Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waste Water Test
Waste Water Test
Uploaded by
munawar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThis document discusses potential irrigation problems based on water quality parameters including salinity, sodium absorption ratio (SAR), specific ions like sodium, chloride, and boron, as well as other factors like nitrogen, bicarbonate, and pH. It provides guidelines for classifying the degree of restriction on water use based on electrical conductivity (EC) and total dissolved solids (TDS) for salinity, and EC and SAR for infiltration problems. Maximum recommended concentrations are also given for trace elements that can cause toxicity issues.
Original Description:
Original Title
waste water test.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses potential irrigation problems based on water quality parameters including salinity, sodium absorption ratio (SAR), specific ions like sodium, chloride, and boron, as well as other factors like nitrogen, bicarbonate, and pH. It provides guidelines for classifying the degree of restriction on water use based on electrical conductivity (EC) and total dissolved solids (TDS) for salinity, and EC and SAR for infiltration problems. Maximum recommended concentrations are also given for trace elements that can cause toxicity issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesWaste Water Test
Waste Water Test
Uploaded by
munawarThis document discusses potential irrigation problems based on water quality parameters including salinity, sodium absorption ratio (SAR), specific ions like sodium, chloride, and boron, as well as other factors like nitrogen, bicarbonate, and pH. It provides guidelines for classifying the degree of restriction on water use based on electrical conductivity (EC) and total dissolved solids (TDS) for salinity, and EC and SAR for infiltration problems. Maximum recommended concentrations are also given for trace elements that can cause toxicity issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
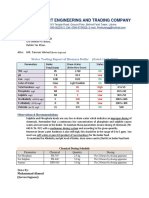
Potential irrigation problem Units Degree of restriction on use
None Slight to moderate Severe
Salinity
Ecw1 dS/m < 0.7 0.7 - 3.0 > 3.0
or
TDS mg/l < 450 450 - 2000 > 2000
Infiltration
SAR2 = 0 - 3 and ECw > 0.7 0.7 - 0.2 < 0.2
3 -6 > 1.2 1.2 - 0.3 < 0.3
6-12 > 1.9 1.9 - 0.5 < 0.5
12-20 > 2.9 2.9 - 1.3 < 1.3
20-40 > 5.0 5.0 - 2.9 < 2.9
Specific ion toxicity
Sodium (Na)
Surface irrigation SAR <3 3-9 >9
Sprinkler irrigation me/I <3 >3
Chloride (Cl)
Surface irrigation me/I <4 4 - 10 > 10
Sprinkler irrigation m /l3
<3 >3
Boron (B) mg/l < 0.7 0.7 - 3.0 > 3.0
Trace Elements
(see Table 10)
Miscellaneous effects
Nitrogen (NO3-N)3 mg/l <5 5 - 30 > 30
Bicarbonate (HCO3) me/I < 1.5 1.5 - 8.5 > 8.5
pH Normal range 6.5-8
ECw means electrical conductivity in deciSiemens per metre at 25°C
2
SAR means sodium adsorption ratio
3
NO3-N means nitrate nitrogen reported in terms of elemental nitrogen
Element Recommended Remarks
maximum
concentration (mg/l)
Al (aluminium) 5.0 Can cause non-productivity in acid soils (pH < 5.5), but
more alkaline soils at pH > 7.0 will precipitate the ion and
eliminate any toxicity.
As (arsenic) 0.10 Toxicity to plants varies widely, ranging from 12 mg/l for
Sudan grass to less than 0.05 mg/l for rice.
Be (beryllium) 0.10 Toxicity to plants varies widely, ranging from 5 mg/l for kale
to 0.5 mg/l for bush beans.
Cd (cadmium) 0.01 Toxic to beans, beets and turnips at concentrations as low
as 0.1 mg/l in nutrient solutions. Conservative limits
recommended due to its potential for accumulation in plants
and soils to concentrations that may be harmful to humans.
Co (cobalt) 0.05 Toxic to tomato plants at 0.1 mg/l in nutrient solution. Tends
to be inactivated by neutral and alkaline soils.
Cr (chromium) 0.10 Not generally recognized as an essential growth element.
Conservative limits recommended due to lack of knowledge
on its toxicity to plants.
Cu (copper) 0.20 Toxic to a number of plants at 0.1 to 1.0 mg/l in nutrient
solutions.
F (fluoride) 1.0 Inactivated by neutral and alkaline soils.
Fe (iron) 5.0 Not toxic to plants in aerated soils, but can contribute to soil
acidification and loss of availability of essential phosphorus
and molybdenum. Overhead sprinkling may result in
unsightly deposits on plants, equipment and buildings.
Li (lithium) 2.5 Tolerated by most crops up to 5 mg/l; mobile in soil. Toxic to
citrus at low concentrations (<0.075 mg/l). Acts similarly to
boron.
Mn (manganese) 0.20 Toxic to a number of crops at a few-tenths to a few mg/l, but
usually only in acid soils.
Mo (molybdenum) 0.01 Not toxic to plants at normal concentrations in soil and
water. Can be toxic to livestock if forage is grown in soils
with high concentrations of available molybdenum.
Ni (nickel) 0.20 Toxic to a number of plants at 0.5 mg/l to 1.0 mg/l; reduced
toxicity at neutral or alkaline pH.
Pd (lead) 5.0 Can inhibit plant cell growth at very high concentrations.
Se (selenium) 0.02 Toxic to plants at concentrations as low as 0.025 mg/l and
toxic to livestock if forage is grown in soils with relatively
high levels of added selenium. As essential element to
animals but in very low concentrations.
Sn (tin)
Ti (titanium) - Effectively excluded by plants; specific tolerance unknown.
W (tungsten)
C (vanadium) 0.10 Toxic to many plants at relatively low concentrations.
Zn (zinc) 2.0 Toxic to many plants at widely varying concentrations;
reduced toxicity at pH > 6.0 and in fine textured or organic
soils.
You might also like
- Astm B633Document6 pagesAstm B633Ho Bach100% (2)
- Water Treatment PlantDocument56 pagesWater Treatment PlantPiriyangan B100% (1)
- Discharge Standards in Dubai PDFDocument6 pagesDischarge Standards in Dubai PDFHRK65No ratings yet
- ADF Health Manual Vol 20, Part3, Chp1Document22 pagesADF Health Manual Vol 20, Part3, Chp1Seema NihalaniNo ratings yet
- 2014 Enthalpy Tutorial With Solution UpdatedDocument17 pages2014 Enthalpy Tutorial With Solution Updatedmenglay100% (4)
- Wms For Granite Flooring: Method StatmentDocument3 pagesWms For Granite Flooring: Method StatmentDeepak PatilNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Water QualityDocument4 pagesIrrigation Water QualityShahnaz GullNo ratings yet
- Environmental Quality Standards For Irrigation WaterDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Quality Standards For Irrigation Waterfurqan343No ratings yet
- Quality of Irrigation WaterDocument5 pagesQuality of Irrigation WatersaurabhNo ratings yet
- WKS G 8Document23 pagesWKS G 8debu1985No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Water Chemistry 1Document10 pagesUnit 5 Water Chemistry 1shishirNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Introduction: Genotech Inc. / USADocument21 pagesEnzyme Introduction: Genotech Inc. / USATuanNo ratings yet
- Salinity PartDocument54 pagesSalinity Partlunabellek13No ratings yet
- Salinity of WaterDocument6 pagesSalinity of WaterSoil Water EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Which Water Is Most Suitable For The Purpose of IrrigationDocument5 pagesWhich Water Is Most Suitable For The Purpose of IrrigationShahab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Which Water Is Most Suitable For The Purpose of IrrigationDocument6 pagesWhich Water Is Most Suitable For The Purpose of IrrigationShahab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nitrification Ammonia Oxidation in Wastewater Treatment Plants 1 2Document4 pagesNitrification Ammonia Oxidation in Wastewater Treatment Plants 1 2Mohannan RajamahendranNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Water QualityDocument47 pagesIrrigation Water QualityfarzanNo ratings yet
- ພັນທະສິນ ຄັນທະວົງ Tin Muang AyeDocument13 pagesພັນທະສິນ ຄັນທະວົງ Tin Muang AyeErika Ruth LabisNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Filtration & Water QualityDocument116 pages3.3 Filtration & Water QualityALINDA BRIANNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control For ETPDocument2 pagesPollution Control For ETPRiyanNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water ChlorinationDocument28 pagesDrinking Water ChlorinationHidroterm Plantas Electricas-VenezuelaNo ratings yet
- Water Quality ReportDocument12 pagesWater Quality Reportahmednoor765No ratings yet
- BLUEBERRY IRRIGATION Quality WaterDocument8 pagesBLUEBERRY IRRIGATION Quality WaterDaniel Alejandro GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water Standards of BIS (IS: 10500: 1991)Document7 pagesDrinking Water Standards of BIS (IS: 10500: 1991)kavurimaruthiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Water Quality ADocument34 pagesModule 5 Water Quality AAli ZubairNo ratings yet
- RGoB NEC Env Standards 2020Document17 pagesRGoB NEC Env Standards 2020wdNo ratings yet
- Cec603 13Document5 pagesCec603 13Facebook comNo ratings yet
- Cec603 13Document5 pagesCec603 13Swagstar SubhamNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engg. 3160611 - Lab ManualDocument64 pagesEnvironmental Engg. 3160611 - Lab ManualShreyas PatelNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment 2014Document81 pagesWaste Water Treatment 2014ankur neogNo ratings yet
- Amit Hanat - SHE - 807 - TWDocument2 pagesAmit Hanat - SHE - 807 - TWAmit HanatNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 Water Quality and ParametersDocument35 pagesModule - 2 Water Quality and ParametersEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- 6.1. Water Quality Test StandardsDocument3 pages6.1. Water Quality Test StandardsakbarifareedullahNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Part 1Document81 pagesWater Treatment Part 1Anonymous 8S7URr4F3vNo ratings yet
- Dupont Regenerant Quality IEX - 45-D01105-EnDocument5 pagesDupont Regenerant Quality IEX - 45-D01105-EnDFMNo ratings yet
- Vietnamese Standard TCVN 5945Document20 pagesVietnamese Standard TCVN 5945titsxuNo ratings yet
- ENVE102 Recitaion3 AnswersDocument6 pagesENVE102 Recitaion3 Answersdtokat04No ratings yet
- Water QualityDocument34 pagesWater QualitySarim ChNo ratings yet
- L3 T2 Try2 Soil Testing StarterDocument7 pagesL3 T2 Try2 Soil Testing Starterastaaus keeNo ratings yet
- Vol No 6 Water Quality & TreatmentDocument22 pagesVol No 6 Water Quality & TreatmentRaju AryalNo ratings yet
- Design of Water Treatment PlantDocument15 pagesDesign of Water Treatment PlantYousef ZamNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For DWQ in NL Sept 2020Document3 pagesGuidelines For DWQ in NL Sept 2020kabutiko24No ratings yet
- Effluent For Use in Irrigation RegulationsDocument3 pagesEffluent For Use in Irrigation RegulationsMatthieu QuevauvilliersNo ratings yet
- B S Recommendation For Treatment of Water of Steam Boilers & Water HeatersDocument5 pagesB S Recommendation For Treatment of Water of Steam Boilers & Water HeatersMahmoud Mahmoudm100% (3)
- Plenary Paper For The International Vetiver Conference, Thailand, January 2000Document16 pagesPlenary Paper For The International Vetiver Conference, Thailand, January 2000Tanya HannaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Unit 1 - Water Technology (2020)Document28 pagesNotes - Unit 1 - Water Technology (2020)Rakesh SawaiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-14 at 15.34.37Document5 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-14 at 15.34.37ogonogilizibe1No ratings yet
- Water Quality Standards For Best Designated UsagesDocument7 pagesWater Quality Standards For Best Designated UsagesSagar ApteNo ratings yet
- Basic Water 1Document21 pagesBasic Water 1ainmnrhNo ratings yet
- Bhu 202080Document8 pagesBhu 202080Mario Jesus Eguia CanchanyaNo ratings yet
- Bhu 202080Document8 pagesBhu 202080anilkumarak9532No ratings yet
- 3 Water QualityDocument98 pages3 Water QualityPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Biomass Boiler Report 11-02-2022Document1 pageBiomass Boiler Report 11-02-2022Mohammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- RODocument10 pagesROShahrooz Leo QureshiNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard Specifications For Drinking Water-1Document4 pagesIndian Standard Specifications For Drinking Water-1Thalakayala PraveenNo ratings yet
- Comparative Assessement of Heavy Metal Levels in Soil, Vegetables and Urban Grey Waste Water Used For Irrigation in Yola and KanoDocument9 pagesComparative Assessement of Heavy Metal Levels in Soil, Vegetables and Urban Grey Waste Water Used For Irrigation in Yola and KanoAshraf AhmadNo ratings yet
- WQ Report Z0056 HurlinghamDocument11 pagesWQ Report Z0056 HurlinghamkaddourNo ratings yet
- EPA RequiremnetDocument2 pagesEPA RequiremnetMicroChem MicroChemNo ratings yet
- Research On Effluent-Oxidation PondDocument6 pagesResearch On Effluent-Oxidation PondCHIN FelleNo ratings yet
- GARNETDocument1 pageGARNETtabdou16No ratings yet
- CP Cleaning Product ListDocument2 pagesCP Cleaning Product ListMarian SerbanNo ratings yet
- PIONIER 2076P Data SheetDocument1 pagePIONIER 2076P Data SheetAlexis GaydaNo ratings yet
- PDF - 16012777053 SABIT PRIMER D-41Document1 pagePDF - 16012777053 SABIT PRIMER D-41MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hawaii Department of Health MemoDocument18 pagesHawaii Department of Health MemoHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet
- Keller & BohacekDocument3 pagesKeller & BohacekCarlos TomeyNo ratings yet
- Yane BrochureDocument2 pagesYane BrochureOmah HijaoeNo ratings yet
- Biodata VirendraDocument4 pagesBiodata VirendraChant SalaNo ratings yet
- Explosives Report (3 Bscrim C)Document21 pagesExplosives Report (3 Bscrim C)Cloaue Camari�asNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Installation of Fire ProDocument4 pagesMethodology For Installation of Fire Proswamy100% (1)
- w03 Burn-Lab-WorksheetDocument3 pagesw03 Burn-Lab-Worksheetapi-541412091No ratings yet
- Black Cotton SoilDocument4 pagesBlack Cotton Soilibson045001256100% (2)
- Swagelok SS RL3S4Document2 pagesSwagelok SS RL3S4dewNo ratings yet
- Bom For Residential BuildingsDocument3 pagesBom For Residential BuildingsAaron Casey LorectoNo ratings yet
- Some Engineering Characteristics of Lime-Treated Soil of Semeel Region With Emphasis On Compaction DelayDocument16 pagesSome Engineering Characteristics of Lime-Treated Soil of Semeel Region With Emphasis On Compaction DelayRafi Mahmoud SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Vel Api603 99 Web PDFDocument10 pagesVel Api603 99 Web PDFAndres CortezNo ratings yet
- EVAPCO Fill Offerings 1Document4 pagesEVAPCO Fill Offerings 1Walter J Naspirán CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Stearyl Acrylate (SA 18 BASF)Document2 pagesStearyl Acrylate (SA 18 BASF)Rashid SaleemNo ratings yet
- 1.-Alambre Tubular Flux Core Hobart-Fabco-803-MSDS PDFDocument4 pages1.-Alambre Tubular Flux Core Hobart-Fabco-803-MSDS PDFluis armandoNo ratings yet
- Educationprogramme: The School of Concrete TechnologyDocument28 pagesEducationprogramme: The School of Concrete TechnologyThabiso Jacob MokwenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1Dr. Aung Ko LattNo ratings yet
- Decalcification and DehydrationDocument5 pagesDecalcification and DehydrationAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialDocument15 pagesBuilding Materialbirendra prasadNo ratings yet
- Uht 75 Uht 79Document1 pageUht 75 Uht 79ALI MESSAOUDINo ratings yet
- Smartcare Damp Block Sample TdsDocument2 pagesSmartcare Damp Block Sample TdsrudrabirNo ratings yet
- Mandals - AquamanDocument1 pageMandals - Aquamanplain xiaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Questions IndiabixDocument22 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Questions IndiabixPavan KalyanNo ratings yet