Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson - 7 Chemical Kinetics: Average Rate
Lesson - 7 Chemical Kinetics: Average Rate
Uploaded by
Annamalai Boomika0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesThis document discusses key concepts in chemical kinetics including:
- Average rate and instantaneous rate, which refer to the change in concentration over time or at an instant.
- Integrated rate laws for first order and zero order reactions based on how the reaction rate depends on reactant concentration.
- Half life period as the time for the reactant concentration to reach half the initial amount.
- Pseudo first order reactions where one reactant is in excess.
- Collision theory which states that chemical reactions occur due to collisions between reacting molecules that must possess minimum activation energy.
Original Description:
thanks . For pdf
Original Title
Boo Mika
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts in chemical kinetics including:
- Average rate and instantaneous rate, which refer to the change in concentration over time or at an instant.
- Integrated rate laws for first order and zero order reactions based on how the reaction rate depends on reactant concentration.
- Half life period as the time for the reactant concentration to reach half the initial amount.
- Pseudo first order reactions where one reactant is in excess.
- Collision theory which states that chemical reactions occur due to collisions between reacting molecules that must possess minimum activation energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesLesson - 7 Chemical Kinetics: Average Rate
Lesson - 7 Chemical Kinetics: Average Rate
Uploaded by
Annamalai BoomikaThis document discusses key concepts in chemical kinetics including:
- Average rate and instantaneous rate, which refer to the change in concentration over time or at an instant.
- Integrated rate laws for first order and zero order reactions based on how the reaction rate depends on reactant concentration.
- Half life period as the time for the reactant concentration to reach half the initial amount.
- Pseudo first order reactions where one reactant is in excess.
- Collision theory which states that chemical reactions occur due to collisions between reacting molecules that must possess minimum activation energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
[Enter Post Title Here]
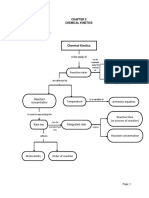
Lesson – 7; Chemical Kinetics
Average Rate is defined as the change in
the concentration of the reactant
In a given interval of time.
Instantaneous Rate is defined as the rate
of the reaction of the particular
Instant.
INGRATED RATE LAW FOR FIRST ORDER
REACTION:
A reaction whose rate depends on the
rate of concentration of the
Reactant raised to the first power.
HALF LIFE PERIOD:
Half life period is defined as the time
required for the reactant concentration
To reach its one half of its initial
concentration.
INGRATED RATE LAW FOR ZERO ORDER
REACTION:
A reaction whose rate is independent of
the concentration of the reactant
Over a wide range of concentration.
PSEUDO FIRST ORDER REACTION:
A second order reaction is altered to a
first order reaction by taking one
Of the reactant in large excess.
ELEMENTARY REACTION:
Each and every single step in a reaction
mechanism.
MOLECULARITY:
The total number of reactant species that
are involved in an elementary
Steps.
COLLISION THEORY:
According to the chemical kinetics,
chemical reactions occur as a result
Of collision between the reacting
molecules.
ACTIVATION ENERGY:
The colliding molecules must possess a
minimum energy.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE REACTION RATE:
1. Nature and state of the reactant.
2. Concentration of the reactant.
3. Surface area of the reactant.
4. Temperature of the reactant.
5. Presence of the catalyst.
CATALYST:
A catalyst is a substance which alters the
rate of a reaction without
Itself undergoing any permanent chemical
change.
You might also like
- Chemical Kinetics - NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Kinetics - Notesn611704No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Kinetics LPDocument41 pagesKinetics LPHarkritSinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4 PDFDocument60 pagesChemistry Unit 4 PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4: Chemical KineticsDocument21 pagesChapter - 4: Chemical KineticsJeffrey ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-04 Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChapter-04 Chemical Kineticsshrey4602No ratings yet
- FactorDocument2 pagesFactorJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 2Document39 pagesChemical Kinetics 2Md. Hasanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageChemical KineticsSachinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics GibbsDocument35 pagesChemical Kinetics GibbsTHE CREATORSTERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Reaction RatesDocument3 pagesChapter 17 - Reaction RatescaffeinewriterNo ratings yet
- Fair Use NoticeDocument15 pagesFair Use NoticeImran UnarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: By:-Divyam Verma Ankur Kumar Deepak KumarDocument36 pagesChemical Kinetics: By:-Divyam Verma Ankur Kumar Deepak KumarAnindya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- CHem InalsDocument3 pagesCHem InalsAbigail OconNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Report Class 10Document28 pagesPhysics Project Report Class 10Deepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Clase II-Fundamentos en Quím. Amb. - Actualizada 25-Feb-19Document39 pagesClase II-Fundamentos en Quím. Amb. - Actualizada 25-Feb-19Abraham JulioNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument71 pagesChemical KineticsLoraine Andrei DeLeonNo ratings yet
- L-Chemical KineticsDocument96 pagesL-Chemical Kineticssalma khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document18 pagesChapter 9JeromeNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction and Various Factors That Influence ItDocument28 pagesRate of Reaction and Various Factors That Influence Itjulie cadungonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Defination and Theory Q and Ans PDFDocument5 pagesChemical Kinetics Defination and Theory Q and Ans PDFabdullahausafmalikNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rates Collision Theory PDFDocument4 pagesReaction Rates Collision Theory PDFpieNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes: Chemical Kinetics: HomepageDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes: Chemical Kinetics: HomepageBHAVYA BNo ratings yet
- Bahria College Karachi Chapter # 8: Introduction To Chemical KineticsDocument15 pagesBahria College Karachi Chapter # 8: Introduction To Chemical KineticsNayan RoyNo ratings yet
- Kinetics NotesDocument4 pagesKinetics NotesDharaneesh S.k.No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument10 pagesCHEMISTRYlifep7417No ratings yet
- # Week 5 NotesDocument7 pages# Week 5 Notestimx123yNo ratings yet
- 1-Chemical Kinetics First LectureDocument27 pages1-Chemical Kinetics First LecturealakaolamuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering: Subject Code:Ch.E-325Document103 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering: Subject Code:Ch.E-325muhammad shahadat awanNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Kinetics and Stability-Lec-2Document27 pagesPharmaceutical Kinetics and Stability-Lec-2husseinkamilhamid123456789No ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument23 pagesRate of ReactionVirly vcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Chemical KineticsDocument32 pagesLesson 9 Chemical KineticsLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry & Physiology 3 Semester (Bs Biochemistry) Presentation of Chemistry Submitted To:dr - Yasmeen Submitted by Group#1Document15 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry & Physiology 3 Semester (Bs Biochemistry) Presentation of Chemistry Submitted To:dr - Yasmeen Submitted by Group#1Abera BatoolNo ratings yet
- SS 2 Week 3Document71 pagesSS 2 Week 3Denzel MusaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Puspanjali PDFDocument85 pagesChemistry Notes Puspanjali PDFDURGA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument8 pagesChemical Kinetics PDFAlexandra minNo ratings yet
- Short Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 1 Rate of ReactionDocument4 pagesShort Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 1 Rate of Reactionsalamah_sabri100% (1)
- Module 2 Kinetics of Materials Reading MaterialsDocument14 pagesModule 2 Kinetics of Materials Reading MaterialsmayNo ratings yet
- Collssion TheoryDocument3 pagesCollssion TheoryJherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Chemical KineticsDocument60 pagesWeek 5 Chemical KineticsLuke BelmarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of ReactionMr GaMeR SMNo ratings yet
- Rates OF ReactionDocument6 pagesRates OF ReactionAdam WilliamsNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 - Chemical Kinetics - Chemistry Short Notes ?Document11 pagesCH - 3 - Chemical Kinetics - Chemistry Short Notes ?kushwahakingxNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 RATES AND REACTION-IRVANE ROVIC RAMOSDocument2 pagesActivity 3 RATES AND REACTION-IRVANE ROVIC RAMOSkiara menesesNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory and Reaction RateDocument9 pagesCollision Theory and Reaction RateabdooufNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory and Reaction RateDocument9 pagesCollision Theory and Reaction RateKarissaNo ratings yet
- English WB IgcseDocument23 pagesEnglish WB Igcsetoleen playzNo ratings yet
- Rates and Rate Laws: SpectrosDocument6 pagesRates and Rate Laws: Spectrosdharul khairNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 11 Reaction KineticsDocument24 pagesChapter # 11 Reaction KineticsAnoshKhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsAyush singh PrinceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - LectureDocument37 pagesChemical Kinetics - LectureEsmira Melić ŠutkovićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4a. Chemical Kinetics 2020Document23 pagesLecture 4a. Chemical Kinetics 2020Montassar DridiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHKenneth TrogonNo ratings yet
- Peter J. NassiffDocument11 pagesPeter J. Nassifflary77No ratings yet
- CFE - 10 - Chemical Kinetics Part 2Document19 pagesCFE - 10 - Chemical Kinetics Part 2Christian C. SuaseNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry - Unit 6 - Chemical Kinetics Study GuideDocument6 pagesIB Chemistry - Unit 6 - Chemical Kinetics Study GuideHamzah JoharNo ratings yet
- 1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023Document3 pages1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023No NameNo ratings yet
- Rate Equation: Zeroth-Order ReactionsDocument16 pagesRate Equation: Zeroth-Order ReactionsBastab DeyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction and Reactions and Molecular CollisionsDocument5 pagesLesson 3 - Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction and Reactions and Molecular CollisionsJeff ValdezNo ratings yet