0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views3 pagesUEC Electronic Engineering Course Overview
This document provides information on the UEC: Electronic Engineering course, including:
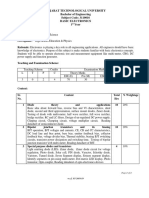
1) The course objectives are to enhance student comprehension of electronic devices, logic gates, minimization techniques, logic families, ICs, and combinational circuits and their applications.
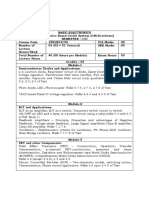
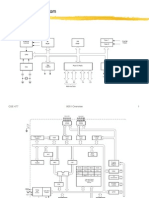
2) Topics covered include semiconductor devices, electronics devices and circuits, operational amplifier circuits, digital systems and binary numbers, combinational and sequential logic, and logic families.
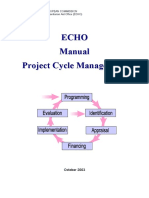
3) Evaluation includes a mid-semester test, end-semester test, and sessionals such as assignments, projects, tutorials, quizzes, and lab evaluations.
Uploaded by
vkv.foeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views3 pagesUEC Electronic Engineering Course Overview
This document provides information on the UEC: Electronic Engineering course, including:
1) The course objectives are to enhance student comprehension of electronic devices, logic gates, minimization techniques, logic families, ICs, and combinational circuits and their applications.
2) Topics covered include semiconductor devices, electronics devices and circuits, operational amplifier circuits, digital systems and binary numbers, combinational and sequential logic, and logic families.
3) Evaluation includes a mid-semester test, end-semester test, and sessionals such as assignments, projects, tutorials, quizzes, and lab evaluations.
Uploaded by
vkv.foeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd