Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiac 1.33 Heart Blocks PDF
Cardiac 1.33 Heart Blocks PDF
Uploaded by
Mitzi BelamideOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiac 1.33 Heart Blocks PDF
Cardiac 1.33 Heart Blocks PDF
Uploaded by
Mitzi BelamideCopyright:
Available Formats
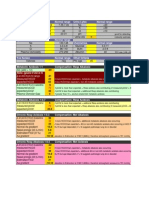
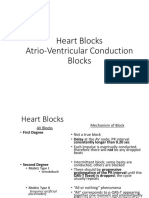
HEART BLOCKS
FAILURE OF THE HEART’S NATURAL PACEMAKER DUE TO OBSTRUCTION
(“BLOCK”) IN THE ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART.
Relationship of P waves to QRSs
All P waves are No P waves are
Some P waves are
followed by a followed by
not followed by QRSs
QRS but PR is >0.20 (associated with)
QRSs (i.e.,
AV dissociation)
First-Degree Progressive Every other PR interval of
AV block lengthening of P wave is not conducted P wave
PR until a conducted (2:1) is consistent
P is not
followed by
a QRS, then
repeated
QRS QRS is Only one More than QRS QRS is
< 0.12 0.12 or > P wave in one P wave < 0.12 0.12 or >
a row is not in a row
conducted is not
conducted
Second- Second- Second- Second- High Complete Complete
degree degree degree degree grade heart block heart block
AV block, AV block, AV block, AV block, AV block with with
Type I Type I Type II Type II junctional ventricular
escape escape
rhythm rhythm
1° 2° Type I 2° Type II 3°
Benign but Block at AV node, Block at Bundle of Ventricular
can progress usually transient, His, occurs with asystole in absence
does not usually anterior MI, often of escape beat
Significance
progress progresses to
complete block
Observation, Close monitoring, Atropine, Pacemaker,
d/c digitalis use d/c digitalis use, transcutaneous atropine, monitor
Treatment treat if patient or transvenous for hypoperfusion
is symptomatic pacemaker
NRSNG.com - “Tools and Confidence to Succeed in Nursing School.”
©2017 TazKai LLC | NRSNG.com - Reproduction Strictly Prohibited
Disclaimer information at NRSNG.com
You might also like
- ECG Apib PDFDocument68 pagesECG Apib PDFArthur KakarekoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Profusion Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Peripheral Tissue Profusion Care Planstacie4roher4smithNo ratings yet
- Oral Dosage Forms That Should Not Be Crushed 2016Document16 pagesOral Dosage Forms That Should Not Be Crushed 2016MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolyte Imbalancessccctutor100% (2)
- Drug Classificati On Indications Action Route/Dos e Side Effects Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument7 pagesDrug Classificati On Indications Action Route/Dos e Side Effects Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJenny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pharm Expansion 17 NDFDocument1 pagePharm Expansion 17 NDFNokz M. Raki-inNo ratings yet
- Parenting Styles: - Dictatorial or AuthoritarianDocument45 pagesParenting Styles: - Dictatorial or AuthoritarianCourseTree LearningNo ratings yet
- Transport of Critically Ill Adults 2011Document1 pageTransport of Critically Ill Adults 2011velocity25No ratings yet
- Ace Inhibutors MailDocument5 pagesAce Inhibutors MailWendy AdaoNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesIschaemic Heart DiseaseEB100% (1)
- Glutamate: Neurotransmitters Disturbed Increased Sympathetic Stimulation Increased Autonomic StimulationDocument3 pagesGlutamate: Neurotransmitters Disturbed Increased Sympathetic Stimulation Increased Autonomic StimulationCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations ListDocument6 pagesAbbreviations ListolivedaisychainNo ratings yet
- SBAR Communication Tool and Progress NoteDocument2 pagesSBAR Communication Tool and Progress Notejrj1111100% (1)
- Ace Inhibitors MnemonicDocument1 pageAce Inhibitors MnemonicGirish Waru0% (2)
- Common Lab ValuesDocument4 pagesCommon Lab ValuesRaf LuisNo ratings yet
- Beta Blockers Cheat Sheet: Happy Nursing!Document1 pageBeta Blockers Cheat Sheet: Happy Nursing!GloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Administering Vaccines To AdultsDocument1 pageAdministering Vaccines To AdultsPaul Anthony LoricaNo ratings yet
- GI Motility DrugsDocument1 pageGI Motility DrugspulmonologistNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument3 pagesDrug CardsDave HillNo ratings yet
- Suffixes and PrefixesDocument2 pagesSuffixes and PrefixesNiksNo ratings yet
- Drugs SummaryDocument23 pagesDrugs Summaryapi-3832811100% (1)
- Cardiac Conditions Cardiac Dysrhythmias: B. Sinus BradycardiaDocument5 pagesCardiac Conditions Cardiac Dysrhythmias: B. Sinus BradycardiaIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument9 pagesEmergency DrugsaldwinngNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agents: Mrs. Michelle A. Iduria, RN, MAN LecturerDocument131 pagesCardiovascular Agents: Mrs. Michelle A. Iduria, RN, MAN LecturerNiala AlmarioNo ratings yet
- An Easy Guide To Head To Toe Assessment Vrtis 2011-1 PDFDocument6 pagesAn Easy Guide To Head To Toe Assessment Vrtis 2011-1 PDFkatherine dayagNo ratings yet
- List of Antidotes: No. Drugs AntidoteDocument3 pagesList of Antidotes: No. Drugs AntidotearjumandNo ratings yet
- 3M CVP Monitoring - Assisting in BMA ECG Interpretation - Final Draft - 3CDocument65 pages3M CVP Monitoring - Assisting in BMA ECG Interpretation - Final Draft - 3CAlexa GoteraNo ratings yet
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews (PDFDrive) - Pages-396Document1 pageLippincott Illustrated Reviews (PDFDrive) - Pages-396Eman ShalabyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- Diabetes Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesDiabetes Cheat Sheetmxy8jkn8pnNo ratings yet
- Conduction System: Rhythm Identification and TreatmentDocument12 pagesConduction System: Rhythm Identification and Treatmenthops23No ratings yet
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Document43 pagesMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- Telemetry Patient Shift ReportDocument2 pagesTelemetry Patient Shift ReportSweta100% (1)
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocument28 pagesAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Regularity Life Threatening CausesDocument3 pagesRhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Regularity Life Threatening CausesLedio XhezairiNo ratings yet
- Management of Hypertension: Affan Syafiqi - Nurul Husna - Audi RahmanDocument77 pagesManagement of Hypertension: Affan Syafiqi - Nurul Husna - Audi RahmanRavi K. ShuklaNo ratings yet
- West Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessDocument4 pagesWest Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessPhylum Chordata100% (1)
- Labs Electrolyte ChartDocument1 pageLabs Electrolyte ChartmdcmepNo ratings yet
- Ecg Crit - CareDocument55 pagesEcg Crit - CarekrismatactayNo ratings yet
- Blank Physical Assessment SheetDocument2 pagesBlank Physical Assessment SheetRenee Hickman RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Acid Base EquationsDocument21 pagesAcid Base EquationsBen JonesNo ratings yet
- Top 93 Nursing SkillsDocument25 pagesTop 93 Nursing SkillsericNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Blood DisordersDocument1 pageDrugs in Blood DisordersSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A ReviewDocument15 pagesPharmacology A ReviewKathrynne MendozaNo ratings yet
- Common Prefixes and SuffixesDocument5 pagesCommon Prefixes and Suffixestriddle1969100% (1)
- Medication Worksheets 4Document3 pagesMedication Worksheets 4AshleighNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 3 - Management of Heart FailureDocument59 pagesPharmacology 3 - Management of Heart Failurealbatros000No ratings yet
- Acs Nstemi PathwayDocument3 pagesAcs Nstemi PathwayAliey's SKeplek NgeNersNo ratings yet
- Neurologic DiseasesDocument13 pagesNeurologic DiseasesCzarinah BacuadoNo ratings yet
- MI MEDIC CARDS - Reference MaterialDocument26 pagesMI MEDIC CARDS - Reference MaterialAylinNo ratings yet
- Cs-Cardiac-023-Essential Cardiac LabsDocument2 pagesCs-Cardiac-023-Essential Cardiac LabsColeen YraolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTheresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Stroke 1Document1 pageStroke 1Trisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- IMG EmpAposterDocument1 pageIMG EmpAposterChiu LeoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac: Heart SoundsDocument4 pagesCardiac: Heart SoundsSara PirmanNo ratings yet
- 100 Beats Per Minute. Many DifferentDocument4 pages100 Beats Per Minute. Many Differentjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Agents Used in Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesAgents Used in Cardiac ArrhythmiasKaye PatriaNo ratings yet
- AV BlocksDocument53 pagesAV Blocksrebebravoiniguez642No ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument149 pagesCardiologyMuhammad SyafiqNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationDocument21 pages2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationmariaNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease: Etiology PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesValvular Heart Disease: Etiology PathophysiologyensiNo ratings yet
- Heart and Vascular SystemDocument12 pagesHeart and Vascular SystemironNo ratings yet
- Medicine Lecture 17,18Document51 pagesMedicine Lecture 17,18Nayela AkramNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesCalcium Channel BlockersBrittany RamirezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MyxomaDocument4 pagesCardiac MyxomaAve FenixNo ratings yet
- Cardio Quiz For NSG 128 HDocument22 pagesCardio Quiz For NSG 128 HMac MacapilNo ratings yet
- Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyDocument10 pagesHypertrophic CardiomyopathySam SonNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Laura AriasDocument2 pagesHomework 1 Laura Ariasapi-725606760No ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Document36 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Nafisa TasnimNo ratings yet
- Fitz Cardiology Paces NotesDocument26 pagesFitz Cardiology Paces NotesMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- AED (Automated External Defibrilation)Document17 pagesAED (Automated External Defibrilation)Ari AsriniNo ratings yet
- ECG Masters' Collection Volume 2Document218 pagesECG Masters' Collection Volume 2Илија Радосављевић100% (1)
- Bradicardy ManagementDocument7 pagesBradicardy ManagementTAUFIK RAMADHAN BIYANo ratings yet
- PathoDocument2 pagesPathohrry stylesNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Anestesiologi INDONESIADocument17 pagesJURNAL Anestesiologi INDONESIAPutri SatrianyNo ratings yet
- Noile Ghiduri de Resuscitare Cardio Respiratorie (RCR) : D. SăndescDocument36 pagesNoile Ghiduri de Resuscitare Cardio Respiratorie (RCR) : D. Săndescragerunner16100% (1)
- Chronic Heart Failure Case FileDocument2 pagesChronic Heart Failure Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Additional Heart Sounds-Part 1 (Third and Fourth Heart Sounds)Document10 pagesAdditional Heart Sounds-Part 1 (Third and Fourth Heart Sounds)Emmanuel Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Atrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Document2 pagesAtrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Maxinne GorospeNo ratings yet
- Mini Test QUIZDocument9 pagesMini Test QUIZAbdul RohimNo ratings yet
- Dapus StemiDocument103 pagesDapus StemiNaufal RizalNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- 2014 CCM Review Notes Jon-Emile S. Kenny M.D, 2014Document142 pages2014 CCM Review Notes Jon-Emile S. Kenny M.D, 2014PkernNo ratings yet
- ACCSAP 10 ArrhythmiaDocument129 pagesACCSAP 10 ArrhythmiaMuhammad Javed GabaNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia - WikipediaDocument76 pagesArrhythmia - WikipediaJamesNo ratings yet
- Cvs - 10 ConsolidatedDocument37 pagesCvs - 10 ConsolidatedezhilNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument47 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeshorosuNo ratings yet
- Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia/Ventricular Fibrillation Algorithm (Figure 8-5)Document1 pagePulseless Ventricular Tachycardia/Ventricular Fibrillation Algorithm (Figure 8-5)Dyan IslamiNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: History and Clinical Assessment Suggest ACSDocument12 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: History and Clinical Assessment Suggest ACSginongNo ratings yet