Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acids, Bases, & The PH Scale
Uploaded by
Sazy Credo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageacid and bases
Original Title
acid and bases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentacid and bases
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageAcids, Bases, & The PH Scale
Uploaded by
Sazy Credoacid and bases
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
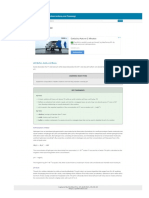
ACIDS, BASES, & THE pH SCALE Name: Answer Key
Date:
Pd:
PART 1: ACIDS AND BASES
Comparing Acids and Bases
Acids Bases (Alkalines)
Sour taste, leaves burning sensation Sharp bitter taste, feels slippery to touch
Increase hydrogen ions (H+) in solution Decrease hydrogen ions (H+) in solution
(Increase hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution)
Example: HCl H+ + Cl- Example: NaOH Na+ + OH-
Turns litmus (pH) paper to red Turns litmus (pH) paper to blue
PART 2: THE pH SCALE
The pH Scale is a measurement of how acidic or how basic a solution is.
The scale goes from 0 to 14.
Compounds are acidic if they have a pH lower than 7.
Compounds with a pH higher than 7 are basic or alkaline.
Compounds with a pH of 7, are neutral.
1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 11 12 13
0 7 14
Increased concentration of H+ ions Decreased concentration of H+ ions
Decreased concentration of OH- ions Increased concentration of OH- ions
pH below 7 = acids pH at 7 = neutral pH above 7 = bases
(pure water)
PART 3: BUFFERS
A buffer is a weak acid or base that prevents sudden changes in pH.
o Maintains homeostasis
A buffer works by binding to H+ ions releasing H+ ions when the solution pH changes.
Buffers bind to H+ ions when the concentration of H= ions in solution increases.
NaOH Na+ + OH- (The OH- will bind to H+ ions to form H2O – neutralization)
Buffers release H+ ions when the concentration of H= ions in solution decreases.
HCl H+ + Cl-
You might also like
- Acids and Bases IGCSE NotesDocument15 pagesAcids and Bases IGCSE NotesMisbah KamranNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument8 pagesAcids and BasesjexNo ratings yet
- CEs-CDL-B5 Acids Bases and Salts-040620Document179 pagesCEs-CDL-B5 Acids Bases and Salts-040620hannah kwonNo ratings yet
- Math 9 TG Draft 3.24.2014Document323 pagesMath 9 TG Draft 3.24.2014Carl Allen Comaling80% (218)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry NotesZaheer Uddin100% (1)
- The Chemistry of Acids and BasesDocument68 pagesThe Chemistry of Acids and BasesHelpful Hand100% (1)
- 13-Acids and BasesDocument44 pages13-Acids and BasesShamier Khent SamsonNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Acid Base TitrationDocument48 pagesUNIT II Acid Base TitrationDr Priti JainNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases - LESSON BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesAcids and Bases - LESSON BIOCHEMJohn CortezNo ratings yet
- Partially Ionised in Water andDocument5 pagesPartially Ionised in Water andHikmaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibria & PH Calculations Analytical Chemistry: December 2018Document16 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria & PH Calculations Analytical Chemistry: December 2018King OzeedNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Chemistry: Manasi MantriDocument16 pagesAcid-Base Chemistry: Manasi MantriSonam ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mod 6 Acid and Base Reactions NotesDocument27 pagesChemistry Mod 6 Acid and Base Reactions NotesdNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- CTSC Matric Masterclasses Acid and Bases 2020-1Document13 pagesCTSC Matric Masterclasses Acid and Bases 2020-1mxolisi mkhumaneNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and PH2Document20 pagesAcids, Bases, and PH2Ohm PawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument14 pagesChapter: Acids, Bases and SaltsCerwin SantosNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of acids and bases grade 12 matric 2024Document13 pagesFundamentals of acids and bases grade 12 matric 2024snothandoxesibe2006No ratings yet
- 8 ACIDS Bases Buffers 09Document4 pages8 ACIDS Bases Buffers 09Sirine AjourNo ratings yet
- Ch. 17 Acids & BaseDocument19 pagesCh. 17 Acids & BaseNick Andrew Dequilla NiervaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and pH2 PDFDocument20 pagesAcids, Bases, and pH2 PDFaprilia nur hidayahNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases pH Scale GuideDocument9 pagesAcids Bases pH Scale GuidejerlynmadulidNo ratings yet
- 1.acid, Base & BufferDocument41 pages1.acid, Base & BufferPiash AnikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Buffer SolutionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Buffer SolutionsGiannaNo ratings yet
- Tut-Acids and BasesDocument30 pagesTut-Acids and BasesThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base PH SlideDocument12 pagesAcid Base PH SlideBee RisaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesChapter 8 Acids and BasesRonnie0209No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and pH2Document20 pagesAcids, Bases, and pH2Arihant JainNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases PresentationDocument21 pagesAcids Bases PresentationMickey MouseNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases SaltsDocument11 pagesAcids Bases Saltsabiodun olaokeNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP Cc8 SB AnswersDocument5 pagesEdgcse TTPP Cc8 SB AnswersRaijin KazeNo ratings yet
- Acid and BaseDocument29 pagesAcid and BasecandysunNo ratings yet
- Local Media7519224990232746656Document45 pagesLocal Media7519224990232746656CRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Chemisty - Lecture 9 Acid-Base Reactions - Power PointDocument25 pagesChemisty - Lecture 9 Acid-Base Reactions - Power PointjaninaD100% (1)
- The Role of Water in Showing Acidic and Alkaline PropertiesDocument33 pagesThe Role of Water in Showing Acidic and Alkaline PropertiesWan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument16 pagesAcids and BasesLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesAcids and Basesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Acid, Base and Salt DNDocument7 pagesAcid, Base and Salt DNtahasheikh822No ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 7 Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesChemistry Unit 7 Acids and Basesshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base 5 PDFDocument22 pagesAcid and Base 5 PDFZenonissya GalwanNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesDocument30 pagesAcids BasesHaniel GalzoteNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument24 pagesAcids and BasesShupandy De Leon LimboNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases (Topic 7) : Designed, Prepared and Edited By: Chemistry Unit Mara Junior Science College Jasin Sept 2005Document13 pagesAcids and Bases (Topic 7) : Designed, Prepared and Edited By: Chemistry Unit Mara Junior Science College Jasin Sept 2005ajakazNo ratings yet
- Chem 1101: Chemistry (EEE/COE)Document9 pagesChem 1101: Chemistry (EEE/COE)Mahmudul IslamNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument35 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsTithiparna SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Acids & BasesDocument28 pagesAcids & Basesunknowncarrier00No ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument29 pagesAcids and BasesVILLIE ALASNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterSumit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases IGCSE NotesDocument15 pagesAcids and Bases IGCSE Notessaowanee toonchueNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Unit 8 - Acids and Bases Study GuideDocument6 pagesIB Chemistry Unit 8 - Acids and Bases Study GuideHamzah JoharNo ratings yet
- AcidsbasesandsaltsDocument46 pagesAcidsbasesandsaltsalimelsayehNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseEqDocument15 pagesAcid BaseEqMuhammed Maryam ometereNo ratings yet
- How to Prepare Buffer SolutionsDocument11 pagesHow to Prepare Buffer SolutionsGissela BTNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance IDocument6 pagesAcid-Base Balance Ior1da2sa3No ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument33 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsOindri MandalNo ratings yet
- Understanding Acid-Base PropertiesDocument103 pagesUnderstanding Acid-Base PropertiesZaina ZaliraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I - Chapter 19 Chemistry I HD - Chapter 16 ICP - Chapter 23Document74 pagesChemistry I - Chapter 19 Chemistry I HD - Chapter 16 ICP - Chapter 23Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Acids Part 2Document4 pagesAcids Part 2Aljim CarcillarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Acids, Bases and SaltscharanNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries ActivityDocument5 pagesPlate Boundaries ActivityMaestro de GrapicoNo ratings yet
- Blue Circles Medical Hospital Clinic Trifold Brochure Covid BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue Circles Medical Hospital Clinic Trifold Brochure Covid BrochureSazy CredoNo ratings yet
- Blue Circles Medical Hospital Clinic Trifold Brochure Covid BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue Circles Medical Hospital Clinic Trifold Brochure Covid BrochureSazy CredoNo ratings yet
- Fraud Services and ProductsDocument6 pagesFraud Services and ProductsSazy CredoNo ratings yet
- 03 Electrochemistry Study Guide - Multiple ChoiceDocument22 pages03 Electrochemistry Study Guide - Multiple ChoiceGopal Penjarla100% (1)
- Full Doc PDFDocument636 pagesFull Doc PDFMeryl PalenciaNo ratings yet