Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Report Discussion: University of Texas Southwestern
Uploaded by
Syahrul Mubarak Danar Sumantri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageasra post herpetic neuralgia
Original Title
Asraworld2018.23e087e.normAL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentasra post herpetic neuralgia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageCase Report Discussion: University of Texas Southwestern
Uploaded by
Syahrul Mubarak Danar Sumantriasra post herpetic neuralgia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Erector Spinae Plane (ESP) Block as Abortive Treatment for Acute
Exacerbation of Post-Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN): A Case Report
John C. Alexander, MD, MBA
University of Texas Southwestern
Introduction Case Report Discussion
Post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a neuropathic pain A 57-year-old female presented to the pain management clinic with an
syndrome of persistent pain following healing of the acute acute episode of 6-10/10 left-sided chest wall pain similar in character and The advantages of the use of ESP block in the setting of acute
painful lesions associated with herpes zoster (HZ) which is intensity to previous PHN exacerbations after a case of acute HZ two years exacerbation of PHN pain result from the relative safety and
caused by inflammation of the dorsal root ganglion before. Examination revealed dysesthesia to light touch over the left T6-9 ease of placement given the lack of major blood vessels, pleura,
following reactivation of the varicella zoster virus (VZV). dermatomes from the medial border of the scapula to the mid-axillary line, and neural structures in the area. Further studies are needed to
Initial treatment consists of gabapentinoids, tricyclic but no allodynia, hyperalgesia, or skin lesions. She reported partial relief confirm the safety and efficacy of this novel regional anesthetic
antidepressants, and topical local anesthetics (2, 3). In using an analgesic regimen consisting of Amitriptyline 20mg PO QHS, technique for abortive therapy in acute exacerbation of PHN as
addition, many interventional procedures have been Robaxin 750mg PO QHS prn, Vicodin 5/500 PO prn, and Lidoderm patch well as whether single injection or continuous infusion via
described as potential treatments (4), but a lack of Q12 hours prn. She did report a dose-limiting side effect of dry mouth with indwelling catheter are more efficacious. In this report, a single
prospective trials coupled with the inherent cost, risk Amitriptyline, and could not tolerate Gabapentin due to sedation. injection effectively abated the PHN exacerbation.
profile, and technical difficulty of interventional
procedures make recommendations of best practices After discussion of the risks, benefits, and alternatives we proceeded with a In summary, this report demonstrates the use of ESP block is a
difficult. trial of ESP block at the T8 level in the manner described by Forero, et al (1) viable option for abortive treatment of acute exacerbation of
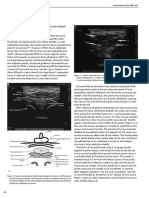
(Figure 1). A total of 20 mL of a solution containing 18ml ropivacaine PHN, but further studies are needed to establish whether ESP
The ESP block is a relatively new regional anesthesia 5mg/ml and 2ml betamethasone 6mg/ml was incrementally injected in 3-5 blocks provide equivalent analgesia when compared with other
technique that has been used for perioperative analgesia mL aliquots with constant visualization of the needle tip and regular interventional techniques.
in the trunk (1, 5). This case report outlines the efficacious aspiration.
use of ESP block for abortive treatment of acute pain due
to exacerbation of PHN. References
The patient noted partial relief immediately, and when contacted six hours
following the procedure she reported a 90% decrease in her pain.
Reassessment at 14 and 90 days revealed pain levels of 0-1/10 and the
1. Forero M, Adhikary SD, Lopez H, Tsui C, Chin KJ. The Erector Spinae Plane Block: A
patient stopped taking Vicodin. Novel Analgesic Technique in Thoracic Neuropathic Pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med.
2016;41(5):621-627. PMID: 27501016
2. John AR, Canady DH. Herpes Zoster in the Older Adult. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2017;
31:811-826 PMID: 29079160
3. Mallick-Searle T, Snodgrass B, Brant JM. Postherpetic neuralgia: epidemiology,
pathophysiology, and pain management pharmacology. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2016;
9;447-454 PMID: 27703368
4. Kim ED, Lee YI, Park HJ. Comparison of efficacy of continuous epidural block and
pulsed radiofrequency to the dorsal root ganglion for management of pain persisting
beyond the acute phase of herpes zoster. PLoS One. 2017; 12(8):e0183559 PMID:
28827823
5. Hamilton DL, Manickam B. Erector spinae plane block for pain relief in rib fractures. Br
J Anaesth. 2017;118(3):474-475. PMID: 28203765
Figure 1: Erector Spinae Plane Block. Arrows denote spread of local anesthetic.
TM (Trapezius Muscle), RMM (Rhomboid Major Muscle), ESM (Erector Spinae
Muscle), TP (Transverse Process).
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- GcMAF Therapy For AutismDocument2 pagesGcMAF Therapy For AutismadivinaperezNo ratings yet
- Nursing InductionDocument114 pagesNursing InductionMichael Long92% (26)
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Sequelae of Dental CariesDocument20 pagesSequelae of Dental Cariesimi4100% (2)
- Fascia Iliaca GuidelineDocument12 pagesFascia Iliaca GuidelineSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Quality Control in Blood BankDocument46 pagesQuality Control in Blood BankTanyaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Intestinal ObstructionDocument21 pagesNeonatal Intestinal ObstructionShahzad Bashir ShamsNo ratings yet
- Primary Skin LesionDocument7 pagesPrimary Skin Lesion_carido_No ratings yet
- 1ST Hope 1Document5 pages1ST Hope 1Jayson RigorNo ratings yet
- Ectropion vs. EntropionDocument1 pageEctropion vs. EntropionAhmed ShafikNo ratings yet
- WCA2024 - George Export - Labour AnalgesiaDocument55 pagesWCA2024 - George Export - Labour AnalgesiaSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Point-of-Care Ultrasonography: The Past and The Future Are in Anesthesiologists' HandsDocument3 pagesPerioperative Point-of-Care Ultrasonography: The Past and The Future Are in Anesthesiologists' HandsSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Splinter Removal With The Aid of Ultrasonography: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesSplinter Removal With The Aid of Ultrasonography: A Case ReportSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Foot & Ankle SurgeryDocument4 pagesThe Journal of Foot & Ankle SurgerySyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Day One, Wednesday, 3 October 2018: Time Topics SpeakerDocument2 pagesDay One, Wednesday, 3 October 2018: Time Topics SpeakerSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Correspondence: A New Ultrasound-Guided Dorsal Penile Nerve Block Technique For Circumcision in ChildrenDocument2 pagesCorrespondence: A New Ultrasound-Guided Dorsal Penile Nerve Block Technique For Circumcision in ChildrenSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- A Longitudinal Supra-Inguinal Fascia Iliaca ComparDocument8 pagesA Longitudinal Supra-Inguinal Fascia Iliaca ComparSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- MSA 16FC Handout Ultrasound 2quadratusDocument2 pagesMSA 16FC Handout Ultrasound 2quadratusSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Critical Care TrolleyDocument3 pagesCritical Care TrolleySyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Instrumen Snars NestwsiDocument4 pagesInstrumen Snars NestwsiSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument8 pagesChest PhysiotherapySyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Egemen PDFDocument36 pagesEgemen PDFSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis WorksheetDocument1 pageDiagnosis WorksheetSyahrul Mubarak Danar SumantriNo ratings yet
- Elisee 350 Product Brochure EngDocument4 pagesElisee 350 Product Brochure EngWidad Mardin Mas JayaNo ratings yet
- Holid Fauzi, Suningsih, Setyo Adi NugrohoDocument6 pagesHolid Fauzi, Suningsih, Setyo Adi NugrohoKholifatun NaziroNo ratings yet
- Knee Arthroscopy (Meniscectomy) : Anatomy and BiomechanicsDocument9 pagesKnee Arthroscopy (Meniscectomy) : Anatomy and Biomechanicsbayan salahNo ratings yet
- Quotation ENHANCED 2 - PLAN 4 - Essential AafiyaDocument24 pagesQuotation ENHANCED 2 - PLAN 4 - Essential AafiyaMelody PacardoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Snake BiteDocument30 pagesLecture 1 Snake BiteZartasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Kit Insert - Anti-SARS-CoV-2Document5 pagesKit Insert - Anti-SARS-CoV-2Yosua Butar ButarNo ratings yet
- DPNDocument7 pagesDPNFikry SyahrialNo ratings yet
- MoclodemideDocument1 pageMoclodemideArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6212 Assessment 2 Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesNURS FPX 6212 Assessment 2 Executive SummaryCarolyn HarkerNo ratings yet
- Medical Certificate: Iv B Mimaropa Palawan F. Lagan Sr. Memorial National High School Caramay, Roxas, PalawanDocument2 pagesMedical Certificate: Iv B Mimaropa Palawan F. Lagan Sr. Memorial National High School Caramay, Roxas, PalawanF. Lagan Sr. Memorial National High School 301694No ratings yet
- IvpDocument18 pagesIvpFranz SalazarNo ratings yet
- Herbalage Products KnowledgeDocument25 pagesHerbalage Products Knowledgemail9246No ratings yet
- The Newborn Early Warning (NEW) System: Development of An At-Risk Infant Intervention SystemDocument5 pagesThe Newborn Early Warning (NEW) System: Development of An At-Risk Infant Intervention Systemeneng latipa dewi100% (1)
- Medical Monitor PDFDocument5 pagesMedical Monitor PDFFábio Vitor MartinsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Schizophrenia: Tomorrow: Chapter 17: Mood Disorders and SuicideDocument65 pagesChapter 16: Schizophrenia: Tomorrow: Chapter 17: Mood Disorders and SuicideRainier Moreno-LacalleNo ratings yet
- AHM Black White Boost FlexiDocument10 pagesAHM Black White Boost FlexiDani Kirky Ylagan100% (1)
- Glucosamine PDFDocument6 pagesGlucosamine PDFChrist FarandyNo ratings yet
- Nose PDFDocument6 pagesNose PDFNiranjanPandeyNo ratings yet
- HazradDocument16 pagesHazradPhan AnNo ratings yet
- 06 - Lec - Stress ReactionsDocument2 pages06 - Lec - Stress Reactionsericka abasNo ratings yet
- Activity The Prescription 1Document7 pagesActivity The Prescription 1Joanna Faye UyNo ratings yet