Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methods Advantages Disadvantages
Uploaded by
Haider AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methods Advantages Disadvantages
Uploaded by
Haider AliCopyright:
Available Formats
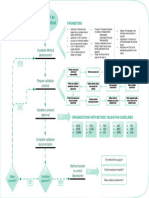
METHODS ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
• easy tounderstand anduse • do not distinguish
• good for site selection and betweendirectand
prioritysetting indirectimpacts
Checklists • simple rankingand weighting • do not link actionand impact
• the processof incorporating
values can be controversial
• difficult to distinguish direct
• link action toimpact and indirect impacts
• good methodlor displaying
• have potentialfordouble-
Matrices EIA results counting of impacts
• link action toimpact
• useful in simplifiedform for
• can become very complex if
checking for second order
Networks used beyond
impacts
simplifiedversion
• handles directand
indirect impacts
• can becumbersome
• easy tounderstand
• poorly suitedto
Overlays • locus and display spatialimpacts addressimpact duration or
• good sitingtool probability
• excellentforimpact identification
Geographic and spatialanalysis • heavy reliance on knowledge
Information • good for 'experimenting' anddata
System • often complex and expensive
Methods
Sr. No Factors
Checklist Matrices Networks Overlays GIS
1. Ease of use × × ×
Ease of Site
2. × × ×
Selection
Impact
3. × ×
identification
Reliance on
4. ×
knowledge
5. Cost effective × ×
6. Experimentation × × ×
7. Complexity × ×
Indirect Impact
8. ×
identification
9. Spatial Analysis × × ×
Impact
10.
probability
You might also like
- Impact Analysis PDFDocument3 pagesImpact Analysis PDFMaria Diaz FrancoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 FinalDocument95 pagesModule 3 FinalNorah ElizNo ratings yet
- ML ComparisonDocument1 pageML ComparisonAkhil DasariNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Shobha C.Hiremath (01FE17MCS019)Document25 pagesPresented By, Shobha C.Hiremath (01FE17MCS019)shobha hiremathNo ratings yet
- Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in DatabasesDocument36 pagesData Mining and Knowledge Discovery in DatabasesPixelsquare StudiosNo ratings yet
- Image Forgery Detection Using GLCNNB AlgorithmsDocument28 pagesImage Forgery Detection Using GLCNNB AlgorithmslaxmannNo ratings yet
- Eia 4Document7 pagesEia 4Nahid H Mazumder L15No ratings yet
- Table D1. Plan Risk Management: Technique Strengths WeaknessesDocument11 pagesTable D1. Plan Risk Management: Technique Strengths WeaknessesMuhammad El-FahamNo ratings yet
- Helland BERAC Oct2019Document30 pagesHelland BERAC Oct2019Emir AvcıoğluNo ratings yet
- Analytical Methods Validation DiagramDocument1 pageAnalytical Methods Validation DiagramMayra SanchezNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Sources of DataDocument7 pagesPrimary and Secondary Sources of DataSHIVANI SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 5bDocument2 pagesLaboratory Exercise 5bSael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PT CH 6 Vulnerability Scan Analysis ReadyDocument25 pagesPT CH 6 Vulnerability Scan Analysis Readykrishnareddy70084No ratings yet
- Video Based Fall Detection For Seniors With Human Pose EstimationDocument26 pagesVideo Based Fall Detection For Seniors With Human Pose EstimationHem RameshNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Digital TwinDocument15 pagesPresentation On Digital TwinAlif RuslanNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning - Types of LearningDocument4 pagesMachine Learning - Types of Learningori otdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Generative Adversarial Networks: Luke de OliveiraDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Generative Adversarial Networks: Luke de OliveiraMD. SHAHIDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- AI - 01 Practice Exercise 1 AnswerDocument2 pagesAI - 01 Practice Exercise 1 AnswerheanicolleschleinezNo ratings yet
- Ai Unit 3Document18 pagesAi Unit 3kakanuruarunkumarNo ratings yet
- HCPP-02 - Campus Network Intelligent O&M and CampusInsight-2022.01Document78 pagesHCPP-02 - Campus Network Intelligent O&M and CampusInsight-2022.01MaheeNo ratings yet
- Vad 16 PitpDocument134 pagesVad 16 PitpAbidzar Muhammad GhifariNo ratings yet
- 02 AbstractionsDocument78 pages02 AbstractionsMichael NaderNo ratings yet
- Image Filtering, Edge Detection, Edge Tracing Using Fuzzy ReasoningDocument11 pagesImage Filtering, Edge Detection, Edge Tracing Using Fuzzy ReasoningMuhammadWaqasNawazNo ratings yet
- Mesh-Intro 17.0 M03 Global Mesh ControlsDocument24 pagesMesh-Intro 17.0 M03 Global Mesh Controlsmarcosandia1974No ratings yet
- Zachry Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Texas A&M University, College StationDocument1 pageZachry Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Texas A&M University, College StationAsim Bashir KhajwalNo ratings yet
- PPTPPTXDocument30 pagesPPTPPTXTanujaa ShriNo ratings yet
- AR2022 Lec 1-FinalDocument25 pagesAR2022 Lec 1-FinalH KNo ratings yet
- The Reliability of Retro-Cues Determines The Fate of by Dorukhan BeyaztaşDocument20 pagesThe Reliability of Retro-Cues Determines The Fate of by Dorukhan BeyaztaşZerinda EllaNo ratings yet
- Feature Extraction and Selection Techniques For High-Dimensional DataDocument6 pagesFeature Extraction and Selection Techniques For High-Dimensional DataInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Finding A Pathfinder: Bjørn Reese Bryan StoutDocument4 pagesFinding A Pathfinder: Bjørn Reese Bryan StoutJon FrisbyNo ratings yet
- 0 THDocument25 pages0 THpadma priyaNo ratings yet
- ML in Mineral ProcessingDocument24 pagesML in Mineral ProcessingMartin.c.figueroaNo ratings yet
- AI Chapter 1,2,3Document9 pagesAI Chapter 1,2,3Sravanthi BoggaramNo ratings yet
- Overview of Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument9 pagesOverview of Wireless Sensor NetworksHemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- ISLR Chap 8 Shaheryar-ZiadDocument21 pagesISLR Chap 8 Shaheryar-ZiadShaheryar ZahurNo ratings yet
- RokDoc Product Sheet v12Document2 pagesRokDoc Product Sheet v12c_b_umashankarNo ratings yet
- Creating Surfaces: Esri International User ConferenceDocument51 pagesCreating Surfaces: Esri International User Conferencecarlos adrianNo ratings yet
- Implementing The Zachman Framework Neal FishmanDocument31 pagesImplementing The Zachman Framework Neal FishmanTom KakanowskiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Elements of Computational Thinking.280155520Document1 page2.1 Elements of Computational Thinking.280155520Mark RobsonNo ratings yet
- Main ProjectDocument21 pagesMain ProjectHarsha GuptaNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument41 pagesBrainNishanth Siva100% (1)
- Cluster AnalysisDocument39 pagesCluster Analysismuhavic36No ratings yet
- Introduction To Gis WorkbookDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Gis WorkbookAbbas AbduNo ratings yet
- Presentation (LR) 3Document8 pagesPresentation (LR) 3purnav2003No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0925231218300602 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0925231218300602 MainPiyush BafnaNo ratings yet
- Math: Statistics: Data Interpretation and Probability: Comprehend DevelopDocument3 pagesMath: Statistics: Data Interpretation and Probability: Comprehend DevelopYanSuoNo ratings yet
- CVlecture 6Document33 pagesCVlecture 6David BNo ratings yet
- Watson Developer Certification - Study AidDocument64 pagesWatson Developer Certification - Study AidAniruddha RayNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument6 pagesREVIEWERJay AnnNo ratings yet
- Iso 18436-2 Vibration Analysis Cat - III Topics Published 1546436736 PDFDocument2 pagesIso 18436-2 Vibration Analysis Cat - III Topics Published 1546436736 PDFDon PabloNo ratings yet
- Catal PDFDocument2 pagesCatal PDFDon PabloNo ratings yet
- 2015.08.26.Lecture01Intro 2Document37 pages2015.08.26.Lecture01Intro 2hinsermuNo ratings yet
- ML Lectures 2022 Part 1Document231 pagesML Lectures 2022 Part 1PRIYANKA SNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument10 pagesMachine LearningMd Shadman SakibNo ratings yet
- BECE352E Module 3Document64 pagesBECE352E Module 3nandini.chakraborty2021No ratings yet
- Variable Message Display (VMD)Document4 pagesVariable Message Display (VMD)kedar majethiyaNo ratings yet
- Technologies: Radio Network Planning ProcessDocument14 pagesTechnologies: Radio Network Planning Processnkapnangluther3099No ratings yet
- Review Slides: Usability and User Experience GoalsDocument16 pagesReview Slides: Usability and User Experience GoalsjohhnNo ratings yet
- The Design and Implementation of Geographic Information SystemsFrom EverandThe Design and Implementation of Geographic Information SystemsNo ratings yet
- Analysis Within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 2 Data Analysis — The MethodsFrom EverandAnalysis Within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 2 Data Analysis — The MethodsNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document20 pagesPresentation 1Puspha Vasanth RNo ratings yet
- Online Shopping ProjectDocument11 pagesOnline Shopping ProjectRaghu CkNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document4 pagesLab 5johnmechanjiNo ratings yet
- 12.2.1.5 Lab - Convert Data Into A Universal FormatDocument11 pages12.2.1.5 Lab - Convert Data Into A Universal Formatc583706No ratings yet
- How Many Sources For A 25 Page Research PaperDocument4 pagesHow Many Sources For A 25 Page Research Papers0l1nawymym3100% (1)
- Mathiesen, Harmonia and Ethos in Ancient Greek MusicDocument16 pagesMathiesen, Harmonia and Ethos in Ancient Greek MusicGiovanni100% (3)
- G9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Document6 pagesG9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Ayuu Nur AfifahNo ratings yet
- DsdsdsdsdsDocument2 pagesDsdsdsdsdssuvendu beheraNo ratings yet
- Practical Slot I SemesterDocument3 pagesPractical Slot I SemesterbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- ABB APTs PDFDocument8 pagesABB APTs PDFSaikat SahaNo ratings yet
- Donors Gala LetterDocument10 pagesDonors Gala LetterpremNo ratings yet
- G1 - LR - 2Y - 1.2.4 Dinosaur HerdsDocument6 pagesG1 - LR - 2Y - 1.2.4 Dinosaur HerdsPhạm SửuNo ratings yet
- On The Reality of Cognitive IllusionsDocument16 pagesOn The Reality of Cognitive IllusionssahooscNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 6 - Q2Document5 pagesPT - Mathematics 6 - Q2Geornie SomohidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document24 pagesLesson 1Juan Carlos Solís RiveraNo ratings yet
- Philosophy 25 Homework Assignment 1Document5 pagesPhilosophy 25 Homework Assignment 1Laurel WeberNo ratings yet
- Study Plan: CFE Exam Prep CourseDocument1 pageStudy Plan: CFE Exam Prep CourseGrace hblNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General BackgroundDocument14 pages1.1 General BackgroundChris TanNo ratings yet
- English Communication Styles Assignment MayDocument3 pagesEnglish Communication Styles Assignment MayÑæqêèb RåhmæñNo ratings yet
- 1 Base SAS Training 12th May 2015Document494 pages1 Base SAS Training 12th May 2015Vedavathy TCNo ratings yet
- History of ER DiagramsDocument7 pagesHistory of ER DiagramsRajesh Insb100% (1)
- T 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesT 2 ReviewAYA707No ratings yet
- WordSegmentationFL PDFDocument50 pagesWordSegmentationFL PDFCarlosSorianoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Trials 2Document16 pagesClinical Trials 2Franz SalazarNo ratings yet
- Output EsPDocument2 pagesOutput EsPGani Gonzales IbarrientosNo ratings yet
- Name F: 4b) TsachosDocument11 pagesName F: 4b) Tsachosabhineet raiNo ratings yet
- Chance & ChoiceDocument259 pagesChance & Choiceakasheh2100% (1)
- PhysiquePictorial Summer57 CompressedDocument16 pagesPhysiquePictorial Summer57 CompressedKrepyshNo ratings yet
- Oracle: IstoreDocument294 pagesOracle: IstoreVenkat BandaruNo ratings yet
- A13 GroupDocument99 pagesA13 Groupshubham kotwalNo ratings yet