Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mlpa Poster Final
Uploaded by
api-4484830100 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageOriginal Title
mlpa poster final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageMlpa Poster Final
Uploaded by
api-448483010Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
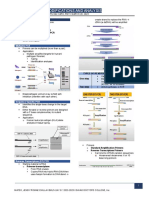
Using Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification to
Determine the Expression of Androgen Receptor Variants
Ruoheng Zeng, Yezi Zhu, Jun Luo, Changxue Lu
Brady Urological Institute, Johns Hopkins Medical Institute
Introduction Methods Gel Electrophoresis Results Conclusion
The androgen receptor is a nuclear receptor unique to mRNA Preparation: • Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification is
prostate cells that activate upon binding to androgenic 1. Extract mRNA from test group cell lines: LNCaP, effective in determining the differentiated
hormones such as testosterone. The transcription of LNCaP95, CWR22Rv1, HeLa, DU145, and PC3. The expression levels of the AR splice variants.
the androgen receptor gene results in a diverse group former three serves as AR positive test group, while • MLPA data for cDNA from prostate cell lines with
of splice variants known as androgen receptor splice the latter three serve as the AR negative test group. known expression levels correlate well with
variants. Abnormally high expression of specific Control for density between test groups through expected expression levels. All the AR positive cell
androgen receptor (AR) splice variants in prostate dilutions. lines (LNCaP, LNCaP95, and CWR22Rv1) show high
cells has been linked to the development of higher 2. Perform reverse transcription on mRNA to make levels of expression for full length AR and
grade castration resistant prostate cancer. As a result, cDNA. significant expression of AR-V9 and AR-V12
measuring the expression of these AR splice variants • Additionally, as compared to LNCap, a cell line
is often used for the diagnosis and prognosis of known for its lack of AR-V7 expression, AR-V7
Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification
prostate cancer. expression LNCaP95 and CWR22Rv1 expression
1. Oligonucleotide probes, consisting of two fragment for AR-V7.
Objectives pairs, are hybridized with the target nucleic acid • MLPA data for probes directed-bound to mRNA
segments in the samples. were less consistent across the board. From
This experiment seeks to use the procedure of 2. Pairs of successfully hybridized fragments are capillary electrophoresis analysis, there were clear
Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification ligated together with enzyme solution. Capillary Electrophoresis Results peaks indicating the presence of the expected
(MLPA) to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness 3. Successfully ligated fragment are amplified through junctions, but there were also many non-specific
of non-invasive methods for detecting prostate PCR, and are collected as final MLPA products. peaks likely due to error.
cancers in patients. Specifically, the goals are to: • The presence of background noise is likely caused
Data Analysis by non-specific bindings in the probes during the
• Design custom oligonucleotide probes which bind hybridization process. This was especially likely for
to the specific exon-exon junctions unique to each 1. Final MLPA products are analyzed using gel mRNA binding, due to the flimsy compatibility of
AR splice variant. electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis. the necessary ligase with the rest of the MLPA kit
• Utilize gel electrophoresis and capillary 2. Gel electrophoresis confirms the presence of
successfully ligated and amplified products, but
electrophoresis to analyze post-PCR products in Graph 1. Expression of CWR22Rv1 Future Direction
order to determine expression levels of each AR doesn’t allow for discrimination between the
splice variant. expression of different AR variants. • The future of this study will largely focus on
• Compare the experimentally determined expression 3. Capillary electrophoresis is done on the same MLPA increasing the precision and accuracy of direct-
level of AR splice variants in prostate cell line cDNA products to quantify the expression levels of each binding oligonucleotide probes to mRNA rather
to manufactured AR splice variant plasmid. AR variant in each sample relative to a control. than cDNA.
• Reconstruct the experiment to test the viability of • There are many advantages to direct-binding to
direct-binding custom oligonucleotide probes to Follow up experiment: mRNA, the main ones being a result of bypassing
mRNA rather than cDNA Cell line cDNA is replaced with raw mRNA, testing the reverse transcription, which leads to increases in
viability of the MLPA probes direct binding. Enzyme efficiency and decreases in cost of the experiment.
Probe Design solutions used in the MLPA, as well as incubation Graph 2. Expression of LNCaP95 • The future of MLPA lies in its efficiency and
times, are modified to allow direct binding of mRNA. simplicity as compared to alternative methods of
Oligonucleotides Probe Design: determining gene expression.
• Probes must be constructed within the parameters
provided by MRC-Holland, the company providing References
the MLPA kits.
• Probes were made to bind to exon-exon junctions Lu CX, Luo J. Decoding the androgen receptor
unique to each AR splice variant. For instance, a splice variants. Translational andrology and
probe was constructed to bind to the exon 7 to exon urology. 2013. [PubMed: 25356377]
8 junction, a junction unique to the full length AR, in Graph 3. Expression of LNCaP
order to detect the presence of full length AR. MRC-Holland MLPA. (n.d.). Retrieved February 19,
• Similarly, the exon 3 to cryptic exon 3 junction is 2019, from MRC-Holland website:
used to detect AR-V7, the exon 3 to cryptic exon 5 https://www.mlpa.com/
junction to detect AR-V9, and the exon 4 to exon 8
junction to detect AR-V12. The exon 1 to exon 2 Sharp, A., & Coleman, I. (n.d.). Androgen receptor
junction exists in all AR splice variants and is used splice variant-7 expression emerges with
as a control. castration resistance in prostate cancer. Journal of
Clinical Investigation. https://doi.org/
10.1172/JCI122819
Acknowledgement
This work was made possible by the primary
investigator Dr. Jun Luo and post-doc fellow Dr. Yezi
Zhu. Additionally, it is supported by the Brady
Graph 4. Expression of AR splice variants in Urological Institute at Johns Hopkins Hospital.
LNCaP95 and CWR22Rv1 normalized to LNCaP
POSTER TEMPLATE BY:
www.PosterPresentations.com
You might also like
- Research Plan SummaryDocument3 pagesResearch Plan Summaryapi-448483010No ratings yet
- Expression ProfilingDocument8 pagesExpression ProfilingSreedurgalakshmi KNo ratings yet
- 4B-Molecular MarkerDocument67 pages4B-Molecular MarkerSharvind Kumar Sharvind KumarNo ratings yet
- A CRISPR Way To Diagnose Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesA CRISPR Way To Diagnose Infectious DiseasesGabriela ArvelaezNo ratings yet
- RFLP & RapdDocument25 pagesRFLP & RapdBalaji Prasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap PracticalDocument28 pagesChap PracticalNL DearestNo ratings yet
- Aug. 31 - Sept. 4, 2014Document49 pagesAug. 31 - Sept. 4, 2014giapvanthuNo ratings yet
- 1 Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques and Their Use in BioanalysisDocument20 pages1 Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques and Their Use in BioanalysisKonstantinNo ratings yet
- Ligation Chain ReactionDocument3 pagesLigation Chain Reactionamaya rajivNo ratings yet
- MOLBIO LAB 3.2 PCR Modifications and Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesMOLBIO LAB 3.2 PCR Modifications and Analysis PDFTy TriciaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Marker:: Quality For A Good Genetic MarkerDocument5 pagesMolecular Marker:: Quality For A Good Genetic MarkerRakesh GedalaNo ratings yet
- RNA Sequencing: An Introduction To Efficient Planning and Execution of RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) ExperimentsDocument6 pagesRNA Sequencing: An Introduction To Efficient Planning and Execution of RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) ExperimentsnareshNo ratings yet
- Cald Poster 2019Document1 pageCald Poster 2019api-299489212No ratings yet
- Human Transcriptom E: by Dr. Ina GargDocument60 pagesHuman Transcriptom E: by Dr. Ina GargIna GargNo ratings yet
- Archer Fusionplex Ngs Assays BrochureDocument4 pagesArcher Fusionplex Ngs Assays Brochurealivio141960No ratings yet
- OK 2014 - Latini - snApSHOT para Grupos SanguineosDocument8 pagesOK 2014 - Latini - snApSHOT para Grupos SanguineosGuilherme VettorazziNo ratings yet
- Cloning StrategiesDocument35 pagesCloning Strategiesskmishra8467% (3)
- Continuous Assessment: Concentration's Increment in Case of Insert and LigaseDocument8 pagesContinuous Assessment: Concentration's Increment in Case of Insert and LigaseDebapriya HazraNo ratings yet
- Quantitation by The Polymerase Chain: of mRNA ReactionDocument6 pagesQuantitation by The Polymerase Chain: of mRNA ReactionHijrawati IrhaeNo ratings yet
- The RT-PCR Test For Covid-19Document14 pagesThe RT-PCR Test For Covid-19Abhrajit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Rna Sequencing Methods Review WebDocument122 pagesRna Sequencing Methods Review WebSenseiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular MarkersDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Molecular MarkersSama MouradNo ratings yet
- Bacterial DetectionDocument7 pagesBacterial DetectionSulaiman AlmajeediNo ratings yet
- AN - RNAscope On LabSat ResearchDocument4 pagesAN - RNAscope On LabSat Researchalexandre larmagnacNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: Lecture By: Yepy Hardi RDocument17 pagesQuantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: Lecture By: Yepy Hardi RTriaKarinaNo ratings yet
- Aflp-Pcr:: Steps: 1.DNA ExtractionDocument3 pagesAflp-Pcr:: Steps: 1.DNA ExtractionArsalan Abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- ArunDocument22 pagesArunB M ARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Revision Tut 3 Block 1Document11 pagesRevision Tut 3 Block 1Matsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- In-Cell Identification and Measurement of RNA-protein InteractionsDocument11 pagesIn-Cell Identification and Measurement of RNA-protein InteractionsHana PejšováNo ratings yet
- Vermeulen Et Al Rna Quality Nar 2011Document12 pagesVermeulen Et Al Rna Quality Nar 2011CeciliaPistolNo ratings yet
- Eberwine 2002Document13 pagesEberwine 2002Michelle Marjorie Rodríguez LauraNo ratings yet
- CLC Genetics Chapter 3Document51 pagesCLC Genetics Chapter 3Châu Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Corona VirusDocument6 pagesCorona VirusCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaNo ratings yet
- Dna Polymorphism and Human IdentificationDocument5 pagesDna Polymorphism and Human Identificationmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Slides Week 10 Classes35-38 Bio200 Win16 1Document44 pagesSlides Week 10 Classes35-38 Bio200 Win16 1api-272470922No ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document67 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Derick SemNo ratings yet
- Scholars: Principles and Procedures of The Northern Blot TechniqueDocument6 pagesScholars: Principles and Procedures of The Northern Blot TechniqueWONDWESEN MITIKUNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNA Function in Development and DiseaseDocument19 pagesMechanisms of Long Noncoding RNA Function in Development and DiseaseManuel HernándezNo ratings yet
- Molecular Markers and Their Characteristics M. R. Meena, M.L. Chhabra, Ravinder Kumar and C. M. MeenaDocument5 pagesMolecular Markers and Their Characteristics M. R. Meena, M.L. Chhabra, Ravinder Kumar and C. M. Meenamintu_uasNo ratings yet
- Genome Res.-1991-Golay-144-5Document3 pagesGenome Res.-1991-Golay-144-5Omeyya TanveerNo ratings yet
- PCR Types and Its ApplicationsDocument68 pagesPCR Types and Its ApplicationsShefali Pawar100% (1)
- Nature 23 Complementary Alu Sequences Mediate Enhancer-Promoter SelectivityDocument32 pagesNature 23 Complementary Alu Sequences Mediate Enhancer-Promoter Selectivitylandau1994No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledALLISON PAMITTANNo ratings yet
- Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNADocument7 pagesLoop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNAChristian Moises CasasNo ratings yet
- Sequencing of BivalentDocument22 pagesSequencing of BivalentDiverneetic Herramientas EducativasNo ratings yet
- DNA LibrariesDocument37 pagesDNA LibrariesMansoor KhalidNo ratings yet
- Brock 06bDocument21 pagesBrock 06bsbdurmanNo ratings yet
- 2017 - RNAseq - Methods For Transcriptome AnalysisDocument17 pages2017 - RNAseq - Methods For Transcriptome AnalysisAntarToumaNo ratings yet
- Molecular MarkerDocument26 pagesMolecular MarkershivamNo ratings yet
- Basic Molecular BiologyDocument10 pagesBasic Molecular BiologyPaolaNo ratings yet
- Rna Isolation and PurificationDocument62 pagesRna Isolation and PurificationBio BookNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction Test Interpretation: Julia PaxsonDocument8 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction Test Interpretation: Julia PaxsonDana MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Spatial Imaging of Glycorna in Single Cells With Arpla: Nature BiotechnologyDocument26 pagesSpatial Imaging of Glycorna in Single Cells With Arpla: Nature Biotechnology郑子豪No ratings yet
- Molecular MarkersDocument4 pagesMolecular MarkersKai RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Final Seminar AmplificDocument60 pagesFinal Seminar AmplificBhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- SNP Discovery and Allele Frequency Estimation by Deep Sequencing of Reduced Representation LibrariesDocument6 pagesSNP Discovery and Allele Frequency Estimation by Deep Sequencing of Reduced Representation LibrariesDhamodaran KannanNo ratings yet
- Target Amplification Methods StudentsDocument16 pagesTarget Amplification Methods StudentsCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaNo ratings yet
- Factor V Liden ImportmantDocument6 pagesFactor V Liden Importmantnbiolab6659No ratings yet
- DNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensFrom EverandDNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensNo ratings yet
- High-Resolution Electrophoresis and Immunofixation: Techniques and InterpretationFrom EverandHigh-Resolution Electrophoresis and Immunofixation: Techniques and InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology 4th Edition 2000Document12 pagesMolecular Cell Biology 4th Edition 2000César FloresNo ratings yet
- The Truth About DnaDocument28 pagesThe Truth About DnaAlonzo Renard-El100% (2)
- From Gene To Protein: Lecture OutlineDocument15 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: Lecture OutlineEiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Science - Report 9Document2 pagesScience - Report 9Borgy DcmcNo ratings yet
- XyzDocument8 pagesXyzrympeikhasiNo ratings yet
- Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesBiology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manualaureliacharmaine7pxw9100% (22)
- Preventest Training PowerpointDocument49 pagesPreventest Training Powerpointapi-256933207No ratings yet
- Yr 10 Evolution BookletDocument40 pagesYr 10 Evolution Bookletstevenyin123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Gene CLONINGDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Gene CLONINGMuhammad Shafiqullah AsadiNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 06-07englishDocument277 pagesAnnual Report 06-07englisharvindftNo ratings yet
- Primer3 Output (Primer3 - Resghults - Cgi Release 4.1.0)Document2 pagesPrimer3 Output (Primer3 - Resghults - Cgi Release 4.1.0)SafeerNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 pagesNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezNo ratings yet
- DNA WorksheetDocument5 pagesDNA Worksheetmaha1986No ratings yet
- Baric INVISIBLE Gene Editing Method For His SARS-CoV-2 JVI.76.21.11065-11078.2002Document14 pagesBaric INVISIBLE Gene Editing Method For His SARS-CoV-2 JVI.76.21.11065-11078.2002Kevin SteinerNo ratings yet
- Bio Modul U6 2010-3Document66 pagesBio Modul U6 2010-3Thuran Nathan100% (1)
- Q1M5Document29 pagesQ1M5Jesus GombaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Evo BioDocument8 pagesReviewer in Evo BioMichaela ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Manuscript - Editing The Genome of CropsDocument20 pagesManuscript - Editing The Genome of CropsNiharika DasNo ratings yet
- Progress of Oil Palm Breeding For Novel Traits Late Abscission Virescence and Long Bunch StalkDocument11 pagesProgress of Oil Palm Breeding For Novel Traits Late Abscission Virescence and Long Bunch StalkHari PriNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and GeneticsDocument144 pagesCell Biology and GeneticsReka Kutasi100% (1)
- Gmo G-10Document6 pagesGmo G-10HAIDEE VASQUEZNo ratings yet
- Principles of Biology 1592953983Document926 pagesPrinciples of Biology 1592953983Abdulfatai LanreNo ratings yet
- NCBI Blast - AF028688 - NR - 028242.1 PDFDocument3 pagesNCBI Blast - AF028688 - NR - 028242.1 PDFmino loliNo ratings yet
- Test Series For Neet-2020Document10 pagesTest Series For Neet-2020kavyareddy100% (1)
- Bioinformatics: Blast and Sequence AnalysisDocument45 pagesBioinformatics: Blast and Sequence AnalysisSalix MattNo ratings yet
- Molecular Regulation and SignalingDocument45 pagesMolecular Regulation and SignalingJovie Esquivias NicolasNo ratings yet
- Karolin Luger - Nucleosomes: Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesKarolin Luger - Nucleosomes: Structure and FunctionDopameNo ratings yet
- Cell NucleusDocument4 pagesCell NucleusrajikrajanNo ratings yet
- BaldnessDocument3 pagesBaldnessMarta Sánchez ReinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Agricultural ScienceDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Agricultural ScienceMichael EsmallaNo ratings yet