Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure Infection
Uploaded by
Jaz Mn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesA Beta Lactamase Inhibitors
Original Title
A Beta Lactamase Inhibitors
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA Beta Lactamase Inhibitors
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesSkin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure Infection
Uploaded by
Jaz MnA Beta Lactamase Inhibitors
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
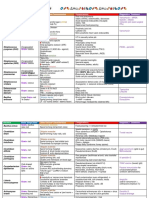
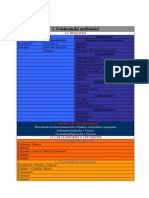
ANTIMICROBIAL
BETA LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
- Have beta lactam ring
1. not used as antibacterial activity
2. only bind and inactivate the beta lactamase
- formulated in combination with beta lactamase sensitive antibiotics (antibiotic yg deactivated by b-lactamase)
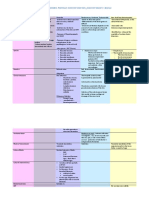
BETA- CLAVULANIC ACID SULBACTAM TAZOBACTAM
LACTAMASE
INHIBITORS
BRAND Augmentin Timentin Unasyn plizer Zosyn: Wyeth
COMPOSITION Amoxicillin + clavulanate Ticarcillin + clavulanate Ampicillin + sulbactam Piperacillin + tazobactam
DOSAGE FORM - Pediatric oral suspension - Intravenous - IV - IV
- Chewable tablet and oral
suspension
- Tablet
- Extended-release tablet
DISEASE - Otitis media - Septicemia - Skin and skin - Appendicitis
- Comminuty required - Lower respiratory tract structure infection - Skin and skin structure
pneumonia of acute infection - Intra abdominal infection (including
bacterial sinusitis - Bone and joint infection diabetic foot infection)
- Sinusitis infection - Gyneocologic - Postpartum endometritis
- Skin and skin structure - UTI infection - Community required
infection - Gyneocologic pneumonia
- UTI infection - Hospital acquired
- Intra abdominal - Ventilator acquired
infection pneumonia
MICROBES - - - -
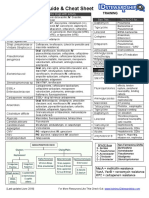
ANTIMICROBIAL
TYPES OF BETA LACTAMASE PRODUCE BY MICROBES
- Differences based on the structure of beta lactamase enzyme and its catalytic mechanisms
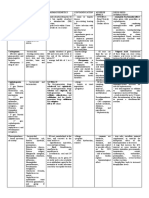
Class A Beta-Lactamase Class B Beta-Lactamase Class C Beta-Lactamase Class D Beta-Lactamase
- Plasmid mediated - Metalloenzyme - Chromosomally - Hydrolizing
resistance (transfer of (enzyme that encoded in most oxacillin
antimicrobial resistant required Zn2+ as a gram –ve bacteria
coding genes at the plasmid cofactor for - Eg:
by horizontal genes transfer) activity) - Cephalosporinase
- Spread widely among gram - Eg: imipenem
–ve
- Eg:
penacillinase-enzyme that
hydrolyse penicillin (higher
activity toward penicillin
than cephalosporins)
- Class A, C and D have serine bound acyl intermediate that catalyse the hydrolysis of Beta-lactam to an inactivated acid.
- Beta- lactamases are normally produce by Staphylococcus, Enterobacteriaceae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, certain anaerobic organism
and Bacteroides.
You might also like
- BZZ BZZ BZZ: Sketchy MicroDocument18 pagesBZZ BZZ BZZ: Sketchy Microkissandtell88% (8)
- Drug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BDocument30 pagesDrug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BCess Lagera Ybanez0% (1)
- Infectious-Disease Tables PDFDocument81 pagesInfectious-Disease Tables PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- BASIC CONCEPTS IN MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, 3RD EDITION. (MARC W.. ZAVOD HARROLD (ROBIN M.) ) (Z-Library)Document1 pageBASIC CONCEPTS IN MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, 3RD EDITION. (MARC W.. ZAVOD HARROLD (ROBIN M.) ) (Z-Library)duy luuNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocument4 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocFrankNo ratings yet
- List of Medicines and Corresponding Maximum Drug Retail PriceDocument3 pagesList of Medicines and Corresponding Maximum Drug Retail PriceLindbergh Espino100% (4)
- Pance Prep Pearls Antibiotics PDFDocument14 pagesPance Prep Pearls Antibiotics PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene Handout PDFDocument32 pagesHand Hygiene Handout PDFms RN100% (1)
- Staphylococcus: Mssa Mrsa Endocarditis Nafcilin VancomycinDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus: Mssa Mrsa Endocarditis Nafcilin VancomycinSijo SunnyNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus AureusDocument4 pagesStaphylococcus AureusTheRHIC21100% (1)
- Materi Pencegahan PlabsiDocument51 pagesMateri Pencegahan PlabsiAnonymous HXyd4E100% (1)
- Bacteria Summary TableDocument10 pagesBacteria Summary TableNur Alia YasminNo ratings yet
- ملخص بكتريا PDFDocument27 pagesملخص بكتريا PDFDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Pseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesDocument14 pagesPseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesTricia Mae JuanitasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseDocument57 pagesAntibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseReshmaaRajendranNo ratings yet
- Drug List 0091Document5 pagesDrug List 0091Mansoor KhanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - 16Document5 pagesMicrobiology - 16karmylle andradeNo ratings yet
- Carlos D. Achondo JR 2MD-1 March 19, 2020Document5 pagesCarlos D. Achondo JR 2MD-1 March 19, 2020Carlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial TaxonomyDocument197 pagesBacterial Taxonomyهدى رشيد توفيقNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document6 pagesModule 9Ian LapidezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial GroupsDocument13 pagesAntimicrobial GroupsLeichel AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside AntibioticsDocument56 pagesAminoglycoside AntibioticsMaharani IndriatyNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Table of BacteriaDocument10 pagesPart 2 Table of BacteriaTeresa Mae Dimen BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors Humayunz CollectionDocument5 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors Humayunz CollectionAsmaa RadwanNo ratings yet
- Types of Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 pagesTypes of Antimicrobial AgentsNur Afiqah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument3 pagesDrug Study PediaDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology by Dhshan Hassan DhshanDocument48 pagesBacteriology by Dhshan Hassan Dhshanعلي الكوافي100% (1)
- MICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY: Infectious Diseases Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesMICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY: Infectious Diseases Affecting The Respiratory SystemLAXA FRANCINENo ratings yet
- Branching, Aerobic, Partially Acid Fast and Non-Acid Fast Gram (+) BacilliDocument2 pagesBranching, Aerobic, Partially Acid Fast and Non-Acid Fast Gram (+) BacilliJustine Marie RevillaNo ratings yet
- 2 Antibacterial DrugDocument7 pages2 Antibacterial DrugGeneto RosarioNo ratings yet
- Daniel - Assignment On AntibioticsDocument6 pagesDaniel - Assignment On AntibioticsArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- Neisse RiaDocument9 pagesNeisse RiaNOEMI BARROGANo ratings yet
- Bacteriology 1: - Non MotileDocument27 pagesBacteriology 1: - Non MotileYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Flora Comensala A OrganismuluiDocument1 pageFlora Comensala A OrganismuluiclaudinaNo ratings yet
- M.02 AMINOGLYCOSIDES (Dr. Buñag) 03-07-2018 (PART 2)Document3 pagesM.02 AMINOGLYCOSIDES (Dr. Buñag) 03-07-2018 (PART 2)PAUL ALINGKAYONNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument1 pageAzithromycinjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- AcinetobacterDocument1 pageAcinetobacterDrashua AshuaNo ratings yet
- Empiric Antibiotic Therapy For Selected Infectious SyndromesDocument2 pagesEmpiric Antibiotic Therapy For Selected Infectious Syndromesazuma12345No ratings yet
- Bacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Document32 pagesBacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Lecture 6: Antibiotics For Anaerobic InfectionsDocument12 pagesAntibiotics: Lecture 6: Antibiotics For Anaerobic InfectionsMuath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus MicrococcusDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus MicrococcusAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- Minocycline One - Pager PDFDocument2 pagesMinocycline One - Pager PDFInês GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Parasites High YoieldDocument4 pagesParasites High Yoieldnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Pointers For Medically Important BacteriaDocument2 pagesPointers For Medically Important BacteriamerryNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic Agents: - Antibiotics - Antifungals - Antivirals - Antiprotozoal - Antihelmintics - Anticancer DrugsDocument29 pagesChemotherapeutic Agents: - Antibiotics - Antifungals - Antivirals - Antiprotozoal - Antihelmintics - Anticancer DrugsSaif ElayanNo ratings yet
- Midterms PharmacologyDocument35 pagesMidterms PharmacologyMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin + Clavulanic AcidDocument37 pagesAmoxicillin + Clavulanic Acidsanish tiwariNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, MetropololDocument7 pagesAzithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Metropolollei_odanNo ratings yet
- For Organisms Like: E. Coli, Klebsiella, P. MirabilisDocument4 pagesFor Organisms Like: E. Coli, Klebsiella, P. MirabilisKayeNo ratings yet
- Disaster Caused BY Biological AgentsDocument25 pagesDisaster Caused BY Biological AgentsKaren Mae Dacoco MamuyacNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: - Ampicilin and Gentamicin Should Not Be Mixed in The Same IV Tubing or Administered ConcurrentlyDocument1 pageDrug Study: - Ampicilin and Gentamicin Should Not Be Mixed in The Same IV Tubing or Administered Concurrentlyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics, Antifungal, Anti-Infective, Anti-Inflammatory, AntiviralDocument24 pagesAntibiotics, Antifungal, Anti-Infective, Anti-Inflammatory, AntiviralKim AmadoNo ratings yet
- Enterococci: S. AureusDocument2 pagesEnterococci: S. AureusShift UallNo ratings yet
- Penicillins MOA: Interfere With The Synthesis of Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis, Peptidoglycan. Exposed Bacterial Membrane Cell LysisDocument2 pagesPenicillins MOA: Interfere With The Synthesis of Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis, Peptidoglycan. Exposed Bacterial Membrane Cell Lysissweetbites cookieNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ATB For ExternDocument64 pagesAntibiotic ATB For ExternKarn AuerkarnnNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology Module 12Document38 pagesClinical Pharmacology Module 12Steven Mark MananguNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal Drugs: Example: CandidiasisDocument4 pagesAnti Fungal Drugs: Example: Candidiasiskaren carpioNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides - Synergistic Bactericidal EffectDocument12 pagesAminoglycosides - Synergistic Bactericidal EffectBern NerquitNo ratings yet
- RiteshDocument4 pagesRiteshPharmacy On FingerTipsNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Tasneem SmeratDocument78 pagesProtein Synthesis Inhibitors: Tasneem Smeratansam hirbaweNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesInhibitors of Protein Synthesiselsayed barhomeNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Bacte 3Document4 pagesQuizlet Bacte 3Michelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside: Bactericidal Transport of Aminoglycoside S Through Bacterial Cell Wall and Cytoplasmic MembraneDocument2 pagesAminoglycoside: Bactericidal Transport of Aminoglycoside S Through Bacterial Cell Wall and Cytoplasmic MembraneNurwahidah Moh WahiNo ratings yet
- Common Cold and InfluenzaDocument5 pagesCommon Cold and InfluenzaJaz MnNo ratings yet
- List of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Document2 pagesList of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesDocument5 pagesThe Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Injury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisDocument5 pagesInjury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsDocument5 pagesSunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsJaz MnNo ratings yet
- General Mechanism of Action1Document2 pagesGeneral Mechanism of Action1Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Function of Pituitary HormonesDocument1 pageFunction of Pituitary HormonesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- 1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionDocument30 pages1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- 1 Anti Bakteri 1.1 Beta LaktamDocument14 pages1 Anti Bakteri 1.1 Beta LaktamNilam atika sariNo ratings yet
- Antiseptik KulitDocument27 pagesAntiseptik KulitAzrul AzlanNo ratings yet
- 6 Langkah Cuci Tangan InggrisDocument3 pages6 Langkah Cuci Tangan InggrisIndah YulianiNo ratings yet
- AntibacterialsDocument2 pagesAntibacterialsakeelNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene: Panitia Pengendalian Infeksi Nosokomial. Dr. Ahmad D. SudrajatDocument40 pagesHand Hygiene: Panitia Pengendalian Infeksi Nosokomial. Dr. Ahmad D. SudrajatpedsquadNo ratings yet
- OAU Antibiotic Class DefinitionsDocument2 pagesOAU Antibiotic Class DefinitionsHenan Educational ServicesNo ratings yet
- Annex A: List of Notified Hand Sanitizers and Rubbing Alcohol ProductsDocument22 pagesAnnex A: List of Notified Hand Sanitizers and Rubbing Alcohol ProductsGigiPasayloonNo ratings yet
- Antibiotice BIDocument26 pagesAntibiotice BISabin MaticiucNo ratings yet
- DM No. 524 S. 2022 2022 GLOBAL HANDWASHING DAY CELEBRATIONDocument7 pagesDM No. 524 S. 2022 2022 GLOBAL HANDWASHING DAY CELEBRATIONEhlee Eton TubalinalNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Personal Higiene Dan Keadaan Sanitasi Industri Tempe Ud Andika Panguripan Di Desa Tagtag Kaja Kecamatan Denpasar Utara TAHUN 2019Document6 pagesGambaran Personal Higiene Dan Keadaan Sanitasi Industri Tempe Ud Andika Panguripan Di Desa Tagtag Kaja Kecamatan Denpasar Utara TAHUN 2019Ausi PalsuNo ratings yet
- Brochure Umic Bimd 01 2023Document6 pagesBrochure Umic Bimd 01 2023nemoNo ratings yet
- Kabizolid Duratrans CompressedDocument1 pageKabizolid Duratrans Compressedemy amiNo ratings yet
- Biology Class Xii Cbse Investigatory Project On AntibioticsDocument37 pagesBiology Class Xii Cbse Investigatory Project On AntibioticsSaveen Kadian75% (4)
- M. L. Agency Net RateDocument3 pagesM. L. Agency Net RateAbhinav GargNo ratings yet
- PRN 059172 Rev 03.a Etest Selection Guide Final Art PDFDocument2 pagesPRN 059172 Rev 03.a Etest Selection Guide Final Art PDFFatima VessaliusNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Class by CoverageDocument3 pagesAntibiotic Class by Coverageayy1No ratings yet
- 9.2 AntisepticsDocument34 pages9.2 AntisepticsSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Best Practice For Dental Hand Hygiene FacilityDocument1 pageBest Practice For Dental Hand Hygiene FacilityEsfandiary 121No ratings yet
- Anti InfectivesDocument4 pagesAnti InfectivesAlecxir PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka-MendeleyDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka-Mendeleynurafiat175No ratings yet
- FDA Updates On Hand Sanitizers Consumers Should Not Use FDADocument5 pagesFDA Updates On Hand Sanitizers Consumers Should Not Use FDAMary Claire Patton100% (1)
- SS-Laktamski Antibiotici: Peroralni Parenteralni Penicilaza Rezistentni PeniciliniDocument5 pagesSS-Laktamski Antibiotici: Peroralni Parenteralni Penicilaza Rezistentni PeniciliniMali PrstNo ratings yet
- Micro Teaching Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesMicro Teaching Lesson PlanFriends ForeverNo ratings yet
- Reegion Nama Toko Brand & FormatDocument56 pagesReegion Nama Toko Brand & FormatRicka MartawatiNo ratings yet
- Fitri BHPDocument3 pagesFitri BHPekadwiyantiNo ratings yet