Professional Documents
Culture Documents
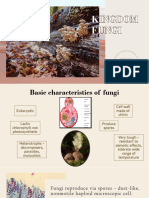
Fungi
Uploaded by
krystal TortolaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fungi
Uploaded by
krystal TortolaCopyright:
Available Formats
Fungi
Classification Mycelium - Network of hyphae
5 Kingdom System (Whittaker, 1969)
- One of the 5 kingdoms which also includes
prokaryota, protista, plantae, and animalia
Three - Domain System of Classification
(Woese,1970s)
- Kingdom under domain Eukarya
Decomposers Saprophytes
• Decomposition • Absorbs
• Break Materials nutrients from
Yeasts
down dead or
▪ Unicellular
decaying
▪ Reproduces by budding
organic matter
▪ Common yeasts ferment sugar to alcohol,
breaks down simple sugar to CO2 and
Characteristic: H2O
- Gets nutrients from dead or decaying organic ▪ Good source of nutrient and vitamins
matter. ▪ Some human pathogens: C, Albicans and
- Found in soil, water and air. Cryptococcus neuformans
- Studied due to its benefits and effects on Moulds
humans. ▪ Often seen in water and soil
- Massive kingdom over 100,000 different ▪ Grow in forms of hyphae
species. ▪ Reproduction by spore
1. Parasite ▪ Used in antibiotic medications, penicillin
- cause disease in plants and animals ▪ Produces amylase, citric acids and other
- absorbs nutrients from tiny organisms organic acids
2. Saprophytes ▪ Also used for flavors in cheese
Fleshy Fungi
Difference from kingdom plantae & algae ▪ Collective term for fungi that are not
microorganisms
Fungi ▪ Includes mushrooms, toadstools,
1. No photosynthesis, No chlorophyll puffballs, and bracket fungi
2. Cell walls Medical Significance
- Chitin • If some fungi are used to manufacture
Plants medications
- Cellulose • There are also fungi that causes infectious
diseases
Types (size) Mycoses
• Macroscopic - Collective term for infectious diseases
• Microscopic caused by fungi
Rhizopus stolonifer - species of fungus
Cap types:
• Bag-like
• Umbrella-like
Stuctures
• Cap
• Stalk
• Hypa (hyphae)
Hyphae Types
(a) Septate hypa (b) Coenocytic hypha
- Has septum (aseptate hypha)
New Section 1 Page 1
Fungi; Diseases
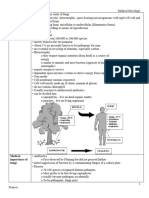
How do Fungi cause disease? Tinea Cruris Tinea
Unguium
Fungal pathogens cause disease by
- Red, ring- - Thickening
invasion and mechanical destruction of
like of the
tissues and/or obstruction of flow of
patches in ends of
bodily fluids.
the groin the nails
area and - Yellow
1. Dermatomycoses - Cutaneous,
inner color to
Hair, and Nail Mycoses
thighs, but the nails
Tinea or Ringworm Infection
not
- Caused by a group of moulds
scrotum
collectively referred to as
- Itching in
dermatophytes
the groin
- Tinea infections are named based
area
of the anatomy infected
- Pain in the
Pathogens
groin area
- Dermatophytes (e.g Microsporum,
Epidermophyton, and
Trichophyton)
Reservoirs and mode of transmission 2. Subcutaneous Mycoses - Sporotrichosis,
- Reservoir: Humans, animals, soil Chromomycosis, and Mycetoma
- Transmission: direct or indirect - Fungal infections of the dermis and underlying
contact with lesion tissues
Laboratory Diagnosis - Results from traumatic implantation of the mould
- Microscopic examinations of skin through the dermis into the subcutaneous tissue
scrapings, hair or nail clippings Sporotrichosis
- Culture - Caused by Sporothrix schenckii
- Often associated with gardeners and called "rose
cutters disease"
Tinea Pedis Tinea Tinea - Reservoir: soil and on plant matter such as
Corporis Capitis sphagnum moss, rose bushes, and hays
- Itchy, - Red, ring- - Red, scaly - Mode of transmission: contact with fungal spores
burning shaped rash on - Portal of entry: enters skin through a small cut or
rash on the patches the scalp scrape
feet with raised, - Itching of - Most commonly seen in hand and arms
- Whitening scaly edges the scalp Signs and Symptoms
and - Itching - Hair loss - Early: Usually a small, painless bump
breakdown on the - develops any time from 1 to 12
of the skin scalp weeks after exposure to the fungus
between - Enlarged - Bump will eventually grow larger and may look
the toes lymph like an open sore or ulcer that is very slow to heal
- Scaling of nodes Phaeohyphomycosis / Chromomycosis
the feet - Caused by various species of moulds
- Blisters on - often associated with Exophiala,
the feet Cladophialophora and Fonsecaea
- Reservoir: soil and wood
- Localized disease of skin presents with swelling,
Induration, or mass (history of trauma)
New Section 1 Page 2
Fungi Diseases
Mycetomas
- Caused by various mould 5. Cryptococcosis
- Fungi may enter the body through a • Specifically: Cryptococcal
break in the skin, often on a person's Meningitis
foot • This disease starts as a lung
- The resulting infection causes firm, infection but spreads to the
usually painless but debilitating masses bloodstream to the brain
under the skin that can eventually affect • Causative agents: Cryptococcus
the underlying bone neoformans and Cryptococcus
- Reservoir: soil and water gatii
- Germ enter wound through wounds or • Both are encapsulated yeasts. The
other small injuries like thorn prick capsule cryptococcus to adhere to
- Does not spread between people (CDC, mucosal surfaces and avoid
2020) pathogenesis
Laboratory Diagnosis • Reservoir: pigeon nests; pigeons,
- Histologic examination of biopsy chicken.
specimen Turkey, and bat droppings
- Culture • Transmission: inhalation of yeasts
Treatment
- Surgery and Anti Fungals Signs and Symptoms
• Headache
3. Thrush • Nausea
- A yeast infection of the oral cavity • Vomiting
- Common in infants, elderly patients, • Mental changes, including
and immunosuppressed individuals confusion, hallucinations, and
- White creamy patches occur on the personality changes
tongue, mucous membranes, and • Lethargy
corners of the mouth • Sensitivity to light
- Causative Agent: Candida Albicans and
related species If left untreated:
- Reservoir: infected humans • Brain damage
- Mode of transmission: occurs by • Coma
contact with secretions or excretions of • Hearing loss
the mouth, skin, vagina, or feces of • Hydrocephalus, which is also
patients called "water on the brain"
- Also mother to neonate during
childbirth
Laboratory Diagnosis - microscopic
examination of wet mounts and by culture
Signs and Symptoms
- Slight bleeding if the bumps are scraped
- Soreness or burning in your mouth
- A cotton-like sensation in your mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- A bad taste in your mouth
- A loss of taste
Yeast Vaginitis
- Infection of the vaginal cavity
Signs and symptoms:
Vulvar pruritus (itching), a burning
sensation, dysuria and a white discharge
Vulvar erythema or rash sometime
occur
New Section 1 Page 3
You might also like
- Fungal InfectionDocument3 pagesFungal InfectionNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Mycology TransDocument11 pagesMycology TransKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To MycologyElena ShresthaNo ratings yet
- (PCH400 T6) AntifungalsDocument10 pages(PCH400 T6) Antifungalsqjamolin210000000237No ratings yet
- Mycovi1 L1Document3 pagesMycovi1 L1MHEKAELLA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- MYCOLOGY 2 WQWQWQWDocument16 pagesMYCOLOGY 2 WQWQWQWDaphne CabaguiNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument33 pagesFUNGIGabz Gabby50% (6)
- Myco ViroDocument76 pagesMyco ViroAnnabelle RaplizaNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument11 pagesFUNGIIzenn De PazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Mycology 2023Document54 pagesIntroduction To Medical Mycology 2023Samuel fikaduNo ratings yet
- Field Crops Diseases Bringher Shalom Part 1 2016Document49 pagesField Crops Diseases Bringher Shalom Part 1 2016carreonrosellejoy8No ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To MycologyTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology ReviewerDocument4 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology ReviewerChrister Jon AcostaNo ratings yet
- CH 26 - The FungiDocument29 pagesCH 26 - The FungiBronwyn JuliusNo ratings yet
- Infestation: ScabiesDocument16 pagesInfestation: ScabiesBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Med Surg (Midterm)Document9 pagesMed Surg (Midterm)Jennica BubanNo ratings yet
- Mycology: Florence Joan S. Te, RMT, EMT, MSMT © College of Nursing Micro-Para UC-BaniladDocument29 pagesMycology: Florence Joan S. Te, RMT, EMT, MSMT © College of Nursing Micro-Para UC-BaniladMary Grace RiveraNo ratings yet
- Mycology: Classification, Structure, Replication, and Pathogenesis of Fungal DiseaseDocument24 pagesMycology: Classification, Structure, Replication, and Pathogenesis of Fungal DiseaseQuinonez Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- Microbial Ecology of the Human BodyDocument2 pagesMicrobial Ecology of the Human BodyIsaiah PascuaNo ratings yet
- (I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensDocument40 pages(I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensellaNo ratings yet
- 5a Discussion ForumDocument4 pages5a Discussion ForumJansen Ira ValdezNo ratings yet
- MYCOLOGYDocument9 pagesMYCOLOGYkabukkabukcuNo ratings yet
- MYCOSESDocument41 pagesMYCOSESDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument16 pagesFungiramkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Basic Mycology GuideDocument46 pagesBasic Mycology GuideMartin Clyde100% (1)
- Micropara Lec:) : Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsDocument12 pagesMicropara Lec:) : Microbial Diseases of The Skin and Woundsriana santosNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-SayedDocument42 pagesKingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-Sayedomar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Microscopes, Prions, Bacteria, Fungi, ProtistsDocument2 pagesMicroscopes, Prions, Bacteria, Fungi, Protistsbookguynelson75% (4)
- Introduction To MycologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Mycologysarguss14100% (2)
- Cutaneous Mycoses Guide: Classification, Agents and Clinical ManifestationsDocument56 pagesCutaneous Mycoses Guide: Classification, Agents and Clinical ManifestationsHafsa ImranNo ratings yet
- Medically Important FungihandoutDocument55 pagesMedically Important FungihandoutHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- MED-ORG-TOPIC-234Document9 pagesMED-ORG-TOPIC-234barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Myco - 05 - Dermatophyte & AsperagillusDocument92 pagesMyco - 05 - Dermatophyte & AsperagillusesraaNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument6 pagesBiology Projectpurest123100% (12)
- Dr.V.Gopalakrishnan's Guide to Medical MycologyDocument41 pagesDr.V.Gopalakrishnan's Guide to Medical MycologydiniNo ratings yet
- Note Chapter 10Document10 pagesNote Chapter 10Amirr4uddinNo ratings yet
- Suggested ResponsesDocument3 pagesSuggested ResponsesVrutika PatelNo ratings yet
- DERMATOPHYTOSES: LAB DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATIONDocument34 pagesDERMATOPHYTOSES: LAB DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATIONKana FajarNo ratings yet
- SBI3U Grade 11 Biology Prokaryotes Viruses and Eukaryotes Biodiversity TestDocument8 pagesSBI3U Grade 11 Biology Prokaryotes Viruses and Eukaryotes Biodiversity TestMockinjayNo ratings yet
- Mycology SOM CJBDocument91 pagesMycology SOM CJBYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To MycologyPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument16 pagesFungipisceuNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Mycoses How Are Dermatophytes Disseminated? AnthropophilicDocument9 pagesCutaneous Mycoses How Are Dermatophytes Disseminated? Anthropophilicbaihern24No ratings yet
- Dermatophytes: Common Fungal Infectors of Skin, Hair & NailsDocument4 pagesDermatophytes: Common Fungal Infectors of Skin, Hair & NailsWpj JanuNo ratings yet
- MycosesDocument2 pagesMycosesMadabout MusicNo ratings yet
- Mycology1 Lec 8Document6 pagesMycology1 Lec 8markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Approach to fungal skin diseases in reptiles and amphibiansDocument5 pagesApproach to fungal skin diseases in reptiles and amphibiansAlfian Yusak MuzakiNo ratings yet
- Medical MyocologyDocument33 pagesMedical MyocologyFrances Lau Yee ChinNo ratings yet
- The Fungi of Medical ImportanceDocument74 pagesThe Fungi of Medical ImportancenrahmaNo ratings yet
- Fungi: Prepared by Elina Shrestha M.SC - MM Pokhara UniversityDocument45 pagesFungi: Prepared by Elina Shrestha M.SC - MM Pokhara UniversityElena ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology FUNGIDocument55 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology FUNGIAce ClaireNo ratings yet
- Biological ClasifficationDocument6 pagesBiological Clasifficationchannel of dhyanaNo ratings yet
- Ectoparasites - 1 2022ADocument50 pagesEctoparasites - 1 2022AMeh AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Ecology of the Human Body's Normal FloraDocument15 pagesMicrobial Ecology of the Human Body's Normal FloraIsabelle Hazel BenemileNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Transes PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 5 - Transes PDFMervi SarsonasNo ratings yet
- 8 Human Health N Disease-NotesDocument5 pages8 Human Health N Disease-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Document68 pagesCutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Marl EstradaNo ratings yet
- 09-Kingdom FungiDocument43 pages09-Kingdom Fungimilky waysssNo ratings yet
- 4 - Introduction To FungiDocument54 pages4 - Introduction To FungiMohamed RabihNo ratings yet
- Hawassa University, College of Natural & Computational Sciences Department of Biology Applied Mycology (Biol. 542, 2 CR - HrsDocument38 pagesHawassa University, College of Natural & Computational Sciences Department of Biology Applied Mycology (Biol. 542, 2 CR - HrsRidwan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Mycoses: Classification Organisms YeastDocument45 pagesOpportunistic Mycoses: Classification Organisms Yeastrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- Introduction To Fusarium Taxonomy: Tatiana GagkaevaDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Fusarium Taxonomy: Tatiana GagkaevaTochi VHNo ratings yet
- 02 - Mucor Spp.Document17 pages02 - Mucor Spp.Ivan Bandiola100% (1)
- Don't Eat Wild Mushrooms Without Proper IdentificationDocument5 pagesDon't Eat Wild Mushrooms Without Proper IdentificationraymondcapeNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Mycoses: Microsporum SPPDocument3 pagesCutaneous Mycoses: Microsporum SPPMaryNo ratings yet
- Concise overview of Deuteromycetes fungal group characteristicsDocument5 pagesConcise overview of Deuteromycetes fungal group characteristicsHendra S BackNo ratings yet
- A Contribution To The Study of Leptosphaeriaceae and Phaeosphaeriaceae (Pleosporales) in Bulgaria. IDocument4 pagesA Contribution To The Study of Leptosphaeriaceae and Phaeosphaeriaceae (Pleosporales) in Bulgaria. Ignomonia73No ratings yet
- Tinea Cruris Abq JournalDocument3 pagesTinea Cruris Abq JournalGustiandari FidhyaNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic Distribution and Evolution of MycorrhizasDocument65 pagesPhylogenetic Distribution and Evolution of MycorrhizasUtanka DeNo ratings yet
- Medically Important FungiDocument14 pagesMedically Important FungiBeenish ChaudryNo ratings yet
- Fungi Economic Importance Bot Coaching Material DR DNR.Document8 pagesFungi Economic Importance Bot Coaching Material DR DNR.Nagaraj DeshaboinaNo ratings yet
- Slide CultureDocument2 pagesSlide CultureSoni VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram (Fungi)Document1 pageVenn Diagram (Fungi)Iah Kriztel BagacinaNo ratings yet
- 3 Klasifikasi CendawanDocument34 pages3 Klasifikasi CendawanAnisa NurfitrianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture FUNGI 2022Document52 pagesLecture FUNGI 2022JenniferNo ratings yet
- 000 - Mycosphere Philippine Studies On Panaeolus Antillarium & Cyanescens Mushrooms PDFDocument7 pages000 - Mycosphere Philippine Studies On Panaeolus Antillarium & Cyanescens Mushrooms PDFEoghan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5-Bio320 (Fungi)Document49 pagesChap 5-Bio320 (Fungi)Radius JuliusNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Study of Different Temperature, CarbonDocument4 pagesIn Vitro Study of Different Temperature, CarbonSunaina VarmaNo ratings yet
- Deep MycosesDocument27 pagesDeep MycosesdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Fungi Classes ChartDocument1 pageFungi Classes ChartManav SinghNo ratings yet
- Ergot Genus Claviceps PDFDocument2 pagesErgot Genus Claviceps PDFBrandonNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis (Brut)Document6 pagesCandidiasis (Brut)Ilyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Bacteria ColoniesDocument27 pagesMorphology of Bacteria ColoniespeefieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document103 pagesChapter 4tenaw100% (1)
- List of Mycotoxins Molecular WeightDocument17 pagesList of Mycotoxins Molecular WeightIgorPintoNo ratings yet
- Zeherli Göbelekler Ve TercümeDocument3 pagesZeherli Göbelekler Ve TercümeMadi ZeynlvaNo ratings yet
- Lysurus Cruciatus (Phallales) - First Record in Bulgaria and Southeastern EuropeDocument2 pagesLysurus Cruciatus (Phallales) - First Record in Bulgaria and Southeastern EuropeBoris AssyovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Evolution of LichensDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Evolution of LichensAgostina MaranoNo ratings yet
- Fungi Lab Questions AnsweredDocument2 pagesFungi Lab Questions AnsweredSyafiqah AzirahNo ratings yet