Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Neil Floyd VenturaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Neil Floyd VenturaCopyright:
Available Formats
RINOXABAN
Class: Anticoagulant (Blood thinner)
Indication: prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation;
treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE); to reduce risk of recurrent DVT
and/or PE. Rivaroxaban is also indicated, in combination with aspirin, for reducing the risk of major
cardiovascular events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease or peripheral artery disease. Due to
a lack of safety studies, it is not recommended for use in those under 18 years old. Its use is also not
recommended in those with severe renal impairment (<30mL/min).
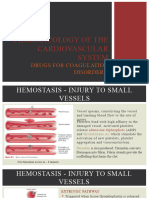
MOA: Rivaroxaban competitively inhibits free and clot bound factor Xa. Factor Xa is needed to activate
prothrombin (factor II) to thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin is a serine protease that is required to activate
fibrinogen to fibrin, which is the loose meshwork that completes the clotting process. Since one molecule
of factor Xa can generate more than 1000 molecules of thrombin, selective inhibitors of factor Xa are
profoundly useful in terminating the amplification of thrombin generation. The action of rivaroxaban is
irreversible.
S/E: Bloody, black, or tar-like bowel movements.
Blood in urine.
Coughing up blood.
Vomiting blood.
Nosebleeds.
Bleeding gums.
Weakness.
Tiredness.
SIMVATATIN
Class:
Indication: For the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and for the reduction in the risk of cardiac heart
disease mortality and cardiovascular events. It can also be used in adolescent patients for the treatment of
heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
MOA: Simvastatin is a prodrug in which the 6-membered lactone ring of simvastatin is hydrolyzed in
vivoto generate the beta,delta-dihydroxy acid, an active metabolite structurally similar to HMG-CoA
(hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA). Once hydrolyzed, simvastatin competes with HMG-CoA for HMG-CoA
reductase, a hepatic microsomal enzyme. Interference with the activity of this enzyme reduces the
quantity of mevalonic acid, a precursor of cholesterol.
S/E: Headache.
Difficulty sleeping.
Flushing of the skin.
Muscle aches, tenderness, or weakness (myalgia)
Drowsiness.
Dizziness.
Nausea or vomiting.
Abdominal cramping or pain.
You might also like
- Multiple Injuries: Drug StudiesDocument10 pagesMultiple Injuries: Drug StudiesTarquin TomadaNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol (Alvedon) Acetylcysteine Fluimucil KCL (Kalium Durule)Document1 pageParacetamol (Alvedon) Acetylcysteine Fluimucil KCL (Kalium Durule)Jesse James Advincula EdjecNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug Studysandal_meenuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJonica CamposNo ratings yet
- XareltoDocument9 pagesXareltoapi-309201467No ratings yet
- Acetazolamide Drug Study SummaryDocument4 pagesAcetazolamide Drug Study Summarygrail carantesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseDocument10 pagesDRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseAntonette PereyraNo ratings yet
- LOSARTANDocument3 pagesLOSARTANReinell GoNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NamePerdie Branden ReizNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleatelichunghkNo ratings yet
- Dextrose 50 InjectionDocument6 pagesDextrose 50 InjectionLip StickNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Xarelto PDFDocument33 pagesXarelto PDFNovita Dewi LestariNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- 66 Drug AnaDocument3 pages66 Drug AnaAlexa RoqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocument6 pagesDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaNo ratings yet
- Filgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyDocument3 pagesFilgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin: A Potent Fluoroquinolone AntibioticDocument2 pagesLevofloxacin: A Potent Fluoroquinolone AntibioticEliza Rahardja100% (1)
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (1)
- Drug Study TableDocument14 pagesDrug Study TableAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- PlasilDocument1 pagePlasilernestjohnNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Dobutamine It Stimulates Heart Muscle and Improves Blood Flow by Helping The Heart Pump BetterDocument3 pagesDobutamine It Stimulates Heart Muscle and Improves Blood Flow by Helping The Heart Pump BetterJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- EsomeprazoleDocument1 pageEsomeprazoleamaliea234No ratings yet
- MidodrineDocument2 pagesMidodrineMihaela VișanNo ratings yet
- Drug study highlights Allegra's mechanism, indications, and nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug study highlights Allegra's mechanism, indications, and nursing responsibilitiesBlitz KriegNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is IndicatedDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is Indicatedianecunar100% (1)
- Sodium Valproate Uses, DosageDocument2 pagesSodium Valproate Uses, DosageKhairul KhairulNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyDanica AbayaNo ratings yet
- Coreg (Carvedilol) 6.25mgDocument3 pagesCoreg (Carvedilol) 6.25mgE100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGrace CadawasNo ratings yet
- Colestipol Hydrochloride Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesColestipol Hydrochloride Nursing ConsiderationsAbby AngNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY: Ranitidine, Ceftriaxone, Tramadol, Diazepam, Intermediate InsulinDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY: Ranitidine, Ceftriaxone, Tramadol, Diazepam, Intermediate InsulinElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Chloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Document3 pagesChloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJoevelyn LaynoNo ratings yet
- Pioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, ActonelDocument3 pagesPioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, Actonelshidyakg100% (1)
- DRUGS Study OrigDocument17 pagesDRUGS Study OrigKiersten Karen Policarpio Verina100% (1)
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNo ratings yet
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Fluticasone PropionateDocument1 pageFluticasone PropionateRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- 13 DexamethasoneDocument2 pages13 DexamethasoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Coagulation Disorders 2023 (1)Document26 pagesDrugs for Coagulation Disorders 2023 (1)aguilarjanicaNo ratings yet
- Pos NoacDocument40 pagesPos NoacSanjeev Harry Budhooram100% (1)
- Pharmacology RCR1 – CardioDocument8 pagesPharmacology RCR1 – CardioeamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs: Mechanisms and Clinical UsesDocument25 pagesAnticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs: Mechanisms and Clinical UsesIdrissa John Sebeh ContehNo ratings yet
- 14 BloodDocument32 pages14 Bloodنور الإسلامNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantsKeerthana KNo ratings yet
- Concept Map, Neil Floyd Ventura PDFDocument1 pageConcept Map, Neil Floyd Ventura PDFNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Ischemic AttackDocument1 pageIschemic AttackNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic ShockDocument1 pageAnaphylactic ShockNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension FNCPDocument3 pagesHypertension FNCPNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Sheehans Na MalupetDocument1 pageSheehans Na MalupetNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- NCM107 OM Syllabus Feb 13 2019Document33 pagesNCM107 OM Syllabus Feb 13 2019Neil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation ToolDocument1 pageEvaluation ToolNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Front PageDocument1 pageCancer Front PageNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Palliative care reflects whole person approachDocument1 pagePalliative care reflects whole person approachNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Name: Ellaine Jhane T. Domede Bsn1VDocument9 pagesName: Ellaine Jhane T. Domede Bsn1VNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Spiritual Care On Anxiety in Adolescents With CancerDocument1 pageThe Effect of Spiritual Care On Anxiety in Adolescents With CancerNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Core Body Temperature with Bair Hugger SystemDocument2 pagesMaintaining Core Body Temperature with Bair Hugger SystemNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Consent 1Document1 pageConsent 1Neil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Record: Saint Louis UniversityDocument1 pageNursing Process Record: Saint Louis UniversityNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet