Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng) PDF
Cold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng) PDF
Uploaded by
maik angeloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng) PDF
Cold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng) PDF
Uploaded by
maik angeloCopyright:
Available Formats
Cold bending DIN 6935
of flat steel products
30 April 2018 15:57
General
This method of calculation applies to bent parts of flat steel products for use
in steel construction and in general mechanical engineering.
When bending flat rolled steel, such as sheets, strips, wide flat steels, etc. is considered
to take the rolling direction, because of better suitability for bending as possible transverse to the
rolling direction
to be bent.
Bending radius
r bending radius
a bending angle
b opening angle
The bending angle a can be between 0 ° and 180 °.
The Thickness is in the rounding up about 20% lower.
To achieve uniform curves on bending rails, it is recommended that only bending radius be
used for bending
to choose from the following series. The bold values are to be preferred.
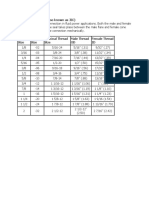
Table 1 gives the smallest permissible bending radius, which at certain sheet thicknesses
and
Materials for the applicable bending machines can be selected. The specified values
apply to bending angle a £ 120 °. For bending angles a> 120 ° insert the next higher table
value,
e.g. would be when bending transverse to the rolling direction of sheets of QSt 42-2 with
the thickness s = 6
mm the smallest permissible bending radius r = 10 mm for a £ 120 ° and r = 12 mm for a
<120 °.
Table 1: Smallest allowable bending radius r
Calculation of the stretched lengths
DIN 6935 Cold bending Page 1
Elongated length = a + b + u. Depending on the value of the bending angle, u is different and
represents one
Compensation value that is negative or positive at opening angle b from 0 ° to 65 ° (exact
value 65 ° 24'30 ")
and at opening angles over 65 ° can only be negative.
Stretched lengths should be rounded to the nearest millimeter.
Opening angle b 0 ° to 90 °: Compensation value u:
Opening angle b> 90 ° to 165 °: Compensation value u:
Opening angle b> 165 ° to 180 °: Compensation value u = 0 The values for u are negligibly small, the
Accuracy is sufficient for the practice.
K Factor
Correction factor k for determining the cutting lengths of bent workpieces
The correction factor k indicates the deviation of the position of the neutral fiber s / 2 and is
calculated
DIN 6935 Cold bending Page 2
For r: s> 5 the equation is no longer valid, then k = 1 has to be set.
example
Material: Q St 37-2 (steel grade up to 390 N / mm² tensile strength)
Completion:
Sum of leg lengths 50 + 170 + 256 + 50 = 516
For b = 90 °, r = 20, s = 12, u = - 25.41
for b = 45 °, r = 20, s = 12, u = - 6,12
for b = 135 °, r = 20, s = 12, u = - 7.25
- 38.78
Total leg length 516.00
- Sum of compensation values - 38.78
stretched length 477.22
»478
DIN 6935 Cold bending Page 3
You might also like
- Welding Rod CalculationDocument4 pagesWelding Rod CalculationuemaaplNo ratings yet
- EE5518 VLSI Digital Circuit Design VLSI Digital Circuit DesignDocument39 pagesEE5518 VLSI Digital Circuit Design VLSI Digital Circuit DesignBharat Kumar100% (1)
- 6935 2011Document13 pages6935 2011Tufan Ünal100% (4)
- BS ISO 8015 - 1985 - Technical Drawings - Fundamental Tolerancing PrincipleDocument12 pagesBS ISO 8015 - 1985 - Technical Drawings - Fundamental Tolerancing PrincipledarlanschulzNo ratings yet
- Asme B4.1-1967 (2009)Document28 pagesAsme B4.1-1967 (2009)vijay pawar100% (3)
- BS-919-2-2007-diş Mastar Toleransları PDFDocument42 pagesBS-919-2-2007-diş Mastar Toleransları PDFalifuat duyguNo ratings yet
- Pastor S HandbookDocument183 pagesPastor S HandbookLarry SheltonNo ratings yet
- Sae J514 37Document1 pageSae J514 37deepakg9No ratings yet
- Pipe Bend RadiusDocument8 pagesPipe Bend RadiusAdagharaNo ratings yet
- St52 Material STD PDFDocument7 pagesSt52 Material STD PDFsardhan.rajender84No ratings yet
- Bend Allowance CalculatorDocument1 pageBend Allowance CalculatorMurtza Arzai100% (1)
- DIN 6930-2 Stamped Steel Parts Part 2 General TolerancesDocument17 pagesDIN 6930-2 Stamped Steel Parts Part 2 General TolerancespopoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad in Mechanical EngineeringDocument16 pagesMathcad in Mechanical Engineeringgato7777777100% (2)
- Studies in IbadhismDocument226 pagesStudies in IbadhismBADAR MOHAMMED100% (2)
- M&I 05-GeometricalTolerancing2017 v01Document20 pagesM&I 05-GeometricalTolerancing2017 v01Akash100% (1)
- Involute Spline and Serration Gages and Gaging: SupersededDocument21 pagesInvolute Spline and Serration Gages and Gaging: Supersededvijay pawarNo ratings yet
- Din 17100Document19 pagesDin 17100X100% (1)
- Cold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng)Document4 pagesCold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng)maik angelo0% (2)
- Gearing AgmaDocument17 pagesGearing AgmaDomingos AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Group Project: Gabungan Aqrs Vs Crest Builder HoldingsDocument43 pagesGroup Project: Gabungan Aqrs Vs Crest Builder HoldingsNURUL SYAFIQAH MOHD IDRISNo ratings yet
- Din 7168 enDocument7 pagesDin 7168 enjose zamoraNo ratings yet
- Din 8140-1Document5 pagesDin 8140-1main46prairieNo ratings yet
- DIN 261 T-Head BoltsDocument14 pagesDIN 261 T-Head BoltsSamira Mns100% (1)
- Din76 2 84Document3 pagesDin76 2 84Luis TestaNo ratings yet
- Din 76-1Document5 pagesDin 76-1mesa142No ratings yet
- Esbm5a-B 1n261-s Aa RSWDocument37 pagesEsbm5a-B 1n261-s Aa RSWChandrajeet Shelke50% (2)
- Din 5463Document4 pagesDin 5463Joel Sousa100% (1)
- Din 8140-1 PDFDocument13 pagesDin 8140-1 PDFOSCAR VALENCIANo ratings yet
- Ring Joint RTJDocument6 pagesRing Joint RTJzulikram100% (1)
- Aisi 8620 Steel - 1.6523 - 21nicrmo2 - Sncm220Document3 pagesAisi 8620 Steel - 1.6523 - 21nicrmo2 - Sncm220duhkacttusNo ratings yet
- Din 7168Document1 pageDin 7168Anderson SantosNo ratings yet
- GD&T Versus Geometrical Product Spec PDFDocument14 pagesGD&T Versus Geometrical Product Spec PDFHusen Taufiq100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsKim Cristian MaañoNo ratings yet
- Din 6930-2Document1 pageDin 6930-2murniNo ratings yet
- WPSASMEDocument76 pagesWPSASMERama TamaNo ratings yet
- Mannesman - Reservorios HidraulicosDocument4 pagesMannesman - Reservorios HidraulicosBilly Zunun100% (1)
- Electrical: Installation CalculationsDocument23 pagesElectrical: Installation CalculationsSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis Proposal ,...Document46 pagesFinal Thesis Proposal ,...louiedespiNo ratings yet
- BS-200&220&330&350 - Service Manual - V8.0 - ENDocument137 pagesBS-200&220&330&350 - Service Manual - V8.0 - ENLuis OvalleNo ratings yet
- Polygon Shafts and HubsDocument6 pagesPolygon Shafts and HubskicklOpNo ratings yet
- Piping - Materials - Elbows and Bends - Reducers - PE & ROTO Lined Carbon Steel PipingDocument52 pagesPiping - Materials - Elbows and Bends - Reducers - PE & ROTO Lined Carbon Steel PipingDesmond Chang100% (1)
- DIN 11024 - Spring Cotters PDFDocument1 pageDIN 11024 - Spring Cotters PDFthisisjineshNo ratings yet
- Din 406-10 1992-12Document6 pagesDin 406-10 1992-12diego mancilla rodriguez50% (2)
- Tower 7 Uputstvo SRBDocument1,041 pagesTower 7 Uputstvo SRBcipsicc100% (4)
- Din 13-1Document4 pagesDin 13-1Sankha Dasgupta100% (3)
- Metric Shoulder ScrewsDocument1 pageMetric Shoulder ScrewsPhillipe SabinoNo ratings yet
- Din 1705Document2 pagesDin 1705Anurag Jain50% (2)
- Bend Calculation DIN 6935Document2 pagesBend Calculation DIN 6935nadimuddinNo ratings yet
- KAMAX - Bolt and Screw CompendiumDocument60 pagesKAMAX - Bolt and Screw Compendiumjzaw65No ratings yet
- HydraulicCylinderTubeST52 ST52 3Document1 pageHydraulicCylinderTubeST52 ST52 3rjramanathanNo ratings yet
- Cargo Terminal Standards 121021Document16 pagesCargo Terminal Standards 121021suryakeshwar singhNo ratings yet
- Din 867Document3 pagesDin 867danielk32No ratings yet
- Splines: Side Splines For Soft Holes in Fittings-Sae J499aDocument4 pagesSplines: Side Splines For Soft Holes in Fittings-Sae J499aSanjay C BhattNo ratings yet
- Instruction ManualDocument88 pagesInstruction ManualSamira Adnan Halilović100% (1)
- BS 6615 Iso 8062-CT7Document2 pagesBS 6615 Iso 8062-CT7Purushothama Nanje GowdaNo ratings yet
- Fos AsmeDocument41 pagesFos AsmeMahender Kumar100% (1)
- Din 8140 AmecoilDocument1 pageDin 8140 Amecoiljuanpalomo74No ratings yet
- Iso 68-1 PDF - Google SearchDocument2 pagesIso 68-1 PDF - Google SearchDeniz Tuncbilek0% (1)
- Saej1459v004 PDFDocument9 pagesSaej1459v004 PDFvishalNo ratings yet
- GD&T - All Slides - Chapters 1-11 - Q&A - AnimatedDocument77 pagesGD&T - All Slides - Chapters 1-11 - Q&A - AnimatedOmar RiosNo ratings yet
- K65 Working Pressure Calculation According To AD2000 RulesDocument1 pageK65 Working Pressure Calculation According To AD2000 RulesDhavalNo ratings yet
- Potash CrystallizationDocument14 pagesPotash CrystallizationUditha Lakshan100% (1)
- Shafts - Precision Standards - : Circularity, Straightness, L Dimension Accuracy Straightness Measurement MethodDocument1 pageShafts - Precision Standards - : Circularity, Straightness, L Dimension Accuracy Straightness Measurement Method86babuNo ratings yet
- C15100 Alloy - CuZr0,15Document17 pagesC15100 Alloy - CuZr0,15kristechnikNo ratings yet
- Insert Shape ... : R S C T DDocument11 pagesInsert Shape ... : R S C T DskidamdnevnoNo ratings yet
- 4 - PDFsam - Designing Fillet Welds For Skewed T-Jointsâ - Part 1 - The James F ...Document1 page4 - PDFsam - Designing Fillet Welds For Skewed T-Jointsâ - Part 1 - The James F ...mechfreeNo ratings yet
- Application Nr. 3 (Ultimate Limit State) : Resistance of Member Cross-SectionDocument48 pagesApplication Nr. 3 (Ultimate Limit State) : Resistance of Member Cross-SectionVictor TvvNo ratings yet
- Cuzr0,15: Uns:C15100 En:Cw120CDocument17 pagesCuzr0,15: Uns:C15100 En:Cw120CNut AssanaiNo ratings yet
- Production Conventional Question and AnswerDocument10 pagesProduction Conventional Question and AnswerRamesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- CK45 (1.1191)Document3 pagesCK45 (1.1191)alextentwentyNo ratings yet
- Compression MembersDocument172 pagesCompression Membersbsitler100% (1)
- Bend Allowance Part 2Document21 pagesBend Allowance Part 2Jhalbert BelmonteNo ratings yet
- SavijanjeDocument76 pagesSavijanjeSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Single Unit 2 Cars Suitable For Condominium and Office Buildings. Double Unit 4 Cars For Permanent Use Only!Document6 pagesSingle Unit 2 Cars Suitable For Condominium and Office Buildings. Double Unit 4 Cars For Permanent Use Only!Samira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Industry in Focus 2010: Lift and Escalator Industry AssociationDocument12 pagesIndustry in Focus 2010: Lift and Escalator Industry AssociationSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Forces From T-GuidesDocument1 pageForces From T-GuidesSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- RAL KartaDocument6 pagesRAL KartaSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinders Series Ȋ.1: Ȋ.1 Type Dimensions (MM)Document1 pageHydraulic Cylinders Series Ȋ.1: Ȋ.1 Type Dimensions (MM)Samira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Vxf2aidrDocument132 pagesVxf2aidrSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik Za LiftDocument1 pageUpitnik Za LiftSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument54 pagesTissueNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Step 7Document3 pagesStep 7api-665222821No ratings yet
- Week 8 Perdev LasDocument8 pagesWeek 8 Perdev LasMay AnneNo ratings yet
- Audit of ReceivableDocument14 pagesAudit of ReceivableMr.AccntngNo ratings yet
- Career Essay Eng 1302Document4 pagesCareer Essay Eng 1302Madison MorenoNo ratings yet
- RLMXtreme UV-Full Submittal Package 1.11Document17 pagesRLMXtreme UV-Full Submittal Package 1.11Oscar SiriasNo ratings yet
- The Case Study of Polish Migration Into The UKDocument3 pagesThe Case Study of Polish Migration Into The UKAbeera AliNo ratings yet
- MELODY 5.3 Treatment Methods Theoretical - V2.0 - 211122Document19 pagesMELODY 5.3 Treatment Methods Theoretical - V2.0 - 211122MelodyNo ratings yet
- ch4 Standard DeviationDocument14 pagesch4 Standard DeviationAkbar SuhendiNo ratings yet
- Condor PaperDocument12 pagesCondor Paperarafath1985No ratings yet
- Stilmas Vapour Compression StillsDocument2 pagesStilmas Vapour Compression StillsKarim PanjwaniNo ratings yet
- Ac SequenceDocument4 pagesAc SequencejenolivaNo ratings yet
- Keph205 PDFDocument18 pagesKeph205 PDFRohit Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- L293D Motor Control Shield: FeaturesDocument6 pagesL293D Motor Control Shield: FeaturesJefferson HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Power, Promise, Potential, and Posibilities of ParksDocument2 pagesPower, Promise, Potential, and Posibilities of ParksRizza Joy Sariego EsplanaNo ratings yet
- Hf1016414 Hoffman VentiladorDocument4 pagesHf1016414 Hoffman VentiladorMoises AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Questions With "Nandao" - Chinese Grammar WikiDocument3 pagesRhetorical Questions With "Nandao" - Chinese Grammar WikiluffyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Set I II NRM 121 2011 2Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Set I II NRM 121 2011 2hangkattesia82No ratings yet
- PreviewDocument55 pagesPreviewNway Moe SaungNo ratings yet
- M56 Anchor Bolt: Lion Brand 1000 KN Cast Steel Bollard Qty - 32 NosDocument1 pageM56 Anchor Bolt: Lion Brand 1000 KN Cast Steel Bollard Qty - 32 NossanaNo ratings yet
- God Created Integers PDFDocument3 pagesGod Created Integers PDFBryan0% (6)