0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageMechanics of Solids: Strain Analysis
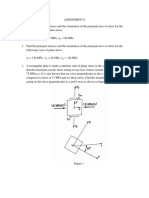
This document contains mechanics of solids practice problems involving determining strain components and principal strains from strain gauge readings under different conditions. It includes problems finding principal strains from a state of plane strain with given strain components, from strain rosette readings, and from a 600 strain rosette. It also provides equations to determine strain components in polar and cylindrical coordinates.
Uploaded by
HCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageMechanics of Solids: Strain Analysis
This document contains mechanics of solids practice problems involving determining strain components and principal strains from strain gauge readings under different conditions. It includes problems finding principal strains from a state of plane strain with given strain components, from strain rosette readings, and from a 600 strain rosette. It also provides equations to determine strain components in polar and cylindrical coordinates.
Uploaded by
HCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd