Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathv2 PDF
Uploaded by
Aime Lamoste0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
mathV2.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesMathv2 PDF
Uploaded by
Aime LamosteCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
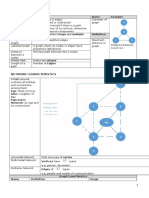
ONE-SIDED LIMITS LIMIT THEOREMS
The limit of f(x) as x approaches a from the left If f is a polynomial function, then
is L if the values of f(x) get closer and closer to
L as the values of x get closer and closer to a,
but are less than a. The notation is:
The limit of f(x) as x approaches a from the right
is L if the values of f(x) get closer and closer to
L as the values of x get closer and closer to a,
but are greater than a. The notation is:
ROADS
TO
If f is a rational function and f(a) is defined, then
For the right-handed limit we now have (note
the “+”) which means that we know will only Other Theorems:
look at x>a. Likewise for the left-handed limit
we have (note the “-”) which means that we
LIMITS
will only be looking at x<a.
Also, note that as with the “normal” limit, the
function should settle down to a single number,
in order for the limit to exist, on either the right
side of or the left side of depending on the
one-sided limit.
Submitted by:
Aime Lamoste
Shaina Sardanas
Nikko Salomon
Mark Pagalan
both sides of 2 to assure that any trends that we For x=2 we find:
might be seeing are in fact correct. The table of
WHAT IS A LIMIT? values are shown:
x f(x) x f(x) g(2) is indeterminate. It is not defined when x=2
A limit is said to be the quantity a function 1 2.0 3 8 but that does not mean that its limit as it
“approaches” as the input come close to 1.5 2.75 2.5 5.75 approaches x=2 is indeterminate. The definition
some value. Suppose that a function f(x) is 1.9 3.71 2.1 4.31 of states that we take into account the values
defined when the values of x are close to 1.99 3.9701 2.01 4.0301 close to a but not equal to a. The table of values
some real number a, then we can write: 1.999 3.997001 2.001 4.003001 below show that the limit of g(x) as x approaches
1.9999 3.99970001 2.0001 4.00030001 2 is equal to 4.
x f(x) x f(x)
This equation is said as: “The limit of f(x), as From this table it appears that the as the values of x 1.5 5.0 2.5 3.4
x approaches a, equals L” get closer and closer to 2, the values of f(x) get closer 1.9 4.15789 2.1 3.85714
and closer to 4. We can state this as “the limit of the
1.99 4.01507 2.01 3.98507
This tells us that the values of f(x) gets closer function as x approaches 2 is equal to 4 and written
as: 1.999 4.00150 2.001 3.99850
and closer to the value of L as x approaches
the value of a but not equal to a. 1.9999 4.00015 2.0001 3.99985
It can be confusing for some time but limits 1.99999 4.00001 2.00001 3.99998
are very important in dealing with derivatives
Graphical representation
and integrals in calculus.
In finding limits, we only consider the values is shown on the left.
of x very close to a on both sides but not Coincidentally, the limit
exactly a. Let us investigate and consider the of f(x) is equal to
function and we want to find the limit as x Graphical representation
approaches 2. We write: is shown on the left.
However this is not the
case for all functions.
Solution: Consider the function
We will choose quantities of x that get closer
and closer to 2 and plug these values into the
function. Take note to pick values of x on
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- MEC Maths SyllabusDocument13 pagesMEC Maths SyllabusAnil Kumar80% (5)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Grafos PDFDocument344 pagesGrafos PDFManuel acuñaNo ratings yet
- IS4241 - RevisionDocument13 pagesIS4241 - RevisionjieboNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Stability Analysis of Large-Scale Power Systems PDFDocument219 pagesDynamic Stability Analysis of Large-Scale Power Systems PDFMd. Arifur KabirNo ratings yet
- The Mother of All Calculus QuizzesDocument56 pagesThe Mother of All Calculus QuizzesKeri SawyerNo ratings yet
- Special Mathematics:: Counting Problems, Discrete Probabilities, Graphs TheoryDocument137 pagesSpecial Mathematics:: Counting Problems, Discrete Probabilities, Graphs TheoryLiviaMariaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programs in Standard FormDocument16 pagesLinear Programs in Standard FormSteve YeoNo ratings yet
- LQR LagrangeDocument18 pagesLQR LagrangearjunNo ratings yet
- Complex SyllabusDocument2 pagesComplex SyllabusMiliyon TilahunNo ratings yet
- 4.6 1 TransformationsDocument4 pages4.6 1 TransformationsBradley SinghNo ratings yet
- Second Quarterly Examination in Mathematics-11: Libertad National High SchoolDocument2 pagesSecond Quarterly Examination in Mathematics-11: Libertad National High SchoolAngie A. RabinoNo ratings yet
- Using The Fundamental Theorem of AlgebraDocument11 pagesUsing The Fundamental Theorem of AlgebraEmma GoebelNo ratings yet
- Two-Sided Laplace TransformDocument6 pagesTwo-Sided Laplace Transformshiena8181No ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument23 pagesInverse Trigonometric FunctionsSudeepNo ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationsDocument6 pagesNumerical DifferentiationsSaurabh TomarNo ratings yet
- Computational Method For Numerical Analysis With RDocument13 pagesComputational Method For Numerical Analysis With RRasheed OlatunbosunNo ratings yet
- 7.weighted Residual Methods Galerkin - English - 2022Document36 pages7.weighted Residual Methods Galerkin - English - 2022Pavlos YioukkasNo ratings yet
- Practical No 1 AimDocument17 pagesPractical No 1 AimPrachi BorlikarNo ratings yet
- Bounded Variation & Helly's Selection TheoremDocument16 pagesBounded Variation & Helly's Selection TheoremPaul BenedictNo ratings yet
- Series and Matrices Assignment IIT MadrasDocument1 pageSeries and Matrices Assignment IIT MadrasVishwajit HegdeNo ratings yet
- Unit-3-Greedy Method PDFDocument22 pagesUnit-3-Greedy Method PDFTéjã SâìNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Double and Triple IntegrationDocument25 pagesChapter 6 Double and Triple IntegrationLol KekNo ratings yet
- Smt. S.R.Patel English Medium School STD 12: Maths Work SheetDocument10 pagesSmt. S.R.Patel English Medium School STD 12: Maths Work SheetShreya mauryaNo ratings yet
- MATH-1201 Note Jan 19, 2022Document9 pagesMATH-1201 Note Jan 19, 2022Kunal KNo ratings yet
- L6 - Linear Algebra - Sub SpaceDocument15 pagesL6 - Linear Algebra - Sub SpaceHarshini MNo ratings yet
- AP Question Bank AdvancedDocument5 pagesAP Question Bank AdvancedVanshika KaulNo ratings yet
- Maths 3 SyllabusDocument2 pagesMaths 3 SyllabusShashwat TripathiNo ratings yet
- Math RemedialDocument3 pagesMath Remedialqwerty TelestnesiaNo ratings yet
- Unit - II: Simultaneous Equations (MCQ) : 1 A B C D C 2Document6 pagesUnit - II: Simultaneous Equations (MCQ) : 1 A B C D C 2DeathSky GamingNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Diffrentiability MCQSDocument5 pagesContinuity and Diffrentiability MCQSNoo EntryNo ratings yet