Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparative Study of Slurry Erosion Behaviour On SS304 and SS202 in A Slurry Erosion Test Pot Rig Under Different Operating Parameters
Uploaded by
Rajkumar MuthumanickamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparative Study of Slurry Erosion Behaviour On SS304 and SS202 in A Slurry Erosion Test Pot Rig Under Different Operating Parameters
Uploaded by
Rajkumar MuthumanickamCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) | Volume V, Issue III, March 2018 | ISSN 2321–2705
Comparative Study of Slurry Erosion Behaviour on
SS304 and SS202 in a Slurry Erosion Test Pot Rig
under Different Operating Parameters
S.Surya, K.M.Eazhil, S.Rishikesh, R.Satheesh Raj, R.Venkatesh
Department of Mechanical Engineering, SNS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract- A slurry erosion wear problem occurs generally in Erosion in tribology is the progressive loss of original material
transportation of solid liquid mixtures, pumps, hydro turbines, from a solid surface due to mechanical interaction between
petroleum extraction well. In this project test samples of stainless that surface and a fluid,or impinging liquid or solid particles.
steel (304) and stainless steel (202) were casted and their slurry Erosion rate is the determination of the rate of loss of material
erosion behaviours were statically studied by using slurry pot
[erosion] with exposure duration.
tester machine. Study of slurry erosion is important as it
adversely affects the useful life and performance of the B.Types of erosion
equipment handling slurries such as heat exchangers, pumps etc.
The main objective of the present study is to find the effect of a) Solid particle impingement
change in operating parameters on erosion wear of sample
subjected to sand-water slurry. The main operating parameters Solid particle impingement is a form of erosion produced by a
which are examined are molarity and slurry concentration. continuing succession of impacts from solid particles on a
Experiments are conducted in nine sets with three combinations surface. The impacting particles are smaller than the solid
of particle velocity, slurry concentration and molarity. The subjected to the erosion, and if all the impacts are
erosion of the samples was measured by mass loss of the superimposed on the same spot, the them repeated impact is
materials. In this study the design of experiments was considered used
using Taguchi technique. A comparison has been made for the
experimental and Taguchi technique results. b) Fluid impingement
Keywords-slurry erosion, ss304, ss202, speed Fluid impingement is a form of erosion caused by a
continuing succession of impact from a jet of fluid on a
I. INTRODUCTION surface
III. SLURRY EROSION
I n the contemporary industrial world, fluidpower,
particularly the hydraulics branch of it, is a magic world for
energy transmission. The major elements used in hydraulics
Slurryis the suspension of solid material in liquid. Slurries are
transported and processed by a wide range of equipment in the
systems are pumps,valves,pipes, etc. These elements play a mining, power generation and dredging industries. Centrifugal
major role in power transmission and controls. In the passage pumps and cyclone are used extensively in these applications.
of time, these components undergo erosion and corrosion and A major consideration of equipment operators in these
leads to the fatigue failure.Erosion-corrosion dominates the industries is the wear life of equipment.
overall failure of the materials of many components, such as
pumps, valves, coupling, etc., which encounter high velocity The predominant type of wear in slurry handing equipment is
of acidic and alkaline flow. Erosion is a physical phenomenon erosion. Studies into the factors contributing to erosive wear
of degradation process. Ductile erosion occurs when the have focused on particle size, shape,impingement angle,
impacting particles cause severe localized plastic strain on the impact velocities and material characteristics.
material. Material removal occurs when the strain to the
failure of the deformed material is exceeded. However, brittle IV.SELECTION OF THE MATERIAL
mode of erosion damage of material is based on cracking, The two materials compared in this project are SS 304 and SS
fragmentation, and removal of flakes. Slurry Erosion is a 202A. Stainless Steel 304
complex phenomenon which influenced by the factors, such
as flow field parameters, target material properties, and Type 304, with its chromium-nickel content and low carbon,
erodent particle characteristics. is the most versatile and widely used of the austenitic stainless
steel. They can meet a wide variety of physical requirements,
II.DEFINITION making them excellent materials for applications including
A.Erosion storage tanks, pressure vessels and piping.
www.rsisinternational.org Page 104
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) | Volume V, Issue III, March 2018 | ISSN 2321–2705
Composition impact angle, mixed type of micro indentations and pitting
SS-304
action is observed. At normal impact angle 90°, the material
removal pattern was observed in form of indentation and
Element (Weight %) rounded lips. From the comparison of experimental and
Mn 2.00 Taguchi experimental design results it is found that the
S 0.030 percentage deviation was very small with a higher correlation
coefficient (r2) 0.987 which is agreeable.
P 0.045
Mo -
The E-C 29123 coating applied by OFP process onto AISI304
stainless steel reported the best slurry erosion resistance of the
Cr 7.50-19.50 studied materials, mainly as a consequence of the combined
Si 0.75 properties of hard, wear-resistant particles and a ductile
Ni 8-12 metallic matrix.
N 0.10 The studied coatings showed ability to deform plastically
C 0.030 when submitted to slurry erosion conditions, with little
evidence of mass removal by brittle fracture mechanisms. Un-
B. Stainless Steel 202 melted particles and droplets are easily removed from the
surface, but this does not affect the overall performance of the
To avoid the above fatigue failures by erosion the stainless coatings in terms of volume loss and main wear
steel202 with nitrogen content can be used. It is nitrogen
mechanisms.The applied coatings are an interesting
enhanced duplex stainless steel that was developed to combat
alternative to enhance the wear resistance of components used
common Erosion problems encountered with the 300-series
in hydraulic machines, in particular under grazing incidence
stainless ' steels. “Duplex” describes a family of stainless
conditions and moderate-to-low mean impactvelocities.
steels that are neither fully austenitic, like 304 stainless, nor
purely ferritic, like 430 stainless steels.
VI. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
Composition
A.Slurry Erosion Test
SS-202
The method used for testing the erosion wear rate under
Element (Weight %) varying experimental conditions is known as slurry erosion
Mn 7.5-10 test this carried out by Using a slurry erosion tester. The
S 0.030 test is carried-out by measuring the loss of mass of the
specimen by weighing it before and after the process in the
P 0.060
tester.
Mo -
B.Construction
Cr 17-19
Si 1
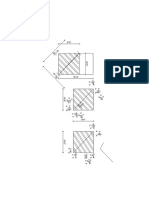
The samples or specimen are fixed on a slot along its surface
through the holding arrangement, which is attached to the
Ni 4-6 shaft. The assembly is immersed in the acrylic container drum
C 0.15 containing the slurry. Other end of the shaft is attached to a
motor through the bearing arrangement. So that when the
motor starts rotating the shaft holding the samples will also
Fig 1.Material before testing
rotate.
S.NO COMPONENTS SPECIFICATION
1 AC Motor Three Phase (0-2880rpm)
Variable Frequency
0-1500HZ
2 Drive
(VFD)
Height-250mm
3 Container
Dia-200/190mm
Height-20mm
4 Shaft
Dia-32mm
I)Length-160mm, Height-
V. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION 38mm,
5 Sample Holder Thickness-13mm
At shallow impact angle 30°, the material removal pattern was Ii)Two Slots 25.4X25.4 Mm2
observed in the form of micro displacing, scratching and Depth- 5mm
ploughing with plastic deformation of the material. At 60° 6 Samples 25X25 mm2
www.rsisinternational.org Page 105
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) | Volume V, Issue III, March 2018 | ISSN 2321–2705
Fig.2. Slurry Pot Rig applied for carrying out robust design of processes and
products and solving several complex problems in
manufacturing industries. Further this technique determines
the most influential parameters in the overall performance.
Furthermore, a statistical analysis of variance
(ANOVA) can be performed to see which process parameter
is statistically significant for each quality characteristics.
LEVEL LEVEL LEVEL
FACTORS
1 2 3
SPEED
1200 1500 1800
(rpm)
SLURRYCONCENTRATION
% 5 10 5
MOLARITY (M) 0.1 0.5 1
C. Working Principle
The specimen to be tested are first thoroughly cleaned and
weighed in Precisions weighing machine. These Specimens VIII.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
having a standard size fixed onto the slots with the help of A.Result of the experiment after completion of test
alien screws. The holder along with the specimens is dipped
into the slurry contained in the container. The motor is then a) Stainless 304
started and the specimens are rotated at the desired speed for a
given duration. The specimen are removed, cleaned and Mass
S.NO Solution Slurry
Speed Loss
weighed after the test is over. Concentration Concentration
The loss of mass of the specimen during the test is found 1 0.1 5 1200 0.005
out. The rate of erosion is calculated as the rate of loss of 2 0.1 10 1500 0.020
mass with respect to various experimental parameters. 3 0.1 15 1800 0.035
4 0.5 5 1500 0.056
VII. DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS
5 0.5 10 1800 0.080
A.Erosion Test
6 0.5 15 1200 0.043
The erosion tests were conducted based on three- 7 1.0 5 1800 0.075
factor three-level L9 orthogonal array using slurry erosion
tester, as shown in the Fig, The surfaces and edges of the cast 8 1.0 10 1200 0.054
test specimens of size 3125 m3 were polished and ground, to 9 1.0 15 1500 0.062
remove oxide scales and dirt, using standard metallographic
techniques. The testing parameters as shown in the Table were b) Stainless Steel 202
varied according to the design matrix, for each test. Silica
sand particles of mesh size 90 microns were used as erodent. Mass
S.NO Solution Slurry
Speed Loss
The weight of each sample was measured, before and after the Concentration Concentration
test, to find thedifference in the mass loss. 1 0.1 5 1200 0.010
B.Taguchi Method 2 0.1 10 1500 0.024
Taguchi methods are statistical methods developed 3 0.1 15 1800 0.075
by Genichi Taguchi to improve the quality of manufactured 4 0.5 5 1500 0.083
goods and more recently also applied to engineering,
5 0.5 10 1800 0.190
biotechnology, marketing and advertising. Professional
statisticians have welcome the goals and improvements 6 0.5 15 1200 0.097
brought about by Taguchi methods, particularly by Taguchi’s 7 1.0 5 1800 0.130
development of designs for studying variations, but have 8 1.0 10 1200 0.093
criticized the inefficiency of some Taguchi’s proposals.
9 1.0 15 1500 0.112
Taguchi method is an efficient problem-solving tool, which
can upgrade/improve the performance of the product, process, B. Interaction plots
design and system with a significant slash in experimental An interaction plots displays the levels of one variable on the
time and cost. This method that combines the experimental X axis and has a separate line for the means of each levels of
design theory and quality loss function concept has been the other variable. The Y axis is the dependent variable. An
www.rsisinternational.org Page 106
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) | Volume V, Issue III, March 2018 | ISSN 2321–2705
interaction occurs when the response achieved by one factor C. Direct effect on process parameters
depends on the levels of another factor. On interaction plot
1. Stainless steel 304
when lines are not parallel, there is an interaction.
The direct effect of stainless steel 304 at solution
Based on the results, contour plots for the interaction effects
concentration increases from 0.020gm and again increases to
of the factors influencing mass loss have been generated using
0.052gmwhereas the direct effect of slurry concentration starts
MINITAB 18.
from 0.043gm and increases to 0.056gm and then decreases to
1. Interaction effect of slurry concentration with molarity on 0. 047gm.For speed of 1200rpm it starts from 0.035gm mass
mass loss. loss and increases to 0.0.47gm and increases to 0.070 gm for
1800rpm.
The figure predominantly depicts a marginal mass loss in the
range of 0.00-0.50g confirming the influence on the mass loss Fig.5.Main effects plot for 304
to a very minimum level of contribution. Based on visual
inspection, it is inferred that corrosion-dominated wear
phenomenon appears to be operative at lower pH values.
2. Interaction effect of speed with molarity on mass loss.
Since the contribution of Molarity factor is low compared
with all the factors influencing the mass loss, it is evident that
velocity plays a major role in contributing to the mass loss of
the material. The interactive trend as shown in Fig.3&4 for the
interaction of the speed with molarity on the mass loss of
stainless steel clearly depicts that at the maximum velocity
and minimum value of molarity, a higher mass loss was
observed.
Fig.3.Interaction Plot for SS202 2. Stainless steel 202
The direct effect of stainless steel 202 at solution
concentration increases from 0.010 gm and again increases to
0.024 gm whereas the direct effect of slurry concentration
starts from 0.083gm and increases to 0.190 gm and then
decreases to 0.097gm. For speed of 1200rpm it starts from
0.065gm mass loss and increases to 0.078gm and increases to
0.130 gm for 1800rpm.
Fig.6.Main effects of SS202
Fig.4. Interaction Plot for SS304
D.Contour plots
A contour plot is a graphic representation of the relationship
among the three numeric variables in two dimensions. Two
variables are for X and Y axes, and a third variable Z is for
contour levels. The contour level are plotted as curves, the
area between the curves can be colour coded to indicate
www.rsisinternational.org Page 107
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) | Volume V, Issue III, March 2018 | ISSN 2321–2705
interpolated values. The various contour plot for the three 2. Stainless Steel 304
variables are discussed below for both SS 304 and SS 202.
a) Contour plot of mass loss vs Solution concentration and
1. Stainless Steel 202 Slurry Concentration.
a) Contour plot of mass loss vs Solution concentration and
Slurry Concentration.
Contour Plot of Mass loss vs Solution Concent, Slurry Concentra
1.0
Mass loss
< 0.015
0.9
0.015 – 0.030
0.030 – 0.045
0.8 0.045 – 0.060
Solution Concentration
0.060 – 0.075
0.7 > 0.075
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
b) Contour plot of mass loss vs Solution concentration and
0.1
5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 Speed.
Slurry Concentration
b) Contour plot of mass loss vs Solution concentration and
Speed.
Contour Plot of Mass loss vs Solution Concentration, Speed
1.0
Mass loss
< 0.015
0.9
0.015– 0.030
0.030– 0.045
0.8 0.045– 0.060
Solution Concentration
0.060– 0.075
0.7 > 0.075
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
c) Contour plot of mass loss vs Solution concentration and
0.1
1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700 1800 Speed.
Speed
c) Contour plot of mass loss vs Solution concentration and
Speed.
Contour Plot of Mass loss vs Slurry Concentration, Speed
15.0
Mass loss
< 0.015
0.015– 0.030
0.030– 0.045
12.5 0.045– 0.060
0.060– 0.075
Slurry Concentration
> 0.075
10.0
7.5
E. Effects on the material
5.0
1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700 1800 The below figure shows the effects of test over the material.
Speed
www.rsisinternational.org Page 108
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) | Volume V, Issue III, March 2018 | ISSN 2321–2705
Fig.7.Material after test 4. Interaction effects of speed, slurry concentration and
molarity erosion rate have been discussed.
REFERENCES
[1]. K. M. Nilkar, A. S. Runwal, N. S. Bhole, P. R. Jagtap, B. D.
Nandre“Experimental Study and Analysis of Slurry Erosion Wear
of SS304L Materia “e-ISSN: 2278-1684, p-ISSN: 2320-334X.
[2]. S.R. More a, D.V. Bhatt a, J.V. Menghani“Study of the Parametric
Performance of Solid Particle Erosion Wear under the Slurry Pot
Test Rig “Vol. 39, No. 4 (2017) 471-481, DOI:
10.24874/ti.2017.39.04.06.
[3]. K.M. Eazhil, R. Sudhakaran, M.Jayakumar “Optimization of the
process parameter to maximize the tensile strength in 6063
aluminium alloy using Grey based Taguchi method “Advances in
IX. CONCLUSION Natural and Applied Sciences, 235-241
[4]. K. M Eazhil, , S. Mahendran S Ganesh Kumar, “Optimization of
1. The following conclusion were conducted by varying Tungsten Inert Gas Welding on 6063 Aluminium Alloy on
the factors namely speed, slurry concentration and Taguchi Method”International Journal of Research and Scientific
Innovation 1 (III), 2321-2705.
molarity values in three levels, using Taguchi L9 [5]. Gaurav Kumar, Satish R More, Dhananjay V. Bhatt and Jyoti V
orthogonal array. Menghani “ Study of Slurry Erosion Wear Behaviour of SS-304 in
2. The effect of the factors on erosive wear a Slurry Pot test Rig under different operating parameters”,SKIT
characteristics of SS304 and SS202 were compared RESEARCH JOURNAL VOLUME 7; ISSUE 2: 2017.
[6]. J.F. Santa, J.C. Baena, A. Toro “Slurry erosion of thermal spray
and studied. coatings and stainless steels for hydraulic machinery”
3. Contour plots for interaction effects of the factors
influencing mass loss have been generated using
MINITAB 16 statistical analysis software.
www.rsisinternational.org Page 109
You might also like
- Failure Case Studies in Civil EngineeringDocument135 pagesFailure Case Studies in Civil Engineeringpratip_b100% (2)
- Steel Casting HandbookDocument74 pagesSteel Casting Handbooktang weng wai100% (2)
- METTL PERSONALITY TEST REVEALS INDIVIDUAL STRENGTHSDocument6 pagesMETTL PERSONALITY TEST REVEALS INDIVIDUAL STRENGTHSVijeesh MNo ratings yet
- FIRST-TERM FORM TEST (2020/21) Form Two Integrated Science: Instructions Multiple-Choice Answer SheetDocument14 pagesFIRST-TERM FORM TEST (2020/21) Form Two Integrated Science: Instructions Multiple-Choice Answer SheetYuki LiNo ratings yet
- Promoting Self Esteem: Presented by Shilpa Hotakar MSC Nursing Dept of Psychiatric NursingDocument23 pagesPromoting Self Esteem: Presented by Shilpa Hotakar MSC Nursing Dept of Psychiatric NursingShilpa Vhatkar0% (1)
- Bsce Quarantine Reviewer Diagnostic Exams PDFDocument27 pagesBsce Quarantine Reviewer Diagnostic Exams PDFLaurence CervoNo ratings yet
- George and Mallery (2003), PDFDocument63 pagesGeorge and Mallery (2003), PDFDixon Choo0% (2)
- Brittle Fracture in Steel StructuresFrom EverandBrittle Fracture in Steel StructuresG.M. BoydNo ratings yet
- Fractured Fairytale Unit-Year 7 Leah 2012Document12 pagesFractured Fairytale Unit-Year 7 Leah 2012api-111350055No ratings yet
- 04 ET EXCERPTS Field Guide To Human Centered DesignDocument49 pages04 ET EXCERPTS Field Guide To Human Centered DesignMahesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Laguna Camacho2013Document8 pagesLaguna Camacho2013Saravanakumar DhanasekaranNo ratings yet
- Wear and AbbrassionDocument5 pagesWear and AbbrassionNikhilNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0924013616301480 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0924013616301480 MaintarnsonNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Jmapro 2013 06 010Document14 pages10 1016@j Jmapro 2013 06 010SamuelshrlyNo ratings yet
- Erosion-Corrosion Resistance of Engineering Materials in Various Test ConditionsDocument11 pagesErosion-Corrosion Resistance of Engineering Materials in Various Test ConditionsYesy ConstanteNo ratings yet
- 2013 - Laguna Camacho - A Study of Cavitation Erosion On Engineering MaterialsDocument10 pages2013 - Laguna Camacho - A Study of Cavitation Erosion On Engineering MaterialsCesar Fernando BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Grinding+uit 1-s2.0-S092401361500179X-mainDocument8 pagesGrinding+uit 1-s2.0-S092401361500179X-mainMd MehtabNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: ProceedingsDocument6 pagesMaterials Today: ProceedingsSREEJITH S NAIRNo ratings yet
- Study On Heat Treatment and Coating of Copper ScreDocument8 pagesStudy On Heat Treatment and Coating of Copper ScreNikolaNo ratings yet
- The Abrasion Resistance Estimation of The C120 Steel by A Multi-Pass Dual-Indenter Scratch TestDocument12 pagesThe Abrasion Resistance Estimation of The C120 Steel by A Multi-Pass Dual-Indenter Scratch TestMohammed YunusNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heat Treatment on Erosion Resistance of SteelDocument3 pagesEffect of Heat Treatment on Erosion Resistance of SteelVyom AgarwalNo ratings yet
- IJETR021817Document3 pagesIJETR021817erpublicationNo ratings yet
- Wear and tribocorrosion of 304L SS, Zr alloys, and Ti in nitric acidDocument11 pagesWear and tribocorrosion of 304L SS, Zr alloys, and Ti in nitric acidMarioNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Slurry Erosion Resistance of The Body Materials of Oil & Gas Drill Bits With A Modified Abrasive WaterjetDocument15 pagesEvaluation of The Slurry Erosion Resistance of The Body Materials of Oil & Gas Drill Bits With A Modified Abrasive Waterjetcse crteNo ratings yet
- Corrossion Protection of Offshore Steel Structures - Case StudyDocument6 pagesCorrossion Protection of Offshore Steel Structures - Case StudyJaikumarNo ratings yet
- J Wear 2012 12 027Document8 pagesJ Wear 2012 12 027jovaniNo ratings yet
- Casting Defects in Structural Components Are They All Dangerous A 3D StudyDocument14 pagesCasting Defects in Structural Components Are They All Dangerous A 3D StudyVictor RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Constantin 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 252 012038 PDFDocument9 pagesConstantin 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 252 012038 PDFMeet PatelNo ratings yet
- 2019 A Review On Resistance Spot Welding of Steel MaterialDocument13 pages2019 A Review On Resistance Spot Welding of Steel Materialguravshubham7777No ratings yet
- The Effect of Sea Water Corrosion On Tensile Strength of CombinationDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Sea Water Corrosion On Tensile Strength of CombinationBRAYAN ALEJANDRO REYES VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Astm G109.1 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm G109.1 PDFsantoruno lupinottiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On Sliding Wear of AISI 316 L (N) Stainless Steel  " Analysis of Measured Wear and Surface Roughness of Wear TracksDocument7 pagesEffect of Temperature On Sliding Wear of AISI 316 L (N) Stainless Steel  " Analysis of Measured Wear and Surface Roughness of Wear TracksSamir BoseNo ratings yet
- Corten Steel 1Document3 pagesCorten Steel 1Gurjeet Singh LallNo ratings yet
- Ashiri 2014Document10 pagesAshiri 2014Febin EbyNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S004316481300080X MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S004316481300080X MainGustavo FagundesNo ratings yet
- Wear Characteristics of Adis A Comprehensive Review On Mechanisms and Effective ParametersDocument12 pagesWear Characteristics of Adis A Comprehensive Review On Mechanisms and Effective ParametersBiruk YifruNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Squeeze Cast 2024 Al AlloyDocument5 pagesMicrostructure and Tensile Properties of Squeeze Cast 2024 Al AlloyKumar SouravNo ratings yet
- 2005 - Viafara Et Al - Unlubricated Sliding Wear of Pearlitic and Bainitic SteelsDocument7 pages2005 - Viafara Et Al - Unlubricated Sliding Wear of Pearlitic and Bainitic SteelsccviafarNo ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings Technology: N. Padhy, Subhash Kamal, Ramesh Chandra, U. Kamachi Mudali, Baldev RajDocument7 pagesSurface & Coatings Technology: N. Padhy, Subhash Kamal, Ramesh Chandra, U. Kamachi Mudali, Baldev RajNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Erosion Behaviour of Hydro Turbine SteelDocument52 pagesErosion Behaviour of Hydro Turbine SteelAkhileshChauhanNo ratings yet
- V. Heino, M. Kallio, K. Valtonen, V.-T. Kuokkala: ArticleinfoDocument7 pagesV. Heino, M. Kallio, K. Valtonen, V.-T. Kuokkala: ArticleinfojoeljNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Ceramic Coating Using Plasma Spray and Hvof MethodDocument9 pagesExperimental Investigation of Ceramic Coating Using Plasma Spray and Hvof Methodmacosta1234No ratings yet
- Microstructural evolution during friction surfacing of tool steelDocument6 pagesMicrostructural evolution during friction surfacing of tool steelVikas Mani TripathiNo ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings Technology: Yucel Birol, Behiye YukselDocument6 pagesSurface & Coatings Technology: Yucel Birol, Behiye YukselChitranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- 2021 Influence of Immersion Corrosion AISI 430 AISI 316L - IJE - Volume 34 - Issue 5 - 2021Document11 pages2021 Influence of Immersion Corrosion AISI 430 AISI 316L - IJE - Volume 34 - Issue 5 - 2021cesold delcaribeNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Electrochemical Measurements Made During Micro Scale Abrasion CorrosionDocument10 pagesInterpretation of Electrochemical Measurements Made During Micro Scale Abrasion CorrosionJesus ZilchNo ratings yet
- 6395 ArticleText 11267 2 10 20200423Document12 pages6395 ArticleText 11267 2 10 20200423FergiawanNo ratings yet
- J Wear 2010 12 018Document7 pagesJ Wear 2010 12 018jovaniNo ratings yet
- Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of HVOF Sprayed WC Co Based Composite Coatings in Simulated Mine Water Environments-1Document13 pagesTribological and Corrosion Behavior of HVOF Sprayed WC Co Based Composite Coatings in Simulated Mine Water Environments-1grokking StuffNo ratings yet
- Sliding Wear and Solid-Particle Erosion Resistance of A Novel High-Tungsten Stellite AlloyDocument11 pagesSliding Wear and Solid-Particle Erosion Resistance of A Novel High-Tungsten Stellite Alloyshahin azNo ratings yet
- Journal of Manufacturing Processes: Full Length ArticleDocument14 pagesJournal of Manufacturing Processes: Full Length ArticleSudish Jay MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1526612517302542 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S1526612517302542 Mainsudish mishraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Manufacturing Processes: Jastej Singh, A.S. ShahiDocument10 pagesJournal of Manufacturing Processes: Jastej Singh, A.S. ShahiSorabh SinghalNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Wear Behaviour of Heat Treated En31 Steel: ISIJ International January 2013Document9 pagesAbrasive Wear Behaviour of Heat Treated En31 Steel: ISIJ International January 2013NABIL HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 0833Document8 pages0833Edmilson OtoniNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0043164819302261 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0043164819302261 MainAndys HernandezNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Aspects of Steels Designed To Resist Abrasion, and Impact-Abrasion WearDocument17 pagesMetallurgical Aspects of Steels Designed To Resist Abrasion, and Impact-Abrasion WearAlexis Guzmán MéndezNo ratings yet
- 2012-Fracture Toughness of Friction Hydro-Pillar Processing Welding in C-MN SteelDocument5 pages2012-Fracture Toughness of Friction Hydro-Pillar Processing Welding in C-MN SteelPedro CunhaNo ratings yet
- GIORDANI Journal FatigueDocument8 pagesGIORDANI Journal Fatiguekayron limaNo ratings yet
- GravimetriDocument11 pagesGravimetriAlifa Puti RahmadantiNo ratings yet
- Erosion-Corrosion of 316 SSDocument43 pagesErosion-Corrosion of 316 SSNikhilNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Analysis of Friction Stir-Welded AA 7075 Aluminium AlloyDocument7 pagesCorrosion Analysis of Friction Stir-Welded AA 7075 Aluminium AlloyDilipNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Induced HE of 2024 and 6013 ALDocument11 pagesCorrosion Induced HE of 2024 and 6013 ALNils VerkleijNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Re Bars During BendiDocument3 pagesFailure Analysis of Re Bars During BendiAhmed KassemNo ratings yet
- 25 Ijmperdaug201825Document8 pages25 Ijmperdaug201825TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Behavior of Friction Welded Medium Carbon Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel Dissimilar JointsDocument7 pagesFatigue Behavior of Friction Welded Medium Carbon Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel Dissimilar JointsVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- VijayaKumar2014 Article IdentificationOfSuitableProcesDocument11 pagesVijayaKumar2014 Article IdentificationOfSuitableProcesCyril Joseph DanielNo ratings yet
- The Salt Spray Environments For Mechanical Degradation of Welded SS304 Stainless SteelsDocument5 pagesThe Salt Spray Environments For Mechanical Degradation of Welded SS304 Stainless SteelserpublicationNo ratings yet
- MARTENSITIC ALLOY GUIDE FOR PRESSURE PARTSDocument1 pageMARTENSITIC ALLOY GUIDE FOR PRESSURE PARTSRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- SCH, S9, High Alloy Data SheetsDocument60 pagesSCH, S9, High Alloy Data SheetsMiki JaksicNo ratings yet
- TN VNR-DGL I 1905 08891Document2 pagesTN VNR-DGL I 1905 08891Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Barcola DrawingDocument1 pageBarcola DrawingRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- No. of Persons: No. of Laddus:: Special Entry Darshan Receipt ( .300/-)Document1 pageNo. of Persons: No. of Laddus:: Special Entry Darshan Receipt ( .300/-)Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Incoloy Alloy 825Document4 pagesIncoloy Alloy 825Roman PaduaNo ratings yet
- Grain Boundary Chemistry and Intergranular Corrosion in Alloy 825Document52 pagesGrain Boundary Chemistry and Intergranular Corrosion in Alloy 825Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Institute Fees 2019 20Document6 pagesInstitute Fees 2019 20Mr Ravi SivaprakashNo ratings yet
- 04 Method of Separation of VariablesDocument15 pages04 Method of Separation of VariablesRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Progress Energy's Experiences with Quality Issues on Cast C12A Valve BodiesDocument28 pagesProgress Energy's Experiences with Quality Issues on Cast C12A Valve BodiesinorwoodNo ratings yet
- Handbook DTCPDocument68 pagesHandbook DTCProhit_singh_2100% (1)
- Low-alloy Cast Steel Cracking CausesDocument6 pagesLow-alloy Cast Steel Cracking CausesRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Low-alloy Cast Steel Cracking CausesDocument6 pagesLow-alloy Cast Steel Cracking CausesRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Satellite CommunicationDocument6 pagesSatellite CommunicationRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Name: AIP Z Drive Server IP Address: 192.168.166.254 OS Platform:Win Server 2016Document1 pageName: AIP Z Drive Server IP Address: 192.168.166.254 OS Platform:Win Server 2016Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- 04 PotentialDocument6 pages04 PotentialRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Workshop Inspection Checklist October 2010Document11 pagesWorkshop Inspection Checklist October 2010Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Ch5 - Rotation SpectraDocument13 pagesCh5 - Rotation SpectraRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- 02 - 09atomic Physics - 232-262Document14 pages02 - 09atomic Physics - 232-262eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- 3 Molecular Spectroscopy Script Part1Document20 pages3 Molecular Spectroscopy Script Part1Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- 4 237-M SC - PhysicsDocument112 pages4 237-M SC - PhysicsRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Welding of Duplex Stainless SteelDocument7 pagesWelding of Duplex Stainless SteelHibozoNo ratings yet
- Green Gates Resort AC Cottage PackageDocument3 pagesGreen Gates Resort AC Cottage PackageRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Brick Foundry SandDocument8 pagesBrick Foundry SandRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Coke AnalysisDocument1 pageCoke AnalysisRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- J FactorDocument3 pagesJ FactorRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- NMD Atm Brochure 2012Document9 pagesNMD Atm Brochure 2012Rajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Efland School Art StyleDocument9 pagesEfland School Art StyleinglesaprNo ratings yet
- Parramatta High School Year 9 Individual Research Project: ContextDocument18 pagesParramatta High School Year 9 Individual Research Project: ContextVikram BologaneshNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Regarding Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring & Reporting Amongst Physicians in A Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Ahmedabad Indian Journal of Applied ResearchDocument4 pagesKnowledge, Attitude and Practice Regarding Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring & Reporting Amongst Physicians in A Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Ahmedabad Indian Journal of Applied ResearchChandresh DumatarNo ratings yet
- Arabic SyntaxDocument26 pagesArabic SyntaxagahNo ratings yet
- LDC LP No. 06 DTD 8th January 2024Document12 pagesLDC LP No. 06 DTD 8th January 2024Shubhajit ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Login to subscribe e-version of NORTH EAST ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND INVESTMENT SCENARIODocument32 pagesLogin to subscribe e-version of NORTH EAST ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND INVESTMENT SCENARIOManas RanjanNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Ph/redox and Temperature Sensor Model PH20 and FU20Document8 pagesGeneral Specifications: Ph/redox and Temperature Sensor Model PH20 and FU20HolicsNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance: Department of Computer Science Ncba&E EccDocument16 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance: Department of Computer Science Ncba&E EccAqib AsadNo ratings yet
- 1w5q Chapter 3 Dynamics of Linear MotionDocument2 pages1w5q Chapter 3 Dynamics of Linear MotionKHOO YI XIAN MoeNo ratings yet
- F: Fundamentals, D: Designer, A: Architect, L: Landmark, S: Spotlight, R: RenderworksDocument28 pagesF: Fundamentals, D: Designer, A: Architect, L: Landmark, S: Spotlight, R: RenderworksVERÓNICA PRISCILLA RIOS SALAZARNo ratings yet
- Eng Sample Paper 2 With Ans 1299Document12 pagesEng Sample Paper 2 With Ans 1299Mikky TripathiNo ratings yet
- Lec-1b - Types of StructuresDocument23 pagesLec-1b - Types of StructuresNouman AhmadNo ratings yet
- General Tolerance (From ASME Y14.5M-2009) : Tolerances Can Be ExpressedDocument12 pagesGeneral Tolerance (From ASME Y14.5M-2009) : Tolerances Can Be ExpressedVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan on Colors of LightDocument3 pagesLesson Plan on Colors of LightKristel Joy ManceraNo ratings yet
- 2d Circular Convolution 2 PDFDocument6 pages2d Circular Convolution 2 PDFVincent HanNo ratings yet
- Angular Dispersion and Dispersive PowerDocument6 pagesAngular Dispersion and Dispersive PowerShivkant SinghNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Risk Management and Insurance 12th Edition James S TrieschmannDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Risk Management and Insurance 12th Edition James S TrieschmannGeorgeWangeprm100% (41)
- Seepage and Flow NetsDocument60 pagesSeepage and Flow NetsMavenNo ratings yet
- Numerical Differentiation and Integration: By: Habtamu GaromaDocument53 pagesNumerical Differentiation and Integration: By: Habtamu GaromaAmiin HirphoNo ratings yet
- Nobilis - UnlikelyFloweringsDocument115 pagesNobilis - UnlikelyFloweringsd7an7pijpkerNo ratings yet
- Proof of Performance Mobilith SHC 1500 Zahnradkupplung in Kohleminen EngDocument1 pageProof of Performance Mobilith SHC 1500 Zahnradkupplung in Kohleminen EngLaurent GuyotNo ratings yet
- Understanding Factors in Second Language AcquisitionDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Factors in Second Language AcquisitionfatemehNo ratings yet