Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacotherapy STABLE Coronary Artery Disease
Pharmacotherapy STABLE Coronary Artery Disease
Uploaded by
Jaz MnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacotherapy STABLE Coronary Artery Disease
Pharmacotherapy STABLE Coronary Artery Disease
Uploaded by
Jaz MnCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacotherapy STABLE coronary artery disease
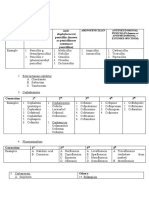
1. Vasculoprotective therapy used to reduce the RISK of future CV events
Vasculoprotective
therapy
1. Behavioural Educate pt
modification Diet (as followed by guidelines CPG 2018)
therapy Physical activity / exercise (active lifestyle) can lower lipid in the blood
Smoking cessation
Weight management
Reduce serum cholesterol level
Treat HTN
Low dose of aspirin
Postmenopausal oestrogen replacement
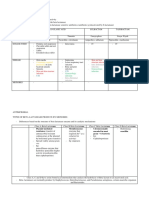
2. Risk factor 1. Statin
modification In pt stable CAD, the level of LDL-C is lower (=improve prognosis-possible outcomes) and thus has better outcome (result)
In pt with higher LDL-C baseline = 2.6 mmol/L statin helps to intensively reduce LDL-C and thus reduce the CV mortality
Before PCI, reloading with high intensity of statin MAY BE CONSIDERED since statin helps to reduce peri-procedural MI
either in statin-naive or chronic statin therapy pt
2. ACEI
Pt post-MI + HFrEF + LVEF ≤ 40% secondary prevention
Stable CAD + reduced LV function should take the following drugs to improve outcome:
ACEI/ARB
BB
MRA (spirolactone and eplerenone)
AR-NI (entresto)
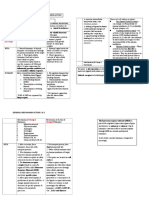
In patients with stable CAD + without MI & without LV damage (taking ACEI ramipril 8 mg & perindopril 10 mg in
respective study) 20 % of them reduce in CV death, MI and stroke
Recently, ACEI / ARB are proved not to reduce CV event. Therefore, stable CAD pt + without HTN / normal LV function
not recommended to take ACEI (so group post MI je yg blh ambik ACEI point mula2)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- AABB Technical Manual 20th EditionDocument841 pagesAABB Technical Manual 20th Editionparag f80% (5)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Viruses Do Not Exist Stefan Lanka 820Document6 pagesViruses Do Not Exist Stefan Lanka 820Phazolle100% (1)
- 1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionDocument30 pages1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Understanding Narcisistic PersonalityDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Narcisistic PersonalityCarla RiveraNo ratings yet
- Common Cold and InfluenzaDocument5 pagesCommon Cold and InfluenzaJaz MnNo ratings yet
- List of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Document2 pagesList of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesDocument5 pagesThe Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsDocument5 pagesSunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Injury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisDocument5 pagesInjury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Skin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionDocument2 pagesSkin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Function of Pituitary HormonesDocument1 pageFunction of Pituitary HormonesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- General Mechanism of Action1Document2 pagesGeneral Mechanism of Action1Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Guide To Hba1C: Blood Glucose Diagnosing DiabetesDocument3 pagesGuide To Hba1C: Blood Glucose Diagnosing DiabetesTayyab Tahir MinhasNo ratings yet
- Maternal in ChildDocument15 pagesMaternal in ChildRenalyn VillasencioNo ratings yet
- NAVLE Anesthetic Pharmacology Review 2018 PDFDocument63 pagesNAVLE Anesthetic Pharmacology Review 2018 PDFmmatthew74No ratings yet
- PEMICU 4 KV CynthiaDocument55 pagesPEMICU 4 KV CynthiaEko SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Administration of O2 TherapyDocument36 pagesAdministration of O2 TherapyFatima Ysabelle Marie RuizNo ratings yet
- Contnursing AmbulatorycareDocument3 pagesContnursing Ambulatorycareapi-663751713No ratings yet
- Cochlear Implants and Their Impact On The Deaf CommunityDocument14 pagesCochlear Implants and Their Impact On The Deaf CommunityNeal W. Jarnagin100% (8)
- Company Rules AND RegulationsDocument5 pagesCompany Rules AND RegulationsJb Cano ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Final General Surgery (1) - 230122 - 192353Document49 pagesFinal General Surgery (1) - 230122 - 192353Lika BukhaidzeNo ratings yet
- Laporan-Laporan ObatDocument83 pagesLaporan-Laporan Obatsofyan hadyNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Discharge Planning Terhadap Kecemasan Pasien Coronary Artery Desease Di Rs Usu MedanDocument11 pagesPengaruh Discharge Planning Terhadap Kecemasan Pasien Coronary Artery Desease Di Rs Usu MedanYanis HildaNo ratings yet
- Skill 23 Perform and Repair An EpisiotomyDocument2 pagesSkill 23 Perform and Repair An EpisiotomyThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Early Pregnancy and The Initial PrenatalDocument16 pagesDiagnosis of Early Pregnancy and The Initial PrenatalPrecious Grace Amoyen-DasigNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Guidelines For Care HomesDocument70 pagesInfection Control Guidelines For Care Homesmariuseek100% (1)
- Recurrent Abscess in An Asian ElephantDocument7 pagesRecurrent Abscess in An Asian ElephantJin-ee LeeNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Factsheet 1Document3 pagesAnaesthesia Factsheet 1thetNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefpodoximeDocument4 pagesDrug Study - CefpodoximeIzza DeloriaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic and Pregnancy: Pradip - Dashraath - Vijayakumar@nuhs - Edu.sgDocument11 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic and Pregnancy: Pradip - Dashraath - Vijayakumar@nuhs - Edu.sgMedecinBissMedNo ratings yet
- Energy Healing TechniquesDocument17 pagesEnergy Healing TechniquesRAMESHBABUNo ratings yet
- MammographyDocument2 pagesMammographybookish33sNo ratings yet
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Management of Mandibular Osteoradionecrosis - A Success Story at Institute of Aerospace Medicine, BangaloreDocument3 pagesHyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Management of Mandibular Osteoradionecrosis - A Success Story at Institute of Aerospace Medicine, BangaloreAnonymous 9PcFdakHcNo ratings yet
- Vibitha Joseph Naramvelil: Compassionate - Rehabilitation and Home Care Experience - MultilingualDocument3 pagesVibitha Joseph Naramvelil: Compassionate - Rehabilitation and Home Care Experience - MultilingualSanish ScariaNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones Pulmonares Asociadas Al Consumo de Cocaína Pulmonary Complications Associated With Cocaine ConsumptionDocument5 pagesComplicaciones Pulmonares Asociadas Al Consumo de Cocaína Pulmonary Complications Associated With Cocaine ConsumptionLuisa LaraNo ratings yet
- Faculty List For The American University of BeirutDocument29 pagesFaculty List For The American University of BeirutEdrees ElrachidiNo ratings yet
- Pros or Postives of Animal TestingDocument3 pagesPros or Postives of Animal TestingsaulaxNo ratings yet
- Editorial Board AdajDocument4 pagesEditorial Board Adajdalal huNo ratings yet
- Kidney Ka Gharelu Ilaj Aur Upay Ke Ayurvedic Nuskhe Hindi MeinDocument5 pagesKidney Ka Gharelu Ilaj Aur Upay Ke Ayurvedic Nuskhe Hindi MeinGovindNo ratings yet