Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP For Hypertension
Uploaded by
Jaic Ealston D. Tampus0%(2)0% found this document useful (2 votes)
7K views6 pages1. The patient presented with occasional blurry vision and elevated blood pressure.
2. An assessment found tachycardia, rales, cool clammy skin, and the use of corrective glasses. The diagnosis was ineffective tissue perfusion related to hypertension and decreased cardiac output.
3. The plan was to monitor vital signs every 1-2 hours, decrease caffeine intake, administer antihypertensive drugs, and maintain blood pressure within normal limits. The goals were to stabilize the patient's condition and maintain normal blood pressure over the short and long term.
Original Description:
hypertension nursing care plan
Original Title
63953059 Ncp for Hypertension
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The patient presented with occasional blurry vision and elevated blood pressure.
2. An assessment found tachycardia, rales, cool clammy skin, and the use of corrective glasses. The diagnosis was ineffective tissue perfusion related to hypertension and decreased cardiac output.
3. The plan was to monitor vital signs every 1-2 hours, decrease caffeine intake, administer antihypertensive drugs, and maintain blood pressure within normal limits. The goals were to stabilize the patient's condition and maintain normal blood pressure over the short and long term.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(2)0% found this document useful (2 votes)
7K views6 pagesNCP For Hypertension
Uploaded by
Jaic Ealston D. Tampus1. The patient presented with occasional blurry vision and elevated blood pressure.
2. An assessment found tachycardia, rales, cool clammy skin, and the use of corrective glasses. The diagnosis was ineffective tissue perfusion related to hypertension and decreased cardiac output.
3. The plan was to monitor vital signs every 1-2 hours, decrease caffeine intake, administer antihypertensive drugs, and maintain blood pressure within normal limits. The goals were to stabilize the patient's condition and maintain normal blood pressure over the short and long term.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
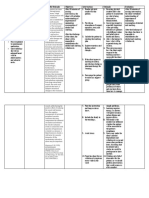
ACTUAL PROBLEM
Problem # 1
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SIGNIFICANT BASIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
S: “usahay malipong ug Decreased Stimulation of vasomotor Short-Term Assess underlying To determine Short-Term
maglabad gamay akong Cardiac center (loc in medulla) send Objective: condition what triggers the Objective:
tan-kugo if musaka Output impulses to CNS elevated BP
akong BP”, as verbalized related to After 8 hours of Changes in BP After 8 hours of
by the patient. elevated Acethylcoline released by nursing Monitor blood may indicates nursing
blood prosta preganglionic neurons intervention the pressure for every changes in intervention the
pressure as clients blood 30 minutes patients status client has no
O: manifested by Preganglionic fiber releases pressure will requiring prompt elevation in his
Conscious and occipital decreased to medical attention blood pressure
coherent headache Norepinephrine(constriction acceptable limits Observe skin color, Peripheral Goal was met
Able to perform of blood vessel thereby temperature, vasoconstriction
ADL’s increasing blood pressure capillary refill, and may result in
Dizziness noted diaphoresis pale,cool,clammy
occasionally adrenal medulla secrets skin,with
With initial vital signs epinephrine prolonged
of capillary refill
BP:140/100mmHg increased blood pressure time
PR: 103 bpm causing it to increase blood Long-Term Do frequent It may decrease Long-Term
RR: 18 bpm supply in the brain causing Objective: positioning to the peripheral Objective:
Temp: 36.9°c occipital headache patient venous pooling
After 3-5 days of that may After 3-5 days of
nursing potentiated by nursing
interventions the vasodilators and intervention the
client will prolong sitting or patient maintains
maintain normal standing a stable blood
and stable blood Administer Inhibits influx of pressure Goal
pressure prescribed drugs Calcium ion was met.
(anti-hypertensive) across cell
as maintenance membrane to
produce
relaxation of
coronary smooth
muscle
Encouraged pt to This are cardiac
decrease intakes of stimulant and
caffeine, cola ,and may adversely
chocolate affect cardiac
function
Emphasize the Hypertension is
concept of life time illness,
controlling controlling it is
hypertension rather the best way to
than curing it. stop it from
reoccurring
Encouraged patient Salty and fatty
to maintain low salt food are one of
low fat diet the common
cause of
hypertension
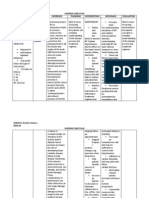
Problem # 2
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SIGNIFICANT BASIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
S: “usahay malipong ug Ineffective Tissue Stimulation of vasomotor Short-Term Monitor VS at least To monitor Short-Term
maglabad gamay akong Perfusion: center (loc in medulla) send Objective: q 1-2 hrs and prn. baseline data. Objective:
tan-kugo if musaka Cardiopulmonary, impulses to CNS
akong BP”, as verbalized Gastrointestinal After 8 hrs of Encourage patient Caffeine is a After 8 hrs of
by the patient. and Peripheral r/t Acethylcoline released by nursing to decrease intake cardiac nursing
hypertension and prosta preganglionic interventions, of caffeine, cola stimulant and interventions,
decreased cardiac neurons blood pressure and chocolates. may adversely blood pressure
O: output as will be within set affect cardiac maintained
Tachycardia manifested by Preganglionic fiber releases parameters for Administer function. within set
Rales blurred vision and the client. vasoactive drugs These frugs have parameters for
Cool, clammy skin increased blood Norepinephrine(constriction and titrate as rapid action and the client.
Noted usage of pressure of blood vessel thereby ordered to may decrease Goal was met.
correctional glasses, increasing blood pressure maintain pressures the blood
blurry vision at set parameters pressure too
occasionally persist adrenal medulla secrets for patient. rapidly, resulting
Increased blood epinephrine in complications.
pressure
With initial vital signs vasoconstriction of Long-Term May indicate
of bloodvessels causing it to Objective: Observe for cyanide toxicity Long-Term
BP:140/100mmHg release renin complaints of from increasing Objective:
PR: 103 bpm After 3-5 days of blurred vision, intracranial
RR: 18 bpm angiotensin I conver to nursing tinnitus or pressure. After 3-5 days of
Temp: 36.9°c angiotensin interventions, confusion. I&O will give an nursing
II(vasoconstriction) the client will indication of interventions,
have an fluic balance or the client had an
secretion of aldosterone adequate tissue Monitor I&O imbalance, thus adequate tissue
causing sodium and water to perfusion to his status. allowing for perfusion to his
retained witch leads to body systems. changes in body systems.
increase intravascular treatment Goal was met.
volume regimen when
required.
poor circulation
less oxygen supply in the Monitor for May indicate
brain & Heart sudden onset of dissecting aortic
chest pain. aneurysm.
leads to blurry vision,
Compensatory Increased of Monitor ECG for Decreased
Heart rate changes in rate, perfusion may
rhythm, result in
dysrhythmias and dysrhythmias
conduction caused by
defects. decrease in
oxygen.
Observe Bedrest
extremities for promotes
swelling, venous statis
erythema, which can
tenderness and increase the risk
pain. Observe for of
decreased thromboembolu
peripheral pulses, s formation. If
pallor, coldness treatment is too
and cyanosis. rapid and
aggressive in
decreasing the
blood pressire,
tissue perfusion
will be impaired
and ischemia
can result.
Instruct client in Promotes
signs/symptoms to knowledge and
report to physician compliance with
such as headache treatment.
upon rising, Promotes
increased blood prompt
pressure, chest detection and
pain, shortness of facilitates
breath, increased prompt
heart rate, visual intervention.
changes, edema,
muscle cramps and
nausea and
vomiting.
POTENTIAL PROBLEM
Problem # 3
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SIGNIFICANT BASIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
S: “usahay malipong ug Ineffective Tissue Stimulation of vasomotor Short-Term Assess for general To determine Short-Term
maglabad gamay akong Perfusion: center (loc in medulla) send Objective: status what causes the Objective:
tan-kugo if musaka akong Cardiopulmonary, impulses to CNS dizziness and
BP”, as verbalized by the Gastrointestinal After 8 hrs of what health After 8 hrs of
patient. and Peripheral r/t Acethylcoline released by nursing teaching to nursing
hypertension and prosta preganglionic interventions, provide interventions,
decreased cardiac neurons blood pressure Assess level of To monitor blood pressure
O: output as will be within consciousness patient’s maintained
Conscious and manifested by Preganglionic fiber releases set parameters changes of within set
coherent blurred vision and for the client. sensorium; parameters for
Dizziness noted increased blood Norepinephrine(constriction Increased BP the client.
Able to do ADL’s pressure of blood vessel thereby may indicates Goal was met.
with assistance increasing blood pressure increased in
Initial v/s of cerebrovascular
BP:140/100mmHg adrenal medulla secrets pressure
PR: 103 bpm epinephrine
RR: 18 bpm Monitor vital To monitor
Temp: 36.9°c vasoconstriction of Long-Term signs especially patients status
bloodvessels causing it to Objective: blood pressure increase in BP Long-Term
release renin indicates Objective:
After 3-5 days of increased in
angiotensin I conver to nursing cerebrovascular After 3-5 days of
angiotensin interventions, pressure nursing
II(vasoconstriction) the client will Monitor for the To determine if interventions
have an side effect of this drugs has the patient is
secretion of aldosterone adequate tissue drugs given something to do now free from
causing sodium and water to perfusion to his with the dizziness and
retained witch leads to body systems. patients able to do ADL’s
increase intravascular dizziness without any fear
volume from being
Limit activities This may help injured.
poor circulation and maintain alleviate
quite, non dizziness by
less oxygen supply in the stressful letting the client
brain & Heart environment have peaceful
rest
leads to blurry vision, Position patient in Trendelenburg
Compensatory Increased of a trendelenburg position
Heart rate position facilitates easy
back flow of
blood from the
heart
Provide safety by To prevent the
raising the side patient from
rails falling down in
the bed
Encouraged to Sudden
avoid sudden movement
movement aggravate the
dizziness
Advised SO to to have
always somebody to
accompany the help her
patient whenever the
dizziness will
occur
You might also like
- Critical Care Note PDFDocument10 pagesCritical Care Note PDFlml100% (1)
- Brief Cope PDF Assessment ScoringDocument2 pagesBrief Cope PDF Assessment ScoringGian100% (2)
- Quality Assurance in The Blood Transfusion LabDocument25 pagesQuality Assurance in The Blood Transfusion LabMichelle AnsahNo ratings yet
- NCP For HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP For Hypertensionrhizalyn1367% (6)
- NCP For Dizziness and HeadacheDocument4 pagesNCP For Dizziness and Headachekarthi karthi100% (1)
- Hypertension NCPDocument1 pageHypertension NCPj4royce100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output NCPmicah1318100% (2)
- Managing Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesManaging Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac Outputanon_9189425950% (2)
- Fdar - 2 HypertensionDocument12 pagesFdar - 2 HypertensionGinena Belarmino100% (3)
- Nursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Document7 pagesNursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Rosalie Valdez Espiritu100% (3)
- Knowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionDocument2 pagesKnowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- Endoscopic DacryocystorhinostomyDocument17 pagesEndoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomyapi-19500641No ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPJusTin Cargason100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionKathleen Dimacali100% (2)
- NCP For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNCP For HypertensionCiariz Charisse83% (6)
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocument6 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaNursesLabs.com100% (7)
- Case Study 3 - HCVDDocument12 pagesCase Study 3 - HCVDJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- NCP DizzinessDocument2 pagesNCP Dizzinesschristine mercadoNo ratings yet
- ANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlexis TineNo ratings yet
- NCP - PreeclampsiaDocument3 pagesNCP - PreeclampsiaRap De la Cruz50% (2)
- The Role of The Registered Nurse As Charge NurseDocument6 pagesThe Role of The Registered Nurse As Charge NurseJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Beta His Tine Drug D TudyDocument2 pagesBeta His Tine Drug D TudyVian ArccenioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hypertensionmariejo89% (82)
- CongenitalcholesteatomaDocument20 pagesCongenitalcholesteatomaMeilina Elin WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (2)
- NCP Acute Pain (HTN Crisis)Document3 pagesNCP Acute Pain (HTN Crisis)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 and Soapie 1Document5 pagesNCP 2 and Soapie 1narsD100% (1)
- Uses of Inhaler DevicesDocument39 pagesUses of Inhaler Devicesluis_chubeeNo ratings yet
- NCP HPNDocument5 pagesNCP HPNGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- NCP HPNDocument5 pagesNCP HPNGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- NCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument22 pagesNCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeAnnNo ratings yet
- Case Study - EmphysemaDocument6 pagesCase Study - Emphysemamackie_041992No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation EffectivenessDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation EffectivenessYnah Sayoc75% (4)
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDocument4 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Hypertension NCPDocument4 pagesHypertension NCPChristian Karl B. Llanes0% (2)
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Hypertensionsinister1781% (27)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionJessy MalloNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument3 pagesNutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementSitty Aizah MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure NCPDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure NCPShaira Ann Calamba100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Hypertensionderic98% (124)
- Nur81 NCP GastroDocument4 pagesNur81 NCP GastroJordan Gonzales100% (1)
- AML Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAML Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- NCP Chest PainDocument2 pagesNCP Chest PainLinsae Troy50% (2)
- Philippine Nursing Act of 2002 SummaryDocument13 pagesPhilippine Nursing Act of 2002 SummaryJenniiLyn Deeo ÜNo ratings yet
- NCP Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decrease Cardiac OutputAnonymous 2hJKVrNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis92% (13)
- Managing Hypertension Through Diet and Lifestyle ChangesDocument1 pageManaging Hypertension Through Diet and Lifestyle ChangesChristian Daayata0% (1)
- NCP Hypertension 2Document3 pagesNCP Hypertension 2Roseben Somido50% (2)
- NCP - Anxiety Hypertension)Document3 pagesNCP - Anxiety Hypertension)Jaja Jaime100% (2)
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Managing Respiratory Issues with Breathing Exercises and MedicationsDocument2 pagesManaging Respiratory Issues with Breathing Exercises and MedicationsGraphaiene Neika WacasNo ratings yet
- NCP For CipDocument22 pagesNCP For CipBing DayaoNo ratings yet
- NCP SGHDocument2 pagesNCP SGHdaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Ncp Sgh DianaDocument2 pagesNcp Sgh Dianadaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageRationale EvaluationAshraf DalumaNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document4 pagesActivity 5AngieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Cues Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Cues Nursing DiagnosisKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR CHEST PAIN AND VOMITINGDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR CHEST PAIN AND VOMITINGApril Kate BanagodosNo ratings yet
- Managing Shortness of Breath in Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesManaging Shortness of Breath in Rheumatic Heart DiseaseGail NamangdanNo ratings yet
- NCP Chest PainDocument2 pagesNCP Chest PainCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Ncpdrug ElectroDocument24 pagesNcpdrug ElectroMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- SkadoodleDocument2 pagesSkadoodleNathan LunaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintAnne SedanzaNo ratings yet
- PositionDocument23 pagesPositionCharlene RojasNo ratings yet
- IICPDocument38 pagesIICPIntira Aom ChainapaengNo ratings yet
- Scientific Explanation of Expected Outcomes and InterventionsDocument4 pagesScientific Explanation of Expected Outcomes and InterventionsGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument1 pageFlowchartCRYPTO KNIGHTNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP 1-3Document6 pagesRevised NCP 1-3MarcieNo ratings yet
- The COVID-19 Vaccine Is Here-Now Who Is Willing To Get It?Document9 pagesThe COVID-19 Vaccine Is Here-Now Who Is Willing To Get It?Jaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Brain Sciences: Design of Fear and Anxiety of COVID-19 Assessment Tool in Spanish Adult PopulationDocument9 pagesBrain Sciences: Design of Fear and Anxiety of COVID-19 Assessment Tool in Spanish Adult PopulationJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Leaf StencilDocument1 pageLeaf StencilJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Isolation GuidelinesDocument203 pagesIsolation GuidelinesAlifia TrisnaningrumNo ratings yet
- How To Scan Documents On Your Iphone, Ipad, or Ipod TouchDocument1 pageHow To Scan Documents On Your Iphone, Ipad, or Ipod TouchJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Prevention & Control of Chronic LifestyleDocument66 pagesPrevention & Control of Chronic LifestyleJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Begun in Manila,: OtherDocument9 pagesBegun in Manila,: OtherJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Venous Return Mechanisms: Smooth MuscleDocument1 pageVenous Return Mechanisms: Smooth MuscleJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- 9 Regions of AbdomenDocument4 pages9 Regions of AbdomenEliza Hanna Guimalan Roldan50% (2)
- Blodchemandhematology PDFDocument7 pagesBlodchemandhematology PDFJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- MMDSTDocument1 pageMMDSTJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug GuidelinesDocument59 pagesEmergency Drug GuidelinesAries TauNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinDocument1 pageCephalosporinJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Comparative NMV Vs IMV On COPD PatientDocument16 pagesComparative NMV Vs IMV On COPD PatientJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Article IV - CNDocument2 pagesArticle IV - CNJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- 2019 NCC Npsgs FinalDocument1 page2019 NCC Npsgs FinalJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Product LiteratureDocument6 pagesProduct LiteratureJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Application Form For HospitalvDocument5 pagesApplication Form For HospitalvGerald MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- 9 Regions of AbdomenDocument4 pages9 Regions of AbdomenEliza Hanna Guimalan Roldan50% (2)
- Example - Mental Status Exam NarrativeDocument1 pageExample - Mental Status Exam NarrativeJaic Ealston D. TampusNo ratings yet
- Magnet Therapy For The Relief of Pain and in Ammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMBRA) : A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Crossover TrialDocument18 pagesMagnet Therapy For The Relief of Pain and in Ammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMBRA) : A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Crossover TrialAmr ElDisoukyNo ratings yet
- Ism-Mentor Interview Assignment Questions: Student Name: PeriodDocument4 pagesIsm-Mentor Interview Assignment Questions: Student Name: Periodapi-377981511No ratings yet
- 3 Main Food Group: Reporter: Mercy Grace Yongco - MPA IDocument11 pages3 Main Food Group: Reporter: Mercy Grace Yongco - MPA ICHOSEN TABANASNo ratings yet
- International Healthcare Conference IHCON 2021 (Virtual) - Free RegistrationDocument8 pagesInternational Healthcare Conference IHCON 2021 (Virtual) - Free RegistrationDr Kishore Kumar D100% (1)
- Joshua Greenlee Mba HT/HTL (Ascp), Scott Webster PHD, Howard Gray Bs MT (Ascp), Patricia Reeves HT (Ascp), Erico Von Bueren PHD MorDocument1 pageJoshua Greenlee Mba HT/HTL (Ascp), Scott Webster PHD, Howard Gray Bs MT (Ascp), Patricia Reeves HT (Ascp), Erico Von Bueren PHD MorRashid AliNo ratings yet
- WHO International Biological Reference PreparationsDocument22 pagesWHO International Biological Reference PreparationsMiguel Ruiz de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Cases to Examine- EuthanasiaDocument1 pageCases to Examine- EuthanasiadamianmackytNo ratings yet
- Seddon and Sunderland Nerve Injury ClassificationDocument8 pagesSeddon and Sunderland Nerve Injury ClassificationAndres AcostaNo ratings yet
- MedVantage - Fellowship Program in Diabetes MillitusDocument2 pagesMedVantage - Fellowship Program in Diabetes MillitusmedvantageNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Sensitivity TestDocument10 pagesAntibiotic Sensitivity TestJ.A. LauronNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Penderita Gangguan Nyeri Akibat Sindrom Piriformis Dengan Teknik Strain Counterstrain Dan Contract Relax StretchingDocument7 pagesPenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Penderita Gangguan Nyeri Akibat Sindrom Piriformis Dengan Teknik Strain Counterstrain Dan Contract Relax Stretchingchyntia eryonzaNo ratings yet
- 9 Months Marathon Training Plan - OdtDocument6 pages9 Months Marathon Training Plan - OdtMichaelKahnertNo ratings yet
- Pex 09 03Document4 pagesPex 09 03Illich Ramirez TantaNo ratings yet
- Query ReplyDocument5 pagesQuery ReplyParakhModyNo ratings yet
- Gamil Sayed Gamil ZeedanDocument48 pagesGamil Sayed Gamil ZeedangamNo ratings yet
- Management of The Infant With Atypical Genitalia (Disorder of Sex Development) - UpToDateDocument31 pagesManagement of The Infant With Atypical Genitalia (Disorder of Sex Development) - UpToDateNicolle SchioNo ratings yet
- HargaDocument1,176 pagesHargaRSUD SOLOKNo ratings yet
- Teeter FitSpine X1 Inversion Table Owners ManualDocument6 pagesTeeter FitSpine X1 Inversion Table Owners ManualhawkjohnNo ratings yet
- 1st History PEdiaDocument6 pages1st History PEdiaDeepak BamNo ratings yet
- Karsto Akmeņu Masāža INGLIŠ - KopijaDocument10 pagesKarsto Akmeņu Masāža INGLIŠ - KopijaAlise KoblinecaNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Program Pemberian Tablet Tambah Darah Pada Remaja Putri Anemia Dan Non Anemia Di Wilayah Puskesmas AntapaniDocument9 pagesEvaluasi Program Pemberian Tablet Tambah Darah Pada Remaja Putri Anemia Dan Non Anemia Di Wilayah Puskesmas AntapaniAgung JayaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Abstract: Bañag, Daraga, Albay Contact Nos.: (Globe) 09271684061 (Smart) 09475160066Document1 pageClinical Abstract: Bañag, Daraga, Albay Contact Nos.: (Globe) 09271684061 (Smart) 09475160066kolintang1No ratings yet
- LVS Chronic Pain WsDocument49 pagesLVS Chronic Pain WsdtncorreoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Keratitis - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment: April 2012Document17 pagesBacterial Keratitis - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment: April 2012Ivonne AffendyNo ratings yet