Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.1 Sources of Funds For Business Operations Funds
Uploaded by
Chz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageSources of funds for a business
Original Title
Sources of Funds
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSources of funds for a business
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page4.1 Sources of Funds For Business Operations Funds
Uploaded by
ChzSources of funds for a business
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CHAPTER 4: SOURCES AND USES OF SHORT TERM used to generate investment income through capital
AND LONG TERM FUNDS appreciation in stock investments or trading through
bond investments
Accounts receivable - increase sales by making
4.1 SOURCES OF FUNDS FOR BUSINESS OPERATIONS buying more attractive to the customer with the
availability of credit
FUNDS 3. Inventory
Supply of capital belonging to numerous investors “product roster”
Money, investment, finance, budget, The more interesting it is, the greater potential sales
what you use to buy for your business
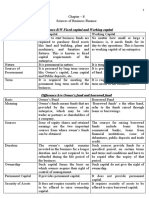
SHORT TERM FUNDS LONG TERM FUNDS
For daily business operations’ working capital Used for start-up business requirements, capital
Sources of fund expenditures, or business expansion
a. Bank loans Ex. Invest in a building or equipment that will sustain the
b. Credit from suppliers growth of his operations
c. Accrued liabilities Long-term funds in a corporate setup: Debt or Equity from
Used to finance current assets: investing public
a. Accounts Receivables (AR) Acquire debts by issuing bonds, raise capital by issuing
b. Inventories stocks (common and preferred)
sales bought on credit; inventory to be paid
short term fund will provide cash to pay for debts or BANKS
expenses (ex. purchase of inventory) financial intermediary that brings together depositors
Debt only and borrowers
One year loan or less major source of funding for working capital requirements
regulated by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP)
FUNDING WORKING CAPITAL
Working capital Current assets used in operations 1. Commercial Banks
a. Cash Clients are mostly retail customers
b. Cash equivalents or marketable securities main business is lending
c. Accounts receivables Transactions are many and usually not very large in
d. Inventory size
Sources of working capital:
put up many branches in different locations to be
a. Savings account
closer to their market so that they may service them
b. Current accounts
better and faster
Larger commercial banks in the Philippines: BDO,
UnionBank, Metrobank, and BPI
Balance
Sheet 2. Universal Banks
Banks that are licensed to do more sophisticated
Total Liabilities banking services than commercial banks
Total Assets
and Equity
Clientele comprises of the top corporations of the
Current Long Term Current country and global businesses
Assets Assets Liabilities Lend to these top business conglomerates
Manage their corporate funds
Cash Long Term
Debt Invest their portfolio
Cash equivalent/ Advise these companies on financial market
Marketable Stockholders'
Securities Equity movements and directions
transactions are usually bigger in size, multicurrency,
Accounts
Receivable and global in nature
Inventory 3. Investment Banks
They are similar to universal banks in terms of
USES OF WORKING CAPITAL sophisticated banking services.
1. Net working capital or working capital They have no branches all around the
current assets less current liabilities country
Helps carry out the normal operations of business They are more specialized and deal
Used to generate sales and profits for a business with top corporations, global businesses, and
Cash uses governments
to be invested in inventory Their marketing making activities are:
pay off short-term obligations to reduce the cost o Trading
of doing business o Fund Management
o Portfolio Management
2. Marketable securities
You might also like
- Business Finance Notes Finals TermDocument3 pagesBusiness Finance Notes Finals TermMary Antonette VeronaNo ratings yet
- Abm 4 Module 7 8Document4 pagesAbm 4 Module 7 8Argene AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Business Finance (Answer Sheet)Document3 pagesWeek 1 - Business Finance (Answer Sheet)Andreana Mae VergaraNo ratings yet
- MBM 507 - Financial Management ReviewerDocument10 pagesMBM 507 - Financial Management ReviewerEdson FenequitoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Test 1 With AnswersDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank Test 1 With AnswersUlugbek BayboboevNo ratings yet
- Bank Valuation Basics: Jay D. Wilson, CFA, CBADocument50 pagesBank Valuation Basics: Jay D. Wilson, CFA, CBAbhaskkarNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument17 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerkassyvsNo ratings yet
- 2.why Do Financial Institutions ExistDocument33 pages2.why Do Financial Institutions ExistАндријана Б. ДаневскаNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - IPO, Investment Bank, Financial RestructionDocument20 pagesChapter 20 - IPO, Investment Bank, Financial RestructionFariza SiswantiNo ratings yet
- Finance PDFDocument6 pagesFinance PDFBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Financial AccountingRomae DomagasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument20 pagesUnit 1 NotesSagar AchNo ratings yet
- R29 Sources of CapitalDocument12 pagesR29 Sources of CapitalSumair ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Financial Management 23Document59 pagesWeek 7 - Financial Management 23jeff28No ratings yet
- Conceptual Frame WorkDocument62 pagesConceptual Frame WorkKavyaNo ratings yet
- Deal CycleDocument38 pagesDeal CycleNandini SuriNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ModuleDocument41 pagesBusiness Finance ModulerhyzeNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS FINANCE Reviewer PrelimsDocument3 pagesBUSINESS FINANCE Reviewer Prelimssushi nakiriNo ratings yet
- Chap-11 Business Finance and Fundamentals of AccountingDocument23 pagesChap-11 Business Finance and Fundamentals of AccountingSiffat Bin AyubNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1: Developing Corporate Entrepreneurship GROUP 2: Entrepreneurial Finance SourceDocument3 pagesGROUP 1: Developing Corporate Entrepreneurship GROUP 2: Entrepreneurial Finance SourceLegendXNo ratings yet
- Finance BasicsDocument6 pagesFinance BasicsBushra HaqueNo ratings yet
- Finmar Final Handouts 1 PDFDocument3 pagesFinmar Final Handouts 1 PDFAcissejNo ratings yet
- MFIN7005 Corporate Finance and Asset Valuation: Lecture 1 Introduction Prof. Wenlan QianDocument53 pagesMFIN7005 Corporate Finance and Asset Valuation: Lecture 1 Introduction Prof. Wenlan QianSIQING LINo ratings yet
- FIN420 Lecture 6 (Working Capital Management)Document20 pagesFIN420 Lecture 6 (Working Capital Management)MUHAMMAD AZRAN AMRANNo ratings yet
- EntrepMind Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesEntrepMind Finals ReviewerShanley Vanna EscalonaNo ratings yet
- S1 IntroDocument20 pagesS1 IntroMayank SinghNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate FinanceDocument258 pagesApplied Corporate Financesirkoywayo6628No ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument10 pagesMerchant BankingMubarak ThangalNo ratings yet
- Ratios: Sr. No Category Formula Interpretation A Liquidity RatiosDocument6 pagesRatios: Sr. No Category Formula Interpretation A Liquidity RatiosShruti MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Ecternal Source of CapitalDocument12 pagesEcternal Source of CapitalTAWHID ARMANNo ratings yet
- Participation in The Market: A Portion ofDocument5 pagesParticipation in The Market: A Portion ofRonah Abigail BejocNo ratings yet
- Business FinanceDocument19 pagesBusiness Financeluci0usfa1ryyNo ratings yet
- Working Capital IntroductionDocument18 pagesWorking Capital IntroductionShanmuka SreenivasNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS FINANCE Chapter 1Document16 pagesBUSINESS FINANCE Chapter 1Melvin J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- 50 Business Words, Meaning and SentencesDocument8 pages50 Business Words, Meaning and Sentencesvener magpayoNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument13 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerMikaella Adriana GoNo ratings yet
- Bus. Fin. WEEk 5-6Document14 pagesBus. Fin. WEEk 5-6Jessa Gallardo100% (1)
- Managing Non Deposit LiabilitiesDocument37 pagesManaging Non Deposit LiabilitiesPrashamsa RijalNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument50 pagesSummarythamtayyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Sources of Business FinanceDocument13 pagesChapter 8 Sources of Business FinanceSHUBHAM SHEKHAWATNo ratings yet
- FRA DossierDocument94 pagesFRA DossierRNo ratings yet
- Financial Management in AgribusinessDocument10 pagesFinancial Management in AgribusinessNidhi NairNo ratings yet
- Scope and Objectives of Financial ManagementDocument23 pagesScope and Objectives of Financial ManagementAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Q.Discuss The Various Sources of Financing Working Capital. (OR) Q. Explain The Sources of Financing of Current AssetsDocument5 pagesQ.Discuss The Various Sources of Financing Working Capital. (OR) Q. Explain The Sources of Financing of Current AssetsSiva SankariNo ratings yet
- Financing M&A (Autosaved)Document17 pagesFinancing M&A (Autosaved)Prabha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Busfin ReviewerDocument4 pagesBusfin ReviewerjeonsnobNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance For Small BusinessDocument4 pagesSources of Finance For Small BusinessAbhilasha JoshiNo ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesINTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 Reviewercelynah.rheudeNo ratings yet
- FM TheoryDocument23 pagesFM TheoryBhavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionGokul BansalNo ratings yet
- Financial Filings and Annual Reports: Separating The Wheat From The ChaffDocument10 pagesFinancial Filings and Annual Reports: Separating The Wheat From The ChaffsuksesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 6 FinancingDocument19 pagesCHAPTER - 6 FinancingtemesgenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Uses and Sources of STF and LTFDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Uses and Sources of STF and LTFChristopher Beltran CauanNo ratings yet
- Chapters 4 6Document8 pagesChapters 4 6Rian EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- MCB Akash Previous Year Question PapersDocument86 pagesMCB Akash Previous Year Question PapersShrid GuptaNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document24 pagesSlide 1Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FMDocument25 pagesIntroduction To FMPalak JainNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: DR Yen Chen Topic 1: Financial Manager Reading: Brealey Ch.1Document22 pagesFinancial Management: DR Yen Chen Topic 1: Financial Manager Reading: Brealey Ch.1charithNo ratings yet
- Card Sizes : Format Dimensions UsageDocument2 pagesCard Sizes : Format Dimensions UsageAnonymous hKt1bjMF2No ratings yet
- National Chenani-Nashri TunnelDocument5 pagesNational Chenani-Nashri TunnelshreyaNo ratings yet
- Higher PurchaseDocument28 pagesHigher PurchaseNitesh ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- Black Book SoftDocument77 pagesBlack Book SoftSiddiqui AlmasNo ratings yet
- Opening Saving Account in HDFC BankDocument31 pagesOpening Saving Account in HDFC BankSukhchain AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Profit Sharing PDFDocument19 pagesProfit Sharing PDFGadisNo ratings yet
- Iifl Gold LoanDocument52 pagesIifl Gold LoanuiopoiuyNo ratings yet
- United States v. Hoffler-Riddick, 4th Cir. (2007)Document10 pagesUnited States v. Hoffler-Riddick, 4th Cir. (2007)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- A Study On Barriers To E-Commerce Adoption in Vadodara District SMEsDocument15 pagesA Study On Barriers To E-Commerce Adoption in Vadodara District SMEsKushagra purohitNo ratings yet
- Water and Sanitation Services Company - WSSC D.I. Khan: Eligibility CriteriaDocument4 pagesWater and Sanitation Services Company - WSSC D.I. Khan: Eligibility CriteriakabirNo ratings yet
- List of AMCs in IndiaDocument1 pageList of AMCs in Indiaajayterdal8471No ratings yet
- Feysel AbdoDocument112 pagesFeysel AbdoAbdi ÀgeNo ratings yet
- AkzoDocument2 pagesAkzoHemanth DesettyNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum Gramin Bank MPDocument60 pagesCorrigendum Gramin Bank MPsaurabhbectorNo ratings yet
- 340 S02 FinalDocument6 pages340 S02 Final2376271No ratings yet
- China Banking Corporation vs. CADocument1 pageChina Banking Corporation vs. CAArmstrong BosantogNo ratings yet
- International Trade Assignment 2Document22 pagesInternational Trade Assignment 2Gayatri PanjwaniNo ratings yet
- Landcorp FLCC Brochure 2013 v3Document6 pagesLandcorp FLCC Brochure 2013 v3Shadi GarmaNo ratings yet
- Banking Letters: 1) Somatie de PlataDocument7 pagesBanking Letters: 1) Somatie de PlataMireanu ElenaNo ratings yet
- Inward RemittenceDocument2 pagesInward Remittencepronab sarkerNo ratings yet
- Kaleem Aslam: Cluster Financial AccountantDocument2 pagesKaleem Aslam: Cluster Financial Accountantabdul waleedNo ratings yet
- October 31, 2011 PostsDocument2,156 pagesOctober 31, 2011 PostsAlbert L. PeiaNo ratings yet
- Cityam 2011-09-19Document36 pagesCityam 2011-09-19City A.M.No ratings yet
- SAPM-1 Assignment-2021 - Rahul MJDocument6 pagesSAPM-1 Assignment-2021 - Rahul MJMujeeb Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- IRA Blank Form 2017 1Document1 pageIRA Blank Form 2017 1ValerieAnnVilleroAlvarezValienteNo ratings yet
- TazaTicket PresentationDocument13 pagesTazaTicket Presentationilyas shabbirNo ratings yet
- 2879596invoice 8Document1 page2879596invoice 8gabrielmaheshe039No ratings yet
- Star Publications (Malaysia) Berhad: Special Dividend Surprise - 13/10/2010Document2 pagesStar Publications (Malaysia) Berhad: Special Dividend Surprise - 13/10/2010Rhb InvestNo ratings yet
- Alfacurrate AAA PMS Jul16Document39 pagesAlfacurrate AAA PMS Jul16flytorahulNo ratings yet
- Conclusion It or EbankDocument1 pageConclusion It or EbankchandamatlaniNo ratings yet