Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 The Normal Eye
Uploaded by
Indranil GoswamiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 The Normal Eye
Uploaded by
Indranil GoswamiCopyright:
Available Formats
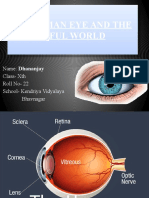
THE NORMAL EYE
EST
AUTHOR (s)
Brien Holden Vision Institute Faculty: Jane Kierath, Sonja Cronjé, Neilsen de Souza, Shoshana Jackofsky,
David Wilson, Mitasha Marolia, Gerd Schlenther, Naomi Freuden, Peter Mohlala Brien Holden Vision Institute,
Sydney, Australia
REVIEWER (s)
Bob Chappell Past President: World Council of Optometry (WCO)
THINK
Somebody in your community has a problem with a sore eyelid and asks you for help. How will you know what is
wrong if you don’t know what a normal eyelid should look like?
WHAT YOU WILL LEARN
When you have worked through this unit you should be able to:
Recognise a normal and healthy eye.
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-1
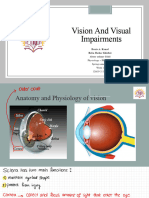
The Normal Eye
EYELIDS
To examine the eyelids you need to look at the skin of the eyelids and the lid margin.
Open and close properly
Look clean
– No white scales
– No pus
– No debris or crust
Look smooth
No lumps
No ulcers
Have lashes that turn away from the
eyeball
Do not look red, puffy or swollen Figure 1: The eyelids protect the eyes
Right and left upper lids are
symmetrical
No drooping lid.
NORMAL EYELIDS:
Figure 2: Eyelashes turning away from the
eyeball
Figure 3: This person’s right eye has a drooping eyelid
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-2
The Normal Eye
EYELID CONJUNCTIVA
Looks pink, not red
Is clear with a few small blood
vessels
Has no lumps or growths
Has no foreign bodies
(like sand or grit)
Has no pus.
NORMAL EYELID
CONJUNCTIVA:
Figure 4:
Palpebral conjunctiva of the upper eyelid
[photo courtesy of the Brien Holden Vision
Institute)
SCLERA AND BULBAR CONJUNCTIVA
To look at the sclera and bulbar conjunctiva:
– Gently hold the eyelids open using your thumb and first finger
– Use your thumb to hold the bottom eyelid against their cheek and your first finger to hold the upper eyelid
against the brow.
–
Should be clear and smooth
No lumps or growths
A HEALTHY Has no foreign bodies
BULBAR Allows a clear view of the white sclera
CONJUNCTIVA: Has only a few small blood vessels, no
red parts
No pus, watering or bleeding.
Figure 6: The bulbar conjunctiva and the
underlying sclera
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-3
The Normal Eye
CORNEA
Should be clear and smooth
No lumps or growths
A HEALTHY No scars
CORNEA: Has no foreign bodies
Allows a clear view of the iris
No blood vessels and no red parts
Figure 7: The cornea is transparent and lets
light into the eye
[Photo courtesy of the Brien Holden Vision
Institute]
PUPILS
Figure 8: The pupils are the black holes in the middle of the iris
Look at the size of both pupils
Look at the colour of both pupils
Shine a light into the person’s right eye
EXAMINING THE Both the right and left pupils should get smaller
PUPILS: Take the light away
Both the right and left pupils should get larger
Shine a light into the person’s left eye
Both the left and right pupils should get smaller
Take the light away
Both the left and right pupils should get larger.
Normal Pupils:
Are black, not grey or white
Are the same size
Are round
Get smaller when a light is shone into either eye
Get bigger when the light is taken away.
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-4
The Normal Eye
INTERNAL EYE EXAMINATION
The normal lens:
Is clear, not cloudy or
discoloured
Has no dark areas in the
HEALTHY fundus reflex
CRYSTALLINE Is located behind the iris,
LENS: not in the anterior chamber.
Figure 9: The clear crystalline lens is behind the iris
The normal vitreous
chamber:
Is clear
Contains no blood (which
could be a haemorrhage in
the vitreous)
Has no new blood vessels
NORMAL Contains no dark spots or
VITREOUS shapes.
CHAMBER:
Vitreous chamber containing vitreous
Figure 10: Vitreous chamber and vitreous
A normal retina:
Should be one solid shade Figure 11: A normal retina with no haemorrhages or leaky
of red blood vessels. [photo courtesy of Pak Sang Lee:
International Centre for Eye Health]
Has blood vessels that are
intact and not leaking
Shows no signs of blood
haemorrhages (dot, blot,
flame)
HEALTHY Has no areas of
RETINA: discolouration (yellow-white
patches)
Contains no new blood
vessels
(neovascularisation)
Shows no signs of rips or
tears or detachment
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-5
The Normal Eye
A normal macula:
Is clear and flat
Has no blood leakage
(haemorrhages)
Has no new blood vessels
(neovascularisation)
Shows no areas of
discolouration (green,
yellow and/or white)
Has no holes or tears
HEALTHY
MACULA: Might show a foveal reflex
in young people
macula
Figure 12:
The macula is located temporal to the optic disc
[photo courtesy of Pak Sang Lee: International Centre for
Eye Health]
A normal optic nerve head:
Is round
Is flat, not swollen or
elevated
Has no new blood vessels
(neovascularisation)
NORMAL OPTIC Has a cup:disc ratio (CD
NERVE: ratio) of no larger than 0.5
Is pink, not pale in colour
Has well defined edges
(no swollen disc)
No haemorrhages
Figure 13: The optic nerve
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-6
The Normal Eye
TEST YOURSELF QUESTIONS
1. How should you examine the eyelid conjunctiva?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
2. What should a healthy cornea look like?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
3. You shine a light into somebody’s right pupil. What should happen to the left pupil?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
light
4. What should you be looking for when examining the macula?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
5. When looking at the macula of a 10-year-old girl, you notice a bright reflex shining back at you.
What is this reflex, and is it normal?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
6. What does a healthy optic nerve look like?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
June 2012, Version 1-1 The Normal Eye, Chapter 3-7
You might also like
- Assessing The EyesDocument61 pagesAssessing The EyessrslytrdNo ratings yet
- 02 Introduction To The EyeDocument12 pages02 Introduction To The EyeMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument4 pagesNursingAndrea Jewel BaladjayNo ratings yet
- 08 Low VisionDocument8 pages08 Low VisionMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Unit IV B. Physical AssessmentDocument116 pagesUnit IV B. Physical AssessmentJules Lorenz AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument72 pagesHuman EyeDhananjayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The EyeDocument18 pagesIntroduction To The EyeJúnior Alves100% (1)
- Topic-The Human Eye: Submitted To. Submitted BYDocument10 pagesTopic-The Human Eye: Submitted To. Submitted BYsanju kumarNo ratings yet
- Corneal Edema CasesDocument9 pagesCorneal Edema CasesKinshuk DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Sense Organs NotesDocument26 pagesICSE Class X Sense Organs Notesprogrammer.ron.akNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment in Tabular Form: HEAD AND NECK: Integumentary SkinDocument13 pagesNursing Assessment in Tabular Form: HEAD AND NECK: Integumentary SkinDerick MacedaNo ratings yet
- Biology Task - The Functionality of Eyes - ScriptDocument4 pagesBiology Task - The Functionality of Eyes - ScriptMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Normal Range of FindingsDocument5 pagesNormal Range of FindingsSafitriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Assessment of The EyesDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Assessment of The Eyesmeena jeerhNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointKemoy Francis100% (1)
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointfathul rahmanNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Notes External Layer: Cornea, ScleraDocument12 pagesSpecial Senses Notes External Layer: Cornea, ScleraJOHN CARL GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Eye PPT 01Document21 pagesEye PPT 01zzzNo ratings yet
- Cataract White ArmyDocument16 pagesCataract White Armyamraayman21No ratings yet
- Visual ImpairmentDocument2 pagesVisual ImpairmentMa Cecilia TransfiguracionNo ratings yet
- Marie Belen C. Tamayor, RNDocument42 pagesMarie Belen C. Tamayor, RNrein_seanNo ratings yet
- S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - LightDocument3 pagesS - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - LightVector HuntNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Assessment of The EyeDocument7 pagesWeek 7 - Assessment of The EyeBLOCK 20 - EULER PABILLONo ratings yet
- Do My Eyes Work Together?: Click HereDocument9 pagesDo My Eyes Work Together?: Click HereJuanita MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 2Document31 pagesLab 1 2Noor FarhanNo ratings yet
- Alecha Case StudyDocument5 pagesAlecha Case StudyEiah Janine AlechaNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument22 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- General Survey and Integumentary I. General Appearance and Mental Status Normal Findings Actual Findings Analysis and InterpretationDocument9 pagesGeneral Survey and Integumentary I. General Appearance and Mental Status Normal Findings Actual Findings Analysis and InterpretationAllana RayosNo ratings yet
- How Can My Eyes See? Sight and the Eye - Biology 1st Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Can My Eyes See? Sight and the Eye - Biology 1st Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- VisionDocument8 pagesVisionapi-367611011No ratings yet
- Ch16 Notes eDocument5 pagesCh16 Notes eJulius CruelNo ratings yet
- Hand WashingDocument7 pagesHand Washinghans leeNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointfatimaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation CataractDocument19 pagesCase Presentation CataractRani GhereNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument8 pagesThe Eyezyrine jhen100% (1)
- External Eye Lacrimal MeatusDocument20 pagesExternal Eye Lacrimal MeatusLyanne SuelloNo ratings yet
- Eye and Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesEye and Colourful WorldutsavpihuNo ratings yet
- Learning Material Topic 7 Eyes and Ears AssessmentDocument4 pagesLearning Material Topic 7 Eyes and Ears AssessmentDevi NurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument22 pagesHuman EyeMary Grace BobaresNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointEmerito PerezNo ratings yet
- ItbrochureDocument3 pagesItbrochureapi-303099896No ratings yet
- Assessing of The Eyes and VisionDocument83 pagesAssessing of The Eyes and VisionZoey FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 07 Crossed Eyes Nystagmus and AmblyopiaDocument7 pages07 Crossed Eyes Nystagmus and AmblyopiaMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- A Report By: Keanu Carig Mark Lenard Taysa Jhaneth Fassong Renz Arielle Pangilinan BSHRM Haa1Document19 pagesA Report By: Keanu Carig Mark Lenard Taysa Jhaneth Fassong Renz Arielle Pangilinan BSHRM Haa1Renz PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Jacob Israel Liberman's Take Off Your Glasses and SeeFrom EverandSummary of Jacob Israel Liberman's Take Off Your Glasses and SeeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Instruction: Check Under Correctly Done If Identified Skill Is Correctly Performed Incorrectly Done If Skill IsDocument12 pagesInstruction: Check Under Correctly Done If Identified Skill Is Correctly Performed Incorrectly Done If Skill IsSIR ONENo ratings yet
- Coweye PDFDocument8 pagesCoweye PDFKatamoNo ratings yet
- SP 23 Unit 2.4 PortfolioDocument13 pagesSP 23 Unit 2.4 PortfolioAnahi ByersNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Visual ImpairmentDocument61 pagesModule 4 Visual ImpairmentMina Agarwal100% (5)
- How We SeeDocument36 pagesHow We SeeAbishaTeslinNo ratings yet
- Ha Semi FinalsDocument16 pagesHa Semi FinalsHielal DumpNo ratings yet
- Eye PDFDocument11 pagesEye PDFManas kumarNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear - 2019Document3 pagesEye and Ear - 2019Mr. RWord100% (1)
- Derma OLUWOLE OLUMODEJIDocument13 pagesDerma OLUWOLE OLUMODEJIbrightagbotuiNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Nursing Chapter 11: EyesDocument3 pagesHealth Assessment Nursing Chapter 11: EyesRobin OommenNo ratings yet
- HairDocument4 pagesHairwisteria_No ratings yet
- Nursing Head-to-Toe Assessment Cheat Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesNursing Head-to-Toe Assessment Cheat Sheet PDFJoebert BangsoyNo ratings yet
- Subconjunctival Hemorrhage: AuthorsDocument8 pagesSubconjunctival Hemorrhage: AuthorsSatrya DitaNo ratings yet
- Logbook New 1Document61 pagesLogbook New 1Shantanu SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic RecordDocument7 pagesOphthalmic RecordandrirombeNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Lectures PDFDocument88 pagesOphthalmology Lectures PDFsharenNo ratings yet
- Complete Head-To-Toe Physical Assessment Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesComplete Head-To-Toe Physical Assessment Cheat SheetjthsNo ratings yet
- Cebu Doctors' University College of Nursing: Module 1F: Group WorksheetDocument55 pagesCebu Doctors' University College of Nursing: Module 1F: Group WorksheetPhilip Anthony FernandezNo ratings yet
- 300 MCQs For The Duke Elder Ophthalmology Exam 21Document173 pages300 MCQs For The Duke Elder Ophthalmology Exam 21Afaf ZayedNo ratings yet
- Gordon's HisDocument4 pagesGordon's HisJee ShangNo ratings yet
- Histology of The EyeDocument48 pagesHistology of The Eyetemesgen belayNo ratings yet
- ML Atlas Del FBIDocument227 pagesML Atlas Del FBIIon Spataru100% (1)
- Opthalmology NotesDocument43 pagesOpthalmology NotesKashif Khan100% (2)
- Daftar Pustaka Paper Oftalmia Neonatorum (Sudah Digabung) PDFDocument153 pagesDaftar Pustaka Paper Oftalmia Neonatorum (Sudah Digabung) PDFDewi Sartika100% (1)
- Concretions (Conjunctival Lithiasis) FINALDocument3 pagesConcretions (Conjunctival Lithiasis) FINALRobby RolandaNo ratings yet
- History Taking: Practical 1 InstructionDocument12 pagesHistory Taking: Practical 1 InstructionDimsyafelNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument24 pagesPhysical AssessmentKathleen Felipe DantesNo ratings yet
- 1.conjunctiva and ConjunctivitisDocument77 pages1.conjunctiva and ConjunctivitisPreeti PatelNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.DDocument78 pagesPathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.Drush73No ratings yet
- Chemical Injuries of The EyeDocument11 pagesChemical Injuries of The EyeMeghana PatilNo ratings yet
- ConjungtivitaDocument85 pagesConjungtivitaFatrisNo ratings yet
- Follicular Conjunctivitis in Dogs: A Retrospective Study (2007-2022)Document8 pagesFollicular Conjunctivitis in Dogs: A Retrospective Study (2007-2022)Akın SeverNo ratings yet
- Ijo 67 1930Document19 pagesIjo 67 1930faraamirNo ratings yet
- External Disease and CorneaDocument105 pagesExternal Disease and CorneaNova CiNg CiNgNo ratings yet
- ROLE OF EYE - A CRUCIAL PATH IN HUMAN LIFE Divya Jonnala, D. Navya, D. Eswar TonyDocument4 pagesROLE OF EYE - A CRUCIAL PATH IN HUMAN LIFE Divya Jonnala, D. Navya, D. Eswar TonyiajpsNo ratings yet
- Red Eye, Conjuctivitis, Vision LossDocument213 pagesRed Eye, Conjuctivitis, Vision LossShashi Royal TNNo ratings yet
- Limbal: Palisades of VogtDocument17 pagesLimbal: Palisades of VogtJosé Eduardo Zaragoza LópezNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Mucosae and Mechanism of Transmucosal PermeationDocument48 pagesPhysiology of Mucosae and Mechanism of Transmucosal PermeationArpita Patel100% (1)
- Assessment of The EyesDocument9 pagesAssessment of The Eyesmarkkkkkkkheeess100% (3)