor Materialshung ngueyn100% (1)
- NWV 303Document12 pagesNWV 303Nguyen An Ninh K15 HCMNo ratings yet
- Title Build Network Topology and Configure Static Routing in Network Topology. (CLO-4, PLO-9)Document4 pagesTitle Build Network Topology and Configure Static Routing in Network Topology. (CLO-4, PLO-9)Hadia RashidNo ratings yet
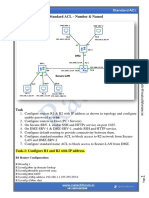
- CCNA 200-301 - Lab-16 ACL - Standard v1.0Document16 pagesCCNA 200-301 - Lab-16 ACL - Standard v1.0netgame76No ratings yet
- Lab Course "Routerlab": Ospf - Open Shortest Path First (RFC 2328)Document20 pagesLab Course "Routerlab": Ospf - Open Shortest Path First (RFC 2328)Bipin BaniNo ratings yet
- About Policy-Based RoutingDocument10 pagesAbout Policy-Based RoutingAvinashNo ratings yet
- Junos RoutingDocument9 pagesJunos RoutingsathyamoorthyNo ratings yet