Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Ergonomics: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)
Computer Ergonomics: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)
Uploaded by
Ansar AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Ergonomics: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)
Computer Ergonomics: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)
Uploaded by
Ansar AliCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTER
ERGONOMICS
C omputers are an integral part
of life and no longer need
specialised training for use.
Many people spend hours a day in
“Listen to your body’s
they become screames!”
indirectly related to job duties or the
whispers before
front of a computer without thinking work environment. Non-work 10 tips for an Ergonomic Computer
about the impact on their bodies. activities and environments can also Workstation:
They physically stress their bodies impact MSDs.
daily without realizing it by extending Signs and Symptoms of an
their wrists, slouching, sitting without Ergonomic Injury or MSD:
foot support and straining to look at Pain in the fingers, wrists, or other
poorly placed monitors. Anyone who parts of the body: may include a
uses a computer for prolonged dull aching pain, a sharp stabbing
periods is at risk for headaches, pain, or even a burning sensation
burning eyes, red eyes, a stiff neck Tingling or numbness, particularly
and many other problems. It can also in the hands or fingers
cause physical stress that eventually Swelling, inflammation, or joint
could lead to a disability. stiffness
Loss of muscle function or
“Ergonomics is a science concerned weakness
with the ‘fit’ between people and Discomfort or pain in the
shoulders, neck, or upper or lower
their work”.
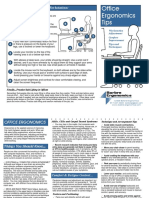
back 1. Use a good chair with a dynamic
It puts people first, taking account of Extremities turning white or feeling chair back
their capabilities and limitations. unusually cold 2. Top of monitor casing 2-3" (5-8
Ergonomics aims to make sure that General feeling of muscle tightness, cm) above eye level
cramping, or discomfort 3. No glare on screen, use an optical
tasks, equipment, information and
Clumsiness or loss of coordination Glass anti-glare filter
the environment suit each worker.
Range of motion loss 4. Sit at arms length from monitor
Computer Ergonomics addresses Discomfort when making certain
ways to optimize your computer 5. Feet on floor or stable footrest
movements
workstation to reduce the specific 6. Use a document holder
risks of injuries & disorders listed 7. Wrists flat in relation to forearms
Risk Factors:
below: to use keyboard & mouse
Repetition (key punching)
Tendonitis Forceful Exertion
8. Arms and elbows relaxed close to
Tenosynovitis body
Direct Mechanical Pressure on wrist
Trigger Finger 9. Center monitor and keyboard in
Static Posture front of you
Epicondylitis Inadequate Recovery Time
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome 10. Take frequent short breaks
Awkward Posture
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Environmental Stressors Benefits of Ergonomics:
Exposure to heat or cold
Adapt Laptops: Laptop computers Reduces costs
Spinal & Back injuries
are not ergonomically designed for Improves productivity &
Repetitive Stress Injuries (RSIs) performance
prolonged use. The monitor and
Repetitive Motion Injuries (RMIs) Improves quality
keyboard are so close together that
Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) they cannot both be in good Improves employee engagement
Cumulative Trauma Disorders positions at the same time. For Creates a better safety culture
(CTDs) prolonged use, it's best to add a
“Ergonomics is not th e separate mouse and keyboard. The
problem - it is the Solution!” laptop can be placed on books so the
top of the screen is at eye level, then
Ergonomic injuries or MSDs can
use an external keyboard so that
affect the muscles, nerves, tendons,
your elbows can rest above 90° by
ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal
your side.
discs. They can be directly or
DGKCC HSE HUB BALOCHISTAN PREPARED: ANSAR ALI (AM HSE)
You might also like
- Daily Observation ReportDocument1 pageDaily Observation ReportAnsar AliNo ratings yet
- Past Papers M2 PDFDocument223 pagesPast Papers M2 PDFisraa jaaboNo ratings yet
- Health BitsDocument2 pagesHealth BitsGarth TommyNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics PDFDocument82 pagesErgonomics PDFKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Submodule Computer Safety and ErgonomicsDocument8 pagesSubmodule Computer Safety and Ergonomicsmohamedmwakuzimu9966No ratings yet
- Safe Use of Laptops: Basic PrinciplesDocument3 pagesSafe Use of Laptops: Basic PrinciplesRudiNo ratings yet
- Where Do I Start?!: A Step by Step Guide To Adjusting Your WorkstationDocument40 pagesWhere Do I Start?!: A Step by Step Guide To Adjusting Your Workstationusman4428No ratings yet
- Computer SafetyDocument4 pagesComputer SafetyZandry YutNo ratings yet
- 03 Ergonomics Human Factor EngineeringDocument32 pages03 Ergonomics Human Factor EngineeringImranNo ratings yet
- Safe Study Space Presentation (CSM)Document5 pagesSafe Study Space Presentation (CSM)Choice AppsNo ratings yet
- Office Ergonomics Tips: Steps For Adjusting Your WorkstationDocument2 pagesOffice Ergonomics Tips: Steps For Adjusting Your Workstationmember1000No ratings yet
- 2 - MALIGALIG, Irish Eloisa G. - CBADocument12 pages2 - MALIGALIG, Irish Eloisa G. - CBAIrish EloisaNo ratings yet
- Computer ErgonomicsDocument5 pagesComputer ErgonomicsMaxim TawoutiaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics and Input DevicesDocument7 pagesErgonomics and Input DevicesY.InayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.2 Health IssuesDocument25 pagesChapter 5.2 Health IssuesRajalakshmi MuthuvelNo ratings yet
- Ergonomicspowerpoint 120531054938 Phpapp01Document10 pagesErgonomicspowerpoint 120531054938 Phpapp01OMKAR09No ratings yet
- EgnonsisDocument8 pagesEgnonsisTanesha JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 OccupationalHealthandSafety (OHS)Document16 pagesChapter8 OccupationalHealthandSafety (OHS)Kyle Dennis SantosNo ratings yet
- 6-COMPUTER PROPER CARE AND MAINTENANCE (Recovered)Document4 pages6-COMPUTER PROPER CARE AND MAINTENANCE (Recovered)nebiat nerayoNo ratings yet
- Wk7 Lec2 ErgonomicsDocument22 pagesWk7 Lec2 ErgonomicsRenuka S MNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: The Study of Human Capabilities in Relationship To Work DemandsDocument10 pagesErgonomics: The Study of Human Capabilities in Relationship To Work DemandsamkmilaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Teacher: Miss Jean MoriahDocument8 pagesErgonomics: Teacher: Miss Jean Moriahஜா டாNo ratings yet
- Greg Rhoades and Derrick MarreroDocument14 pagesGreg Rhoades and Derrick MarreroMohamad TaufikNo ratings yet
- Injuries From The ComputerDocument12 pagesInjuries From The ComputerDjohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Health Problems Caused by Improper Use of ComputersDocument30 pagesHealth Problems Caused by Improper Use of ComputersMary CrisNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ICT - Health IssuesDocument9 pagesIGCSE ICT - Health IssuesblessingNo ratings yet
- ErgonomicsDocument1 pageErgonomicsapi-287083394No ratings yet
- Summary of ErgonomicsDocument1 pageSummary of Ergonomicsapi-286739215No ratings yet
- Ergo 2Document78 pagesErgo 2Aishwarya NaiduNo ratings yet
- Common Hazard at OfficeDocument2 pagesCommon Hazard at OfficeNor HaiqhalNo ratings yet
- 2 Health Hazards Health and SafetyDocument38 pages2 Health Hazards Health and SafetyJada ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 Computer ErgonomicsDocument23 pagesChapter14 Computer ErgonomicsAmber arthurNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Teacher: Jean MoriahDocument8 pagesErgonomics: Teacher: Jean Moriahஜா டாNo ratings yet
- Creating A Healthy Workstation EnvironmentDocument24 pagesCreating A Healthy Workstation EnvironmentBimboy AlegreNo ratings yet
- Computer ErgonomicsDocument48 pagesComputer ErgonomicsNishanth MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- (Employment Relations Today Vol. 30 Iss. 1) Jon Torrey - Understanding Computer Vision Syndrome (2003) (10.1002 - Ert.10073) - Libgen - LiDocument7 pages(Employment Relations Today Vol. 30 Iss. 1) Jon Torrey - Understanding Computer Vision Syndrome (2003) (10.1002 - Ert.10073) - Libgen - LiCinnamon CloverNo ratings yet
- BT 410 Lecture 03Document22 pagesBT 410 Lecture 03Vanessa MhandoNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: (Aspects in Workstation Design and Analysis)Document37 pagesErgonomics: (Aspects in Workstation Design and Analysis)Auto TeaserNo ratings yet
- GD 8 IT End of Sept TestDocument2 pagesGD 8 IT End of Sept TestrenardolettmanNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics PresentationDocument9 pagesErgonomics Presentationapi-545241189No ratings yet
- Ergonomics and Universal Design PrinciplesDocument41 pagesErgonomics and Universal Design PrinciplesSanthi PriyaNo ratings yet
- E RgonomicsDocument24 pagesE RgonomicsanishjohnaNo ratings yet
- Health Concern in Computer Use PDFDocument23 pagesHealth Concern in Computer Use PDFMicah Ellah Reynoso PatindolNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Risks ControlDocument13 pagesHazards and Risks ControlKyle N. BalansagNo ratings yet
- Eduvos Student Ergonomics Presentation 2022Document9 pagesEduvos Student Ergonomics Presentation 2022adriano.c136No ratings yet
- Ergonomics 111024094525 Phpapp01Document24 pagesErgonomics 111024094525 Phpapp01jacky hansdahNo ratings yet
- OSH Slide PresentionDocument7 pagesOSH Slide PresentionAiril AizanNo ratings yet
- 2 ErgonomicsDocument11 pages2 ErgonomicsRainald Avish chandNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Workstation: Risk Factors For Computer UsersDocument4 pagesErgonomics: Workstation: Risk Factors For Computer UsersBilliart KanyangidzeNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics - Jasmine LDocument3 pagesErgonomics - Jasmine Lapi-330469878No ratings yet
- Posture-Related Injuries From Computer UseDocument4 pagesPosture-Related Injuries From Computer UseSejalNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ErgonomicsDocument4 pagesBasic Principles of ErgonomicsJahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- ErgonomicsDocument4 pagesErgonomicsAnshitaNo ratings yet
- Safety and Security NotesDocument4 pagesSafety and Security NotesfaithmapondeNo ratings yet
- Basic Safety Issues: Symptoms IncludeDocument3 pagesBasic Safety Issues: Symptoms IncludeKalkidan AlemuNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE Fit2wrk ClinicalEd Vol1-11Document4 pagesARTICLE Fit2wrk ClinicalEd Vol1-11NesiaNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 Workplace HazardsDocument35 pagesTle 10 Workplace HazardsXavierNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Teacher: Jean MoriahDocument8 pagesErgonomics: Teacher: Jean MoriahIeNvY 110No ratings yet
- Potential Health Problems Related To The Prolonged Use of IT EquipmentDocument5 pagesPotential Health Problems Related To The Prolonged Use of IT Equipmentlil babyNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics Ayesha Aslam 1Document11 pagesErgonomics Ayesha Aslam 1Ayesha AslamNo ratings yet
- The Desk Jockey's Manifesto: The Practical Guide for Modern Computer/Desk WorkerFrom EverandThe Desk Jockey's Manifesto: The Practical Guide for Modern Computer/Desk WorkerNo ratings yet
- Accident InvestigationDocument1 pageAccident InvestigationAnsar AliNo ratings yet
- Work at Height: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)Document1 pageWork at Height: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)Ansar AliNo ratings yet
- Work at Height: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)Document1 pageWork at Height: Prepared: Ansar Ali (Am Hse)Ansar AliNo ratings yet
- Daily Safety Message 06Document1 pageDaily Safety Message 06Ansar AliNo ratings yet
- Noise (Hearing Protection)Document9 pagesNoise (Hearing Protection)Ansar AliNo ratings yet
- Daily Safety Message 06Document1 pageDaily Safety Message 06Ansar AliNo ratings yet
- Daily Safety Message FormateDocument1 pageDaily Safety Message FormateAnsar AliNo ratings yet
- 24-Daily Oservation Report1Document1 page24-Daily Oservation Report1Ansar AliNo ratings yet
- 01 02 2019 HSE ObservationsDocument5 pages01 02 2019 HSE ObservationsAnsar Ali100% (3)
- Kerbs and GuttersDocument1 pageKerbs and GuttersM PNo ratings yet
- History of QuranDocument71 pagesHistory of Quranarifudin_achmad100% (1)
- Ge 08 Ethics Midterm ModuleDocument42 pagesGe 08 Ethics Midterm ModulekingNo ratings yet
- The Draminski Mastitis Detector From Dairy Spares Limited: Early Detection of Subclinical MastitisDocument2 pagesThe Draminski Mastitis Detector From Dairy Spares Limited: Early Detection of Subclinical MastitisRusli SubhanNo ratings yet
- 11Document25 pages11Suraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Tads 3mDocument10 pagesTads 3mtravolta0No ratings yet
- ResumeDocument7 pagesResumedpprasad2No ratings yet
- CLEP Eguides Spanish LanguageDocument49 pagesCLEP Eguides Spanish LanguagekgazooNo ratings yet
- Doctrine ORM For PHPDocument158 pagesDoctrine ORM For PHPpvalenzuelacarcamo100% (1)
- JSOM Resume 2019Document1 pageJSOM Resume 2019Jamie GironNo ratings yet
- Postgresql 14 New Features With Examples (Beta 1)Document86 pagesPostgresql 14 New Features With Examples (Beta 1)KoushikKc ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Slavery - PrimaryDocument10 pagesSlavery - PrimaryA Square ChickenNo ratings yet
- Chinese Remedial Massage (Tuina)Document6 pagesChinese Remedial Massage (Tuina)eamiantiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rosario RDocument3 pagesDr. Rosario Rniks1No ratings yet
- Psychological Capital PowerpointDocument23 pagesPsychological Capital PowerpointwoopyNo ratings yet
- Biology New Article ResearchDocument5 pagesBiology New Article ResearchDaph H.No ratings yet
- Dynamic Image in XML PublisherDocument2 pagesDynamic Image in XML PublisherRavikant YadavNo ratings yet
- The Independence of Suggestibility, Placebo Response, and HypnotizabilityDocument2 pagesThe Independence of Suggestibility, Placebo Response, and Hypnotizabilitymarcelo ponce velozoNo ratings yet
- A Stationary GasDocument10 pagesA Stationary GassugiantobarusNo ratings yet
- 6419B ENU Trainer Handbook Part2Document142 pages6419B ENU Trainer Handbook Part2kaminetaNo ratings yet
- PKC 2007Document40 pagesPKC 2007GeovannyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Game Theory Summer 2017Document8 pagesSyllabus Game Theory Summer 2017Tarang TirumalasettyNo ratings yet
- Icon Manual 2017Document27 pagesIcon Manual 2017Luu LucianNo ratings yet
- COSHH Risk Assessment TemplateDocument3 pagesCOSHH Risk Assessment TemplateFebrian ArianzNo ratings yet
- Core Libraries For Machine LearningDocument5 pagesCore Libraries For Machine LearningNandkumar KhachaneNo ratings yet
- Call 2018-2019 Master Mind ScholarshipsDocument3 pagesCall 2018-2019 Master Mind ScholarshipssteelyheadNo ratings yet
- CUEGIS ExplainedDocument16 pagesCUEGIS ExplainedAida Ayoi100% (2)
- V Feltes 050307 PDFDocument138 pagesV Feltes 050307 PDFVaradharaj VrjNo ratings yet