Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Metal Bar Containing Iron Acquires Dark Orange Color
Uploaded by
PedroPasmayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Metal Bar Containing Iron Acquires Dark Orange Color
Uploaded by
PedroPasmayCopyright:
Available Formats
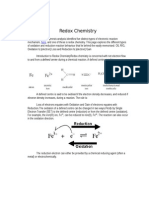
A metal bar containing iron acquires dark orange color
Due to a redox (or oxidation-reduction) reaction, a type of chemical reaction in which electrons
are exchanged between the reagents so that their oxidation states change.
In any redox reaction there are chemical changes in which one substance loses electrons
(oxidizes), acting as a reducer, and another substance gains electrons (reduces), acting as an
oxidizer. An everyday example is iron parts exposed to air and moisture. After a while we see
how a layer of iron oxide forms and we say that it has oxidized.
The elements have oxidation state 0 and thus the iron can oxidize losing electrons, which are
transferred to oxygen, which gains two electrons and is reduced, going from oxidation state 0 to
-2. The global reaction could be summarized as: 2 Fe + 3 O2→2 Fe2O3. As it is only necessary
that there is cession of electrons by an atom and gain of electrons by a different one, the iron
would oxidize equally in an atmosphere of chlorine, sulphur or oxygen.
References
Clickmica Andalucía, Iron oxidation, 2019, Spain.
You might also like
- Metals IGCSE NotesDocument27 pagesMetals IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- OxidationDocument5 pagesOxidationKudzanai MuchatoraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dDocument91 pagesChemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dfitradikojerdsswNo ratings yet
- RedoksDocument33 pagesRedokssanty_vanftowsNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument3 pagesREDOXJeianne Decerie MiguelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Result and Discussion of Rusting MetalDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Result and Discussion of Rusting MetalNeo BerkNo ratings yet
- What Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionDocument8 pagesWhat Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionReal RuchitNo ratings yet
- CH 6,7 NotesDocument18 pagesCH 6,7 NotesAishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Electron Transfer Reactions and Electrochem-IstryDocument31 pagesChapter 11 - Electron Transfer Reactions and Electrochem-IstryDeepraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit I. Electrochemistry: Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesUnit I. Electrochemistry: Learning ObjectivesArdenz Emrey LagascaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Princess...Document34 pagesOxidation-Reduction Reactions Princess...Warren Mark ManguneNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Chap. 2Document53 pagesCorrosion: Chap. 2Daniel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CH 14 and 15Document14 pagesChemistry CH 14 and 15Bhavna RathodNo ratings yet
- Lidza - OxidationDocument3 pagesLidza - OxidationKudzanai MuchatoraNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 5 Chapter 3Cheah Foo KitNo ratings yet
- El Ectrochemi Stry: H + F 2HFDocument39 pagesEl Ectrochemi Stry: H + F 2HFtNo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8Document13 pagesREDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8muralidharhegdenorthsquareNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument23 pagesChemistryAbhishek PawarNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSDocument6 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSKrishnendu NairNo ratings yet
- ppt6 REDOX PDFDocument17 pagesppt6 REDOX PDFOscar Kelvin NsituNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument24 pagesRedox TitrationNamrata patelNo ratings yet
- Curian Science Tutors Chem NotesDocument6 pagesCurian Science Tutors Chem NotesMunashe BinhaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: H + F 2HFDocument41 pagesElectrochemistry: H + F 2HFtNo ratings yet
- Redox ReaxDocument2 pagesRedox ReaxKristine Celaya AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationDocument12 pagesContents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationDocument5 pagesChemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Corrosion and Their Application To Coil-Coated MetalDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Corrosion and Their Application To Coil-Coated MetalkhurshedlakhoNo ratings yet
- Schneider - Chillers RangeDocument10 pagesSchneider - Chillers RangeerreagaaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanism: Prepared By: Ms - Sumina IbrahimDocument17 pagesInorganic Reaction Mechanism: Prepared By: Ms - Sumina IbrahimTuba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument5 pagesRedox ReactionsAthulRKrishnanNo ratings yet
- #1 Soal Diskusi RedoksDocument8 pages#1 Soal Diskusi RedoksAlfi FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions Class 11 Notes Chemistry: - OxidationDocument5 pagesRedox Reactions Class 11 Notes Chemistry: - Oxidation11 A Prasann JamaleNo ratings yet
- Clas 10 Chemistry ch-1 April Day 4Document5 pagesClas 10 Chemistry ch-1 April Day 4gourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 3 Oxidation and Reduction 2014Document97 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 3 Oxidation and Reduction 2014Cheah Foo Kit33% (3)
- Hsslive XI CH 7 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument7 pagesHsslive XI CH 7 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- L.O.13chemistry G 10Document22 pagesL.O.13chemistry G 10bebo atefNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentvermaz2deepNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions NotesDocument4 pagesRedox Reactions Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- Redox Reaction: Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Oxygen TransferDocument28 pagesRedox Reaction: Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Oxygen TransferfaridNo ratings yet
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesDocument5 pagesClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument27 pagesThe Reactivity Series of Metals118latelyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Electricity:: ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesChemistry and Electricity:: ElectrochemistrySuleman TariqNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions: What Is A Redox Reaction?Document2 pagesRedox Reactions: What Is A Redox Reaction?izzati03No ratings yet
- Expt 2 Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument32 pagesExpt 2 Oxidation Reduction Reactionstwinkledreampoppies100% (2)
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentDocument9 pagesOxidizing and Reducing Agentabuzar khalidNo ratings yet
- REDOX Reaction: CombustionDocument13 pagesREDOX Reaction: Combustionanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Oxide Across Period 3Document7 pagesOxide Across Period 3William100% (3)
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Book - Redox (1) YesssDocument10 pagesChemistry - Book - Redox (1) YesssOrnella DappianoNo ratings yet
- S-Block Elements Theory - EDocument27 pagesS-Block Elements Theory - Ethinkiit100% (2)
- S BlockDocument27 pagesS BlockAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Reactivity LO's and IGCSE NotesDocument10 pagesReactivity LO's and IGCSE Notesm.sarmadrehanNo ratings yet
- Metals: The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals: The Reactivity Series of Metalseugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry - Unit - IIDocument21 pagesEngineering Chemistry - Unit - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument43 pagesChapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsTegar MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Redox (Reduction-Oxidation, PronunciationDocument1 pageRedox (Reduction-Oxidation, PronunciationWlader SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Genera Biology 1 (Chemical Reaction)Document3 pagesGenera Biology 1 (Chemical Reaction)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument17 pagesProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)