Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stratification PDF
Uploaded by
Ahmed M. Hashim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document describes the quality control tool of stratification. Stratification involves separating data into categories to identify which contribute most to the problem. It can be used for root cause analysis, sampling, hypothesis testing, and developing solutions. The process involves selecting stratification variables, establishing categories, sorting observations, calculating results for each category, and displaying the results graphically. An example is provided of stratifying 44 defects by assembly type, shift, and technician to provide supplementary information for root cause analysis.
Original Description:
Original Title
Stratification.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the quality control tool of stratification. Stratification involves separating data into categories to identify which contribute most to the problem. It can be used for root cause analysis, sampling, hypothesis testing, and developing solutions. The process involves selecting stratification variables, establishing categories, sorting observations, calculating results for each category, and displaying the results graphically. An example is provided of stratifying 44 defects by assembly type, shift, and technician to provide supplementary information for root cause analysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageStratification PDF
Uploaded by
Ahmed M. HashimThis document describes the quality control tool of stratification. Stratification involves separating data into categories to identify which contribute most to the problem. It can be used for root cause analysis, sampling, hypothesis testing, and developing solutions. The process involves selecting stratification variables, establishing categories, sorting observations, calculating results for each category, and displaying the results graphically. An example is provided of stratifying 44 defects by assembly type, shift, and technician to provide supplementary information for root cause analysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
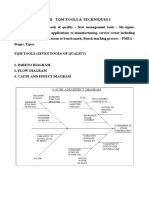
SEVEN BASIC QUALITY CONTROL TOOL
QUALITY TOOLS
Stratification
Description of Stratification: Stratification is the separation of data into
categories. Its most frequent use is during the diagnostic journey to identify which
categories contribute the most to the problem being solved.
When to use Stratification: Stratification can be applied for root cause analysis,
sampling, hypothesis testing, and developing solutions. Stratification help answer
questions as to the frequency of defects, factors that may be contributing to a quality
problem, and the degree to which results may differ across groups.
How to use Stratification:
Steps to stratification:
1) Select the stratification variables.
2) Establish categories that are to be used for each stratification variables.
3) Sort observations into the categories of one of the stratification variables.
4) Calculate the phenomenon being measured for each category.
5) Display the results on a graph – bar chart
6) Prepare and display results for other stratification variables.
Application of Stratification: Applied when performing a root cause analysis. For
example – upon successful completion of a pareto analysis of possible categories of
causes, “wrong component assembled” was identified as a vital few contributing factor
accounting for total of 44 defects. Stratification could be applied to categorize these 44
defects by the following:
- Assembly types: Causes may be specific to assembly type, bill of material, etc.
- By shift: Causes maybe isolated to specific shifts.
- By Tech: There may be correlation between techs and wrong assembly operation.
The resulting stratification of data helps provide supplementary information needed for
root cause analysis.
References:
Juran Quality Handbook Sixth Edition: Joseph M Juran; Joseph A. De Feo
Page 1 of 1 10/14/2012
You might also like
- 7 QC Tools - StratificationDocument3 pages7 QC Tools - Stratificationraja100% (1)
- Data Analysis and Research MethodologyDocument23 pagesData Analysis and Research MethodologySOURASHTRANo ratings yet
- Data Analysis: Analysis of Data Is A Process of Inspecting, Cleaning, Transforming, and ModelingDocument6 pagesData Analysis: Analysis of Data Is A Process of Inspecting, Cleaning, Transforming, and ModelingGhoruk Ce RaymNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Data: Chapter-5Document17 pagesAnalysis of Data: Chapter-5Punit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument18 pagesData AnalysisShouib MehreyarNo ratings yet
- Data AnalyticsDocument8 pagesData AnalyticsgtmangozhoNo ratings yet
- TRIZ Method by Genrich AltshullerDocument5 pagesTRIZ Method by Genrich AltshullerAnonymous JyrLl3RNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Segmentation Approaches: by Beth Horn and Wei HuangDocument12 pagesComparison of Segmentation Approaches: by Beth Horn and Wei HuangPritam GhoshNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Risks Assessment MethodsDocument20 pagesHazards and Risks Assessment Methodsapi-3733731100% (8)
- BRM SSSDocument17 pagesBRM SSSAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Meta Análisis Con RDocument14 pagesMeta Análisis Con R290971No ratings yet
- S Ensitivity A NalysisDocument44 pagesS Ensitivity A Nalysisatul_rockstarNo ratings yet
- BRM Chap 7 and 8 PDFDocument16 pagesBRM Chap 7 and 8 PDFMareyam DnglNo ratings yet
- FMEA Training GuideDocument10 pagesFMEA Training GuideniknenadNo ratings yet
- Research Paper With Factor AnalysisDocument7 pagesResearch Paper With Factor Analysispimywinihyj3100% (1)
- Data Analysis in ResearchDocument29 pagesData Analysis in ResearchIshtiaq Ahmed100% (1)
- VFM Technical Guides: Collecting, Analysing, and PresentingDocument44 pagesVFM Technical Guides: Collecting, Analysing, and PresentingbarassaNo ratings yet
- By @isarojbeheraDocument46 pagesBy @isarojbeheraR&D DaffyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Impact EvaluationDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Impact EvaluationBert AgrisNo ratings yet
- Key Principles of Impact EvaluationDocument9 pagesKey Principles of Impact Evaluationsagugu20004394No ratings yet
- Street Smart Analytics: The Basic Handbook of Analytics To Ace B-School Summer PlacementsDocument23 pagesStreet Smart Analytics: The Basic Handbook of Analytics To Ace B-School Summer Placementsthecoolguy96No ratings yet
- Annual Reviews in Control: Khaoula Tidriri, Nizar Chatti, Sylvain Verron, Teodor TiplicaDocument19 pagesAnnual Reviews in Control: Khaoula Tidriri, Nizar Chatti, Sylvain Verron, Teodor TiplicaHusnain AliNo ratings yet
- MachinelearningDocument3 pagesMachinelearningayesha awanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 Answers - 1225397Document3 pagesAssignment-4 Answers - 1225397Li NaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment MethodsDocument24 pagesRisk Assessment MethodsXie ShjNo ratings yet
- FcthgchgtbelowDocument6 pagesFcthgchgtbelowМагистерски ТрудовиNo ratings yet
- Paper-1 Significance of One-Class Classification in Outlier DetectionDocument11 pagesPaper-1 Significance of One-Class Classification in Outlier DetectionRachel WheelerNo ratings yet
- A Review On Evaluation Metrics For DataDocument11 pagesA Review On Evaluation Metrics For DataSabit EzazNo ratings yet
- Final HomeworkDocument4 pagesFinal HomeworkAngelo GordilloNo ratings yet
- NENGA CourseworkDocument2 pagesNENGA Courseworkm.shoaibsaleem113No ratings yet
- Comparating ClassifiersDocument11 pagesComparating ClassifiersBatista CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis (This Material Is Available @Document8 pagesFailure Analysis (This Material Is Available @leniyanNo ratings yet
- CCPS521 WIN2023 Week05 - ClassificationDocument47 pagesCCPS521 WIN2023 Week05 - ClassificationCharles KingstonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document27 pagesUnit 3Siva MaxNo ratings yet
- HAZOP Training GuideDocument9 pagesHAZOP Training GuideOoAlquimistaNo ratings yet
- 1010 Analytical Data-Interpretation and Treatment UspDocument29 pages1010 Analytical Data-Interpretation and Treatment Uspalexanderaristizabal100% (1)
- Hazop Training GuideDocument9 pagesHazop Training GuideAdyBorsosNo ratings yet
- Hazop Training GuideDocument9 pagesHazop Training GuideAli RizviNo ratings yet
- 11 To 20Document4 pages11 To 2020-CFIS-1038-Ravuri shanmukhaNo ratings yet
- Q2 GPT3 Research Instrument Data Gathering Methods and Data AnalysisDocument15 pagesQ2 GPT3 Research Instrument Data Gathering Methods and Data AnalysisChlzy ArdienteNo ratings yet
- AMI Penetration Test Plan 1 0 RC3 PDFDocument36 pagesAMI Penetration Test Plan 1 0 RC3 PDFAkeem Donald Francis100% (1)
- Aprasial Mix Methode-MMAT 2018 Criteria-Manual 2018-08-01 ENGDocument11 pagesAprasial Mix Methode-MMAT 2018 Criteria-Manual 2018-08-01 ENGAjengNo ratings yet
- MMAT 2018 Criteria-Manual 2018-08-08cDocument11 pagesMMAT 2018 Criteria-Manual 2018-08-08cDiah SaputriNo ratings yet
- HAZOP Training Guide NewDocument13 pagesHAZOP Training Guide NewKhalis RiyanggaNo ratings yet
- Technical Note Evaluation MatrixDocument5 pagesTechnical Note Evaluation MatrixRiya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Task 2 (Refer To Individual Project Instructions)Document9 pagesTask 2 (Refer To Individual Project Instructions)Ikhram JohariNo ratings yet
- Official: Á1010Ñ Analytical Data-Interpretation and TreatmentDocument29 pagesOfficial: Á1010Ñ Analytical Data-Interpretation and TreatmentDilawar BakhtNo ratings yet
- Metodologia de 4 CuadrantesDocument7 pagesMetodologia de 4 CuadrantesJolukalel Camargo0% (1)
- Fim D03 S03 T01 Step PDFDocument19 pagesFim D03 S03 T01 Step PDFlenesaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Improving Prediction and Classification: Theory and Algorithms in C++From EverandAssessing and Improving Prediction and Classification: Theory and Algorithms in C++No ratings yet
- Ensemble LearningDocument21 pagesEnsemble LearningdfnngfffNo ratings yet
- Metaheuristics Algorithms for Medical Applications: Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandMetaheuristics Algorithms for Medical Applications: Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Analyzing the Large Number of Variables in Biomedical and Satellite ImageryFrom EverandAnalyzing the Large Number of Variables in Biomedical and Satellite ImageryNo ratings yet
- Meghan Markle: Humanitarian AdvocateDocument2 pagesMeghan Markle: Humanitarian AdvocateAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Quality ToolDocument7 pagesQuality ToolAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Aconex Guide For Registration and User CreationDocument2 pagesAconex Guide For Registration and User CreationAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Request For Prequalification (RFPQ) : Artwork ConservationDocument29 pagesRequest For Prequalification (RFPQ) : Artwork ConservationAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- The Missing Link - Lean Leadership - DWMann PDFDocument12 pagesThe Missing Link - Lean Leadership - DWMann PDFAhmed M. Hashim100% (1)
- Fabricating Sheldon For SchoolsDocument4 pagesFabricating Sheldon For SchoolsAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Shelter 2.0 "Sheldon"materialsDocument3 pagesShelter 2.0 "Sheldon"materialsAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- CM HillDocument60 pagesCM HillAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Shelter 2.0 - Sheldon - Assembly InstructionsDocument84 pagesShelter 2.0 - Sheldon - Assembly InstructionsAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesQuality Assurance QuestionnaireAbdelkader FattoucheNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Analysis Tools Failure Modes and Effects Analysis - FmeaDocument7 pagesProblem Solving and Analysis Tools Failure Modes and Effects Analysis - FmeaAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- IS IS NOT TemplateDocument1 pageIS IS NOT TemplateAhmed M. Hashim100% (1)
- Correlation Rev 1.0Document5 pagesCorrelation Rev 1.0Ahmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Analysis Tools: "5 Why'sDocument5 pagesProblem Solving and Analysis Tools: "5 Why'sAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Quality Tools Plan Do Check ActDocument4 pagesQuality Tools Plan Do Check ActAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Affinity Diagram 1Document2 pagesAffinity Diagram 1Ahmed M. HashimNo ratings yet