Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbiology - 16
Uploaded by
karmylle andrade0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views5 pagesThis document discusses infectious diseases that affect different parts of the human body. It covers infectious diseases of the skin, ears, eyes, respiratory system, oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, circulatory system, central nervous system, and genital tract. It also briefly discusses opportunistic infections, examples of reemerging infections, and examples of emerging infections.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses infectious diseases that affect different parts of the human body. It covers infectious diseases of the skin, ears, eyes, respiratory system, oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, circulatory system, central nervous system, and genital tract. It also briefly discusses opportunistic infections, examples of reemerging infections, and examples of emerging infections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views5 pagesMicrobiology - 16
Uploaded by
karmylle andradeThis document discusses infectious diseases that affect different parts of the human body. It covers infectious diseases of the skin, ears, eyes, respiratory system, oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, circulatory system, central nervous system, and genital tract. It also briefly discusses opportunistic infections, examples of reemerging infections, and examples of emerging infections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Sdsd| GENERAL MICROBIOLOGY
CHAPTER 16: OVERVIEW OF HUMAN INFECTIOUS DISEASES
TYPES OF SURFACE LESIONS
Pathogens cause two general categories of
diseases:
1. Microbial intoxications
2. Infectious diseases
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
- diseases that are caused by
pathogens following colonization of
some body site by the pathogen
Some infectious diseases affect more than
one anatomical site, and some pathogens
move from one body site to another during
the course of a disease.
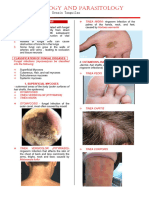
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE SKIN
- Epidermis and dermis
- Dermatitis
- Sebaceous glands
- Folliculitis
- Sty (stye)
- Furuncle
- Carbuncle
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE EARS
- Macule
- Papule Three pathways for pathogens to enter the
- Pustule ear:
- Vesicle 1. Via eustachian (auditory) tube,
from the throat and nasopharynx
2. Via the external ear canal
CROSS SECTION OF THE SKIN 3. Via the blood of lymph
Otitis media
W - Infection of the middle ear
Otitis externa
- Infection of the outer ear canal
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE EYES
- Conjunctiva
- Conjunctivitis
- Keratitis
- Keratoconjunctivitis
- Retinitis
- Laryngitis
- Pharyngitis
- Pneumonia
- Sinusitis
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE ORAL
REGION
ORAL CAVITY
- complex ecosystem
- Suitable for growth of many types
of mcirobrsy
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE - MICROBIOTA in mouth varied
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM ● 300 identified species of
bacteria
Respiratory system can be divided into two
➔ Both anaerobes
parts:
and aerobes
1. Upper respiratory tract (URT)
● Paranasal sinuses
● Nasopharynx
● Oropharynx
● Epiglottis
● Larynx
2. Lower respiratory tract (LRT)
● Trachea
● Bronchial tubes
● Alveoli of the lungs
INDIGENOUS MICROBIOTA OF THE URT
- can cause opportunistic infections
of the respiratory system - Dental caries
LRT INFECTIONS - Periodontal diseases
- Most common cause of death from - Gingivitis
infectious diseases - Periodontitis
- Trench mouth
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
TRANSIENT and RESIDENT MICROBES
- continuously enter and leave the GI
tract
STOMACH and DUODENUM
- where most microbes are destroyed
- Colitis
- Diarrhea
- Dysentery
- Enteritis
- Gastritis
- Gastroenteritis
- Bronchitis - Hepatitis
- Bronchopneumonia Infections of the GI tract having multiple
- Epiglottitis causes
- DIARRHEA
● Have many causes
● Food, drugs. Viruses,
bacteria, protozoa or
helminths
INFECTIONS OF THE GENITAL TRACT
- Bartholinitis
- Cervicitis
- Endometritis
- Epididymitis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Vaginitis
- Vulvovaginitis
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES of
GENITOURINARY (GU) SYSTEM gential tract
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (UTIs) - Include any of the infections
- Divided into: transmitted by sexual activities
1. Upper UTIs - Sometimes include diseases of not
➔ Infections of the only the genital and urinary tract,
kidneys and ureters but other areas of the body as well
2. Lower UTIs
➔ Infections of the
bladder, urethra,
and prostate
- Cystitis
- Nephritis
- Ureteritis
- Urethritis
- Prostatitis
- Pyelonephritis
Escherichia coli
- Most common cause of cystitis and
pyelonephritis
Chlamydia trachomatis
- Most common cause of urethritis
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE CNS terms:
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - Encephalitis
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - Encephalomyelitis
- consists of: - Meningitis
1. cardiovascular system - Meningoencephalitis
● heart - Myelitis
● various vessels
2. lymphatic system
● Lymphatic vessels
● Lymphoid tissue
● Lymph
Cardiovascular system terms:
- Endocarditis
- Myocarditis
- Pericarditis
Lymphatic system terms:
- Lymphadenitis
- Lymphadenopathy
- Lymphangitis
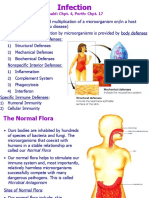
BLOOD
- normally sterile
THE MENINGES AND RELATED STRUCTURES
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE CENTRAL
NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS)
NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Composed of:
1. CNS INFECTIONS OF THE CNS HAVING MULTIPLE
● brain CAUSES
● Spinal cord MENINGITIS
● Three membranes - Inflammation of the meninges
2. PNS - Many causes, including the
● Nerves that branch ingestion of poisons, ingestion or
from the brain and injection of drugs, reaction to a
spinal cord vaccine or a pathogen (e.g., a virus,
There is no indigenous microbiota of the a bacterium, a fungus, or a
nervous system protozoan)
- Three major causes of bacterial
meningitis:
1. Haemophilus influenzae EXAMPLES OF REEMERGING INFECTIONS
2. Neisseria meningitidis ● Cholera
3. Streptococcus pneumoniae ● Dengue fever
● Because of ● Diphtheria
vaccination, these ● Malaria
organisms are not ● Mumps
commonly ● Rift Valley fever
encountered in the ● Tuberculosis
CML's of the ● Yellow fever
developed world ● Infections caused by MRSA and
other "superbugs"
OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS
OPPORTUNISTIC PATHOGENS
(OPPORTUNISTS)
- microbes that usually do not cause
disease
- Have the potential to cause disease
under certain conditions
- Common opportunistic infections:
● Aspergillosis and other
mould infections
● Candidiasis
● Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and
herpes simplex infections
● Tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis
● Mycobacterium avium and
Pneumocystis infections
EXAMPLES OF EMERGING INFECTIONS
● Avian influenza (bird flu)
● Chaga's disease
● Chikungunya virus
● Hemolytic uremic syndrome and
other E.coli O157 infections
● Ebola hemorrhagic fever
● Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
(HPS)
● HIV infection and AIDS
● Human monkeypox
● Lassa fever
● Legionellosis
● Lyme disease
● Marburg hemorrhagic fever
● Middle East respiratory syndrome
(MERS-CoV)
● Zika virus
You might also like
- Antimicrobials Drugs: Dr. Mohammed Al-KhawlaniDocument19 pagesAntimicrobials Drugs: Dr. Mohammed Al-Khawlaniخالد الشرعبيNo ratings yet
- FUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesFUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSKathleen Hazel AndresNo ratings yet
- Major Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal DiseasesDocument75 pagesMajor Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal DiseasesMary LyonNo ratings yet
- 9 Overview of Human Infectious Diseases PDFDocument47 pages9 Overview of Human Infectious Diseases PDFAminah Julianna MarasiganNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 - Overview of Human Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 17 - Overview of Human Infectious DiseasesJacob PallorinaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Communicable DiseasesDocument159 pagesSeminar ON: Communicable DiseasesvishnuNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesDocument12 pagesFungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesHussein QasimNo ratings yet
- Topics For CA. (Yu)Document6 pagesTopics For CA. (Yu)Charlotte CorderoNo ratings yet
- 4 - NematheminthesDocument3 pages4 - NematheminthesAliyah Julianne PayumoNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section VIII. Major Infectious Diseases of HumansDocument29 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section VIII. Major Infectious Diseases of HumansCarmela Laraya Alayon25% (4)
- Odontogenic Infection & Surgical ManagementDocument296 pagesOdontogenic Infection & Surgical ManagementYazid Eriansyah Pradanta100% (2)
- MeningococcemiaDocument5 pagesMeningococcemiazzoOeeNo ratings yet
- Enterococci: S. AureusDocument2 pagesEnterococci: S. AureusShift UallNo ratings yet
- Bacteria & DiseaseDocument7 pagesBacteria & DiseaseAhmed ALiNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemAnaNo ratings yet
- Micp211 Lec MidtermsDocument14 pagesMicp211 Lec MidtermsAlyanna TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic InfectionsDocument36 pagesAnaerobic InfectionsPatriceNo ratings yet
- Clinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicDocument7 pagesClinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- S. Aureus Pneumonia Often Complicates Illness Caused by Influenza VirusesDocument14 pagesS. Aureus Pneumonia Often Complicates Illness Caused by Influenza VirusesRia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungikrystal TortolaNo ratings yet
- Ectoparasites - 1 2022ADocument50 pagesEctoparasites - 1 2022AMeh AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Week7 InfectionDocument18 pagesPathology Week7 InfectionSalifyanji SimpambaNo ratings yet
- Hdp301infectionrevisedoct2020 1Document24 pagesHdp301infectionrevisedoct2020 1Linda NguyenNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis en Peces, Anfibios y ReptilesDocument2 pagesZoonosis en Peces, Anfibios y ReptilesMila Fer D. PridonttNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Micro para Lec FinalsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Micro para Lec FinalsJohn Carl CastilloNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae Opportunistic PathogensDocument1 pageEnterobacteriaceae Opportunistic PathogensMiaoNo ratings yet
- MICP (Autosaved) DONEDocument7 pagesMICP (Autosaved) DONEEdna ChanNo ratings yet
- Includes: Urinary Tract Infections Genital Tract Infections Viral Sexually Transmitted Diseases Bacterial Sexual Transmitted DiseasesDocument37 pagesIncludes: Urinary Tract Infections Genital Tract Infections Viral Sexually Transmitted Diseases Bacterial Sexual Transmitted DiseasesDon Pelicio NgohoNo ratings yet
- Ulcerated Lesion 1Document15 pagesUlcerated Lesion 1ربيد احمد مثنى يحيى كلية طب الاسنان - جامعة عدنNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Infections Of Upper Jaw: حلا ــف دمحم ةـشـئاع Group: C2Document24 pagesOdontogenic Infections Of Upper Jaw: حلا ــف دمحم ةـشـئاع Group: C2Hayder HussienNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative CocciDocument3 pagesGram Negative CocciAlexander PanodNo ratings yet
- Med Org Topic 234Document9 pagesMed Org Topic 234barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- MBL 1 Bacterial PneumoniaDocument5 pagesMBL 1 Bacterial PneumoniaFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 19. Bacterial InfectionsDocument29 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 19. Bacterial InfectionsBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- Pharyngitis, Tonsillitis and Laryngitis: A A H MulderDocument5 pagesPharyngitis, Tonsillitis and Laryngitis: A A H MulderRisang Nur WigunaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections of HumansDocument89 pagesBacterial Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet
- 5.16 Lecture Digestive Diseases and AlcoholismDocument125 pages5.16 Lecture Digestive Diseases and Alcoholismtexasrepublican1976No ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument85 pagesRespiratory System NotesMark Lorenz NaldozaNo ratings yet
- Guía Tarea 1 Unidad I CenatDocument5 pagesGuía Tarea 1 Unidad I Cenatanette sugey beltran felixNo ratings yet
- Principles of EpidemiologyDocument23 pagesPrinciples of EpidemiologyGabz GabbyNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Bacterial Infections Part 2 Dr. E. Lim FinalDocument5 pagesPEDIA Bacterial Infections Part 2 Dr. E. Lim FinalClaire DuNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program of Immunization ReviewerDocument11 pagesExpanded Program of Immunization ReviewerAnn Justine OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Infection ADocument34 pagesInfection ALUNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Jamur: Lies Marlysa RamaliDocument113 pagesPenyakit Jamur: Lies Marlysa RamaliHeru ArifardiNo ratings yet
- Disease of Poultry IiDocument34 pagesDisease of Poultry Iithanh ba matNo ratings yet
- Ent1 18Document45 pagesEnt1 18talya.oliveNo ratings yet
- Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Cocci: Unit 3: Neisseriaceae and Moraxella CatarrhalisDocument18 pagesGram-Positive & Gram-Negative Cocci: Unit 3: Neisseriaceae and Moraxella CatarrhalisKathleen RodasNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 19. Bacterial InfectionsDocument29 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 19. Bacterial Infectionsmirai desuNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectiosnDocument4 pagesBacterial InfectiosnPatrick Z. MascareñasNo ratings yet
- General Pathology of Infectious DiseasesDocument47 pagesGeneral Pathology of Infectious DiseasesAbdullah EmadNo ratings yet
- Enterovirus: Virologi Klinik KDM 726 Pembimbing: Dr. Abu Rohiman, MS, SPMK (K)Document12 pagesEnterovirus: Virologi Klinik KDM 726 Pembimbing: Dr. Abu Rohiman, MS, SPMK (K)Daniel EdbertNo ratings yet
- Approach To Lymphadenopathy in ChildrenDocument39 pagesApproach To Lymphadenopathy in Childrenmrs raamNo ratings yet
- MYCOLOGY 2 WQWQWQWDocument16 pagesMYCOLOGY 2 WQWQWQWDaphne CabaguiNo ratings yet
- Skinl3 WEB09Document50 pagesSkinl3 WEB09Gwyneth Koleen LopezNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dian - Telinga Dan Gangguan PendengaranDocument46 pagesDr. Dian - Telinga Dan Gangguan PendengaranYohana AjaNo ratings yet
- Infection (Course)Document72 pagesInfection (Course)Asmaa RagabNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument33 pagesInfectionHesham EljamlNo ratings yet
- 46 Infectious DiseasesDocument36 pages46 Infectious DiseasesRam NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Ss3 Agric First TermDocument40 pagesSs3 Agric First TermAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Sec D - Intervention of Common Signs & SymptomsDocument30 pagesSec D - Intervention of Common Signs & SymptomsCheryl OrtizNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Infective Immigrants On The Spread of Dog RabiesDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Infective Immigrants On The Spread of Dog Rabiestibebu tuluNo ratings yet
- The Pioneering Work of William J. McCormick, M.D.Document4 pagesThe Pioneering Work of William J. McCormick, M.D.Βόρειο ΣέλαςNo ratings yet
- Biology Part2 BIJUSDocument271 pagesBiology Part2 BIJUSDebasish BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Actions, Origins, ResistanceDocument344 pagesAntibiotics Actions, Origins, Resistancealery ahreally100% (1)
- Infection: Dr. Mehrunnisa Umar Assistant Professor Department of MedicineDocument57 pagesInfection: Dr. Mehrunnisa Umar Assistant Professor Department of MedicinedrusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- 5.infection Control & Standard PrecautionsDocument33 pages5.infection Control & Standard PrecautionsGilbert JohnNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument5 pagesReview of Related LiteratureJeanette CapangpanganNo ratings yet
- Bill Gates, Depopulation, Coronavirus & Values - For The WorldDocument8 pagesBill Gates, Depopulation, Coronavirus & Values - For The WorldBruno MedinaNo ratings yet
- DFOT StemazingDocument12 pagesDFOT StemazingYezhia Angelica GalceranNo ratings yet
- EBOLADocument2 pagesEBOLAamirNo ratings yet
- Pre-Intermediate Unit 8 VocabularyDocument6 pagesPre-Intermediate Unit 8 VocabularyHama CheikhNo ratings yet
- Universal PrecautionDocument46 pagesUniversal PrecautionJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Copy1-Epidemiology Module 1Document50 pagesCopy1-Epidemiology Module 14ttf68m5j5No ratings yet
- 2 Historical Development of Paediatric NursingDocument34 pages2 Historical Development of Paediatric NursingBenkele R.G.83% (6)
- Wisdom of Prophet Muhammad SAWDocument21 pagesWisdom of Prophet Muhammad SAWHeera SinghNo ratings yet
- A Narrative Review On Argentine Hemorrhagic Fever Junin Virus JUNVDocument8 pagesA Narrative Review On Argentine Hemorrhagic Fever Junin Virus JUNVAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Initial and Annual Health RecordDocument2 pagesInitial and Annual Health Recordmariegold mortola fabelaNo ratings yet
- Gr9 English (FAL) November 2021 Question PaperDocument12 pagesGr9 English (FAL) November 2021 Question PapermtshayizukisaNo ratings yet
- Ith2021 Countrylist Final 26may2021Document46 pagesIth2021 Countrylist Final 26may2021el.cadejoNo ratings yet
- Character of Oswald AlvingDocument1 pageCharacter of Oswald AlvingRed ApocalypseNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument31 pagesAMOEBIASISpriyagerard100% (1)
- 2021-11-04 - Affidavit No 1 of Kip Warner (Injection Passport)Document162 pages2021-11-04 - Affidavit No 1 of Kip Warner (Injection Passport)Canadian Society for the Advancement of Science in Public Policy100% (3)
- Physical Exam Form PDFDocument3 pagesPhysical Exam Form PDFOktavianNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 8 3RD PERIODICAL TEST 20pointsDocument7 pagesMAPEH 8 3RD PERIODICAL TEST 20pointsRijah VenzonNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Lyme Disease Presenting With Nonsexual Acute Genital UlcersDocument3 pagesDisseminated Lyme Disease Presenting With Nonsexual Acute Genital UlcersDwi Fikha AprilyantiNo ratings yet
- Flexor Tendon Sheath InfectionsDocument10 pagesFlexor Tendon Sheath InfectionskenthepaNo ratings yet
- Treatment - Bacterial Infections of The SkinDocument3 pagesTreatment - Bacterial Infections of The SkinGembelle Grace MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument7 pagesDaftar PustakaAdilah RamadhaniNo ratings yet