Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eye Floaters
Uploaded by
Ysa VargasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye Floaters
Uploaded by
Ysa VargasCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are ‘Eye Floaters’
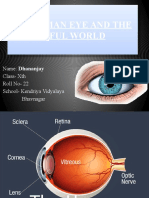
Eye floaters are deposits or condensation in the vitreous, the material that fills the posterior part
of the eye. People use the term eye floaters to describe seeing spots within their vision that move
or "float" when they look around. They may be present in only one eye or both eyes.
What Can Be The Cause?
Most eye floaters are caused by age-related changes that occur as the jelly-like substance
(Vitreous) inside your eyes becomes more liquid. Microscopic fibers within the vitreous tend to
clump and can cast tiny shadows on your retina. The shadows you see are called floaters.
Sometimes a section of the vitreous pulls the fine fibers away from the retina all at once, causing
many new floaters to appear suddenly. This is called a vitreous detachment, which in most cases is
not sight-threatening and requires no treatment.
However, a sudden increase in floaters, possibly accompanied by light flashes or peripheral (side)
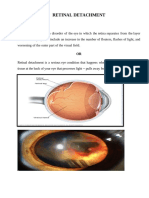
vision loss, could indicate a retinal detachment. A retinal detachment occurs when any part of the
retina, the eye’s light-sensitive tissue, is lifted or pulled from its normal position at the back wall of
the eye.
A retinal detachment is a serious condition and should always be considered an emergency. If left
untreated, it can lead to permanent visual impairment within two or three days or even blindness
in the eye.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye floaters may include:
Small shapes in your vision that appear as dark specks or knobby, transparent strings of
floating material.
Spots that move when you move your eyes, so when you try to look at them, they move
quickly out of your visual field.
Spots that are most noticeable when you look at a plain bright background, such as a blue
sky or a white wall.
Small shapes or strings that eventually settle down and drift out of the line of vision.
When To See A Doctor?
Contact an eye specialist immediately if you notice:
Many more eye floaters than usual.
A sudden onset of new floaters.
Flashes of light in the same eye as the floaters.
Darkness on any side or sides of your vision (peripheral vision loss).
You might also like
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Vitreous DegenerationDocument3 pagesVitreous DegenerationameliaNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument7 pagesCataractNader Smadi100% (2)
- What Are Eye FloatersDocument4 pagesWhat Are Eye FloatersSaravanan ThiruvalathaanNo ratings yet
- What Causes "Eye Floaters"Document3 pagesWhat Causes "Eye Floaters"kekeyaNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument8 pagesRetinal DetachmentMaisarah BakariNo ratings yet
- Entoptic PhenomenaDocument11 pagesEntoptic PhenomenaRizkyAgustriaNo ratings yet
- Eye DisorderDocument14 pagesEye DisorderhuehueNo ratings yet
- Visual SystemDocument6 pagesVisual SystemJobelle Acena100% (1)
- CataractDocument6 pagesCataractKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument2 pagesRetinal Detachmentwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- Rhegmatogenous (reg-ma-TODGE-uh-nus) - These Types of Retinal DetachmentsDocument2 pagesRhegmatogenous (reg-ma-TODGE-uh-nus) - These Types of Retinal Detachmentsmedhat444444No ratings yet
- Eye FloaterDocument10 pagesEye FloaterIka KrastanayaNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument6 pagesRetinal DetachmentNader Smadi100% (3)
- Biology - The Eye (Cateracts)Document5 pagesBiology - The Eye (Cateracts)Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Eye Disorders-1Document11 pagesIntroduction To Eye Disorders-1bhavani GNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument72 pagesHuman EyeDhananjayNo ratings yet
- Ochiul Si Bolile SaleDocument7 pagesOchiul Si Bolile SaleRares PopeiaNo ratings yet
- Sight SavingDocument3 pagesSight SavingenelrahNo ratings yet
- The Most Common Causes of Eye Problems1Document4 pagesThe Most Common Causes of Eye Problems1shree ganeshNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument7 pagesRetinal Detachmentjay dewanagnNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument5 pagesCataractTriXie SorrillaNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument16 pagesRetinal DetachmentCandice Lim Swee LingNo ratings yet
- Causes of Blurred VisionDocument3 pagesCauses of Blurred Visionsintia mariaNo ratings yet
- EyelidDocument3 pagesEyelidCLOYD MARVINNo ratings yet
- Cataracts: What Are They?Document3 pagesCataracts: What Are They?RSarkawyNo ratings yet
- Lens Iris Pupil Retina: Cataract OverviewDocument5 pagesLens Iris Pupil Retina: Cataract Overviewrizky_kurniawan_14No ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument15 pagesRefractive ErrorsMubasher 783No ratings yet
- CataractDocument17 pagesCataractrhopmaeNo ratings yet
- CataractsDocument7 pagesCataractsapi-308128710No ratings yet
- Light Sensitivity Photophobia 2019Document13 pagesLight Sensitivity Photophobia 2019rgrr feNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Refractive ErrorsDocument26 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Refractive ErrorsAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Disorders Related To VisionDocument4 pagesDisorders Related To VisionAkhwand SaulatNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Causes CataractsDocument5 pagesSymptoms and Causes CataractsEmma KalmanNo ratings yet
- Eye DefectsDocument3 pagesEye DefectsAbdul HannanNo ratings yet
- Cataracts: A Leading Cause of Preventable Blindness: Neda Karimi, M.D. Represented by Dr.R.Handoko Pratomo, SPMDocument71 pagesCataracts: A Leading Cause of Preventable Blindness: Neda Karimi, M.D. Represented by Dr.R.Handoko Pratomo, SPMNefri TiawarmanNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Detection: Crystalline Lens Eye Opacity MyopiaDocument5 pagesSymptoms and Detection: Crystalline Lens Eye Opacity MyopiaNica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Visual SystemDocument7 pagesVisual SystemJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Eye Defects and Latest Technological SolutionsDocument26 pagesEye Defects and Latest Technological SolutionsAaron Marcus R. De LeonNo ratings yet
- Eye DiseasesDocument2 pagesEye DiseasesRaju ShresthaNo ratings yet
- A Picture of The Eye: Articles Oneye BasicsDocument5 pagesA Picture of The Eye: Articles Oneye BasicsAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Light Sensitivity FactsheetDocument9 pagesLight Sensitivity FactsheetJuan DevotoNo ratings yet
- Students Will Understand That : NotesDocument5 pagesStudents Will Understand That : Notesapi-143696211No ratings yet
- Cataracts The Mayo ClinicDocument6 pagesCataracts The Mayo ClinicJandz MNNo ratings yet
- Impaired VisionDocument3 pagesImpaired VisionJannelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument5 pagesCataractAbhinandan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prism and StrabismusDocument19 pagesPrism and StrabismusSharon Danisha VaswaniNo ratings yet
- CATARACTDocument9 pagesCATARACTHemant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cataracts Diabetes Diuretics EyeDocument4 pagesCataracts Diabetes Diuretics Eyevandana singhNo ratings yet
- Notes On EyesDocument6 pagesNotes On EyesSashoy AustinNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesBio Investigatory ProjectBushraNo ratings yet
- Coloboma PresentationDocument3 pagesColoboma Presentationaaribatiq2No ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument19 pagesRetinal DetachmentJohn Hans CaturasNo ratings yet
- Reffractive ErrorsDocument13 pagesReffractive ErrorsSagiraju SrinuNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye: Written For Physics 106 Friday, Nov. 7, 2008Document20 pagesThe Human Eye: Written For Physics 106 Friday, Nov. 7, 2008ManishDebNo ratings yet
- CataractsDocument7 pagesCataractsOktovia KakaNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms of Macular DegenerationDocument19 pagesSigns and Symptoms of Macular DegenerationJayveersinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Visual DefectsDocument1 pageVisual DefectsOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument1 pageThe EyeAkshaya RajangamNo ratings yet