Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hi
Uploaded by
Zaza MawarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hi
Uploaded by
Zaza MawarCopyright:
Available Formats
SULIT 2 4541/2
KIMIA
Kertas 2 MODUL STRAIGHT A+ KIMIA
Esei SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA 2019
Cadangan Jawapan
No MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
1(a) Freezing 1
The particles of the compound arrange closer to each other
// Stronger forces of attraction formed among the particles. 1
This will release energy. 1
The energy released is equal to the heat energy lost to the
surrounding.
1 4
(b)(i) At 80oC : Solid 1
At 280oC : Gas
1 2
(ii)
Temperature 80oC (Solid) 280oC (Gas)
Arrangement of Particles are Particles are far
particles orderly and apart.
1
closely packed
together.
Movement of Vibrating and Particles move
particles rotating about in randomly and
their fixed positions. rapidly in all
directions. 1
The forces of Strong Weak 1
attraction
Kinetic energy Low High
1 4
Note: 1 mark for each correct comparison.
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 3 4541/2
(iii) Able to describe the procedure correctly.
Example:
1. A boiling tube is filled with powder of compound M to a
depth of 3 cm. 1
2. A thermometer is placed into powder of compound M in the 1
boiling tube.
3. A 500 ml beaker is filled with coconut oil/palm oil until it is ¾ 1
full.
4. The beaker is then placed on a tripod stand. 1
5. The boiling tube containing compound M is clamped onto a
retort stand and immersed into the coconut oil/palm oil in the
beaker. 1
6. The coconut oil/palm oil is heated slowly and the stopwatch
is started. 1
7. The powder of compound M is stirred slowly with the
thermometer. 1
8. The temperature of the compound M is recorded at 30-
second intervals until the compound M has melted
completely. 1
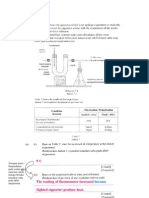
Result:
The temperature reading are recorded in a table as shown below.
Time(s) 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 ….
Temperature
(oC) 1 8
Max 6
The graph of temperature against time for the heating of compound
M is plotted. O
Temperature ( C)
o
TC
Time (s)
Conclusion:
Based on the graph, the temperature remains constant at T oC.
(Must indicate T in the graph) 1
Therefore, the melting point of compound M is T oC. 1
4
20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 4 4541/2
2 (a) (i)
Element C H O
Mass (g) 39.9 6.7 53.5 1
Number of 39.9/12 // 6.7/1 // 6.7 53.5/16 //
mole(mol) 3.33 3.34 1
Ratio of mole 1 2 1
Empirical formula is CH2O 1 3
(ii) Relative Molecular mass of (CH2O)n = 60//
(12 + 2+16)n = 60// 1
n=2
Thus, molecular formula = C2H4O2 1 2
(iii) Ethanoic acid 1 1
(b)
Empirical formula// CH2O Molecular formula // C2H4O2
Shows the .simplest ratio of Shows the actual number of 1+1
atoms of each element in a atoms of each element in a
compound. molecule of the compound.
Consists of 1 carbon atom, 2 Consists of 2 carbon atoms, 4
hydrogen atoms and 1 hydrogen atoms and 2
1+1
oxygen atom oxygen atoms
Both compound contains elements carbon, hydrogen and
oxygen. 1
Both show the same ratio of atoms of each element in a
compound 1 Max:
4
(c) (i) Reactants : Calcium carbonate 1
Ethanoic acid 1
Products : Calcium ethanoate 1
Carbon dioxide 1
Water 1 3
(ii) CaCO3 + 2CH3COOH (CH3COO)2Ca + CO2 + H2O
[Correct formula of reactant and products] 1
[Balanced equation] 1 2
(d) Percentage of N Urea , (NH2)2CO = 28 x 100% = 46.67% 1
60
Ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4: Percentage of N
= 28 x 100% = 21.21% 1
132
Percentage of N Ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3
= 28 x 100% = 35% 1
80
Urea , (NH2)2CO the highest percentage of nitrogen by mass. 1+1 5
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 5 4541/2
3 (a) 1. Hydrogen easily flammable /explode. 1
2. Helium 1
3. Helium is lighter 1
4. Helium is inert gas// unreactive 1 4
(b) 1. Correct formulae of reactants and products 1
2. Balanced equation 1
Fe + 3Br2
3. The reactivity of reaction I is higher than reaction II. 1
4. The atomic size of chlorine is smaller than bromine 1
5. The forces of attraction of the nucleus toward the electrons
is stronger in chlorine atom than in bromine atom 1
6. It is easier for chlorine atom to attract electron 1 6
(c) 1. Cut a small piece of lithium using a knife and forceps 1
2. Dry the oil on the surface of the lithium with filter paper 1
3. Place the lithium slowly onto the water surface in a through 1
4. Record the observations 1
5. Repeat steps 1-5 using sodium and potassium to replace
lithium. 1
6. Lithium moves slowly on the water surface 1
7. Sodium moves faster and randomly on the surface of water//
Sodium ignites with a yellow flame 1
8. Potassium moves vigorously and randomly on the water
surface.// Potassium ignites with a lilac flame // produce
‘pop’ sound 1
9. Correct formulae of reactants and products 1
10. Balanced equation 1
10
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 6 4541/2
4. (a) 1. P : EO 1
2. Q : CO2 1 2
(b) Compound P
1 Electron arrangement of E atom is 2.2 and O atom is 2.6 // 1
[a : Valence electron of atom E is 2 and O is 6].
2 To achieve duplet/octet electron arrangement; 1
3 an atom of E release 2 electrons to form E2+ //
E → E2+ + 2e 1
4 an atom of R receive 2 electrons form R2- //
R + 2e → R2- 1
5 E2+ ion and R2- ion / Oppositely charged ions attract each
other by strong electrostatic force // [Diagram] 1
6 Ionic bond is formed. 1 Max 5
Compound Q
7 Electron arrangement of C atom is 2.4 and O atom is 2.6 1
8 To achieve octet electron arrangement; 1
9 One atom of C contribute 4 electrons to share //
one atom of O contribute 2 electrons for share 1
10 One C atom share four electrons with two oxygen atoms // 1
[Diagram]
11 Covalent bond is formed. 1 5
(c) Compound P
1. High melting point 1
2. Attraction force between oppositely-charged ions is very
strong. 1
3. A lot of heat energy required to overcome the force. 1
4. Conduct electricity in molten state or aqueous solution 1
5. has freely moving/mobile ions. 1
Compound Q
1. Low melting point 1
2. Attraction force between molecules is very weak. 1
3. A small amount of heat energy required to overcome the
force 1
4. Cannot conduct electricity #in any state#. 1
5. Exist as molecules // Does not have ions. 1 Max 8
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 7 4541/2
5 (a) (i) A - glucose solution / (any suitable covalent compound) 1
B – solid sodium chloride / (any suitable ionic 1
compound in solid state )
C – sodium chloride solution / (any suitable ionic compound in 1
aqueous state) 3
A – non electrolyte 1
(ii) B- non electrolyte 1
C- electrolyte 1 3
(iii) 1. A cannot conduct electricity 1
2. because A consist of molecule//has no free moving ions 1
3. B cannot conduct electricity 1
4. Because the ions in B cannot move freely 1
5. C can conduct electricity 1
6. Because the ions in C move freely 1 6
(b) (i) Dissolve the substance in water 1
(ii) Diagram :
[Functional diagram] 1
[Label] 1 2
Sample answer :
carbon electrode
elektrod karbon
Sodium bicarbonate
Elektrod
solution copper
Larutan natrium
bikarbonat
(iii) Procedure :
1. The carbon electrodes were cleaned with a sand paper. 1
2. Sodium bikarbonate solution were poured into a beaker. 1
3. The carbons electrodes were connected to the circuit and
dipped into the sodium bikarbonate solution. 1
4. The circuit was switch on for 15 minutes. 1
5. Observations at the anode and the cathode were
recorded. 1 5
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 8 4541/2
6 (a) Alkali A –sodium hydroxide/ barium hydroxide/ barium 1
hydroxide/potassium hydroxide
Strong alkali 1
Ionises completely in water to produce high concentration of OH- ion. 1
Alkali B – ammonia solution 1
Weak alkali 1
Ionises partially in water to produce low concentration of OH-. 1…6
(b) (i) X : water 1
Y : methylbenzene/tetrachloromethane/any organic solvents 1.....2
(ii) Hydrogen chloride ionizes completely in water 1
To form H+, so solution X shows acidic properties. 1
Without water, hydrogen chloride exist as molecules 1
There are no H+ present, so solution Y does not show acidic properties 1.....4
(c) Calculation :
2.0 x V1 = 0.1 x 500 // 1
V1 = 0.1 x 500
2.0
= 25 cm3 1
1. Use pipette to draw up 25 cm3 2.0 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid. 1
2. Transfer the acid to a 500 cm3 volumetric flask. 1
3. Add distilled water to bring the level of solution until the calibration 1
mark
4. Stopper the flask and shake well. 1…6
(d) Add powdered lime/ lime stone/ ashes of burnt wood 1
Reason : weak alkali, can neutralise acidity in the soil 1.....2
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 9 4541/2
7 (a) (i) 1. Cation : Ba2+ // Pb2+ // Ag+ 1
2. Anion : CO32- 1
3. Ba2+ // Pb2+ // Ag+ reacts with SO42- ion to form insoluble
salt // Pb2+ // Ag+ reacts with Cl- ion to form insoluble salt. 1
4. Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4 // Pb2+ + SO42- PbSO4 // 1
2Ag+ + SO42- Ag2SO4 // Pb2+ + Cl- PbCl2 //
Ag+ + Cl- AgCl
5. CO32- reacts with Ca2+ / Mg2+ ion to form insoluble salt. 1
6. Ca2+ + CO32- CaCO3 // Mg2+ + CO32- MgCO3 1 6
(ii) 1. Ca2+ ion 1
2. Mg2+ ion 1
3. Sodium carbonate // Potassium carbonate 1
4. Measure [20-100] cm3 of river water and pour into a
beaker 1
5. Measure [20-100] cm3 of [0.1-2.0] mol dm-3 sodium
carbonate solution and pour into the beaker 1
6. Stir the mixture 1
7. Filter the mixture 1
8. Double decomposition reaction 1
9. Product is calcium carbonate // magnesium carbonate 1
10. Product is insoluble 1 10
(b) 1. Add barium chloride / nitrate solution into salt J 1
2. white precipitate formed, SO42- present 1
3. Add silver chloride solution into salt L 1
4. white precipitate formed, Cl- present 1 4
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 10 4541/2
8. 2(a) Zn + 2HCl→ ZnCl2 + H2 1+1
Number of moles of zinc = 0.5 // 0.008 1
65
0.008 moles of zinc→ 0.008 moles of hydrogen 1
Volume of gas = 0.008 x 24000 cm3 // 192 cm3 1...5
(b) Volume of gas / cm3
192
III II I
25 50 80 Time / s
[ Axes-labelled and unit] 1
[ Maximum volume and time are shown ] 1
[ Correct label for experiment I,II,III ] 1...3
(c) Experiment I
Average rate = 192 // 2.40 cm3s-1 1
80
Experiment II
Average rate = 192 // 3.84 cm3s-1 1
50
Experiment III
Average rate = 192 // 7.68 cm3s-1 1...3
25
(d) Experiment I and Experiment II
Rate of reaction experiment II is higher 1
Size of zinc in experiment II is smaller 1
The smaller the size of zinc the larger the total surface area 1
Frequency of collision between zinc and hydrogen ions increase 1
Frequency of effective collision increase 1
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 11 4541/2
Experiment II and Experiment III
Rate of reaction experiment III is higher 1
Copper (II)sulphate solution act as catalyst 1
Catalyst reduce the activation energy 1
More colliding particle achieve activation energy 1
Frequency of effective collision increase 1..max 9
20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 12 4541/2
9 (a) (i) 1. Homologous series : Ester 1
2. Compound Z : Methyl butanoate 1
3. Low melting/ boiling point 1
4. Forces of attraction between molecules in compound Z is 1 4
weak.
(ii) 1. Alcohol X : Methanol // CH3OH 1
2. Carboxylic acid Y: Butanoic acid // C3H7COOH 1
3.Correct formula of reactants and products 1
C3H7COOH + CH3OH C3H7COOCH3 + H2O 1
4. No of mole of CH3OH 1
5. Ratio of mole 1
6. Mass of Z with unit 1
n CH3OH = //// 0.0625 1
1 mol of CH3OH produced 1 mol of C3H7COOCH3 // 1
0.0625 mol of CH3OH produced 0.0625 mol of 1
C3H7COOCH3
Mass = 0.0625 x [12(5) + 10 + 32] g // 10
0.0625 x 102 //
6.375 g
(b) (i) 1. Ammonia / NH3 solution 1
2. Type A : Unvulcanised rubber // Natural rubber 1
3. Type B : Vulcanised rubber 1 3
(ii) Able to compare four properties of type A & type B rubber
Unvulcanised rubber Unvulcanised rubber //
// Type A Type B
4 Softer Harder 1
5 Cannot withstand high Can withstand high
temperature temperature 1
6 Less easily oxidised Easily oxidised 1
7 Less elastic More elastic 1
Able to explain type B is more suitable to make tyre compare
to type A
8. presence of cross-linkage of sulphur atoms between
rubber molecules in type B rubber
9. prevent rubber molecules slide each other easily 1
10. Type A rubber easily becomes sticky/soft/easily change 1
shape when high heat/pressure 1 7
TOTAL 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 13 4541/2
No.
Skema Markah
Soalan
10. (a) (i) Logam R : Zn/Mg 1
Zn/Mg CuSO4
Jenis Tindak balas Pengoksidaan Penurunan 1+1
Persamaan setengah Zn Zn2+ + 2e Cu2+ + 2e Cu 1+1
Nama ion yang hadir dalam larutan tidak berwarna ialah ion kuprum(II) 1
(ii)
Zn/Mg CuSO4
Perubahan nombor 0 +2 +2 0 1+1
pengoksidaan
Fungsi Agen penurunan Agen pengoksidaan 1+1
(b) Logam : Zn / Al 1
Prosedur :
1. Bersihkan jalur Zn/Al dan paku besi dengan kertas pasir 1
2. Lilitkan jalur Zn/Al pada paku besi dan masukkan ke dalam tabung uji. 1
3. Masukkan paku besi sahaja ke dalam tabung uji lain. 1
4. Tuangkan campuran larutan agar-agar panas dengan kalium
heksasianoferat(III) dan penunjuk fenolftalein sehingga paku besi
tenggelam ke dalam kedua-dua tabung uji. 1
5. Biarkan tabung uji selama satu hari. 1
Pemerhatian
Pasangan logam Pemerhatian
Zn/Al dan paku besi Tompok merah jambu terbentuk 1
Paku besi Tompok biru terbentuk 1
Setengah persamaan :
Tabung uji I : Zn Zn2+ + 2e 1
Tabung uji II : Fe Fe2+ + 2e 1
Kesimpulan :
Apabila logam yang lebih elektropositif bersentuhan dengan besi, logam
tersebut akan menghalang pengaratan. //
Besi tidak berkarat apabila bersentuhan dengan logam yang lebih elektropositif. 1
JUMLAH 20
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 14 4541/2
11 (a) Exothermic reaction 1
a: neutralisation
Heat of neutralisation between strong acid and strong alkali is 57.3
kJmol-1 1
Experiment I Experiment II
HCl is strong acid // CH3COOH is weak acid // 1+1
Ionises completely in water Ionises partialy in water 1
Some of heat is used to ionise
the molecules 1 6
(b) (i) 1
n= // 0.05
= 0.05 x 57.3 1
= 2865 J 1 3
(ii)
Temp change = [ Total volume = 100 cm3] 1+1
1 3
o
= 6.82 C
(c) Plastic cup , thermometer , 50 cm3 measuring cylinder, 1
[balance]
Procedure : 1
1. Measure 50 cm3 silver nitrate solution 1
2. Pour into a plastic cup. 1
3. Measure the initial temperature, T1 1
4. Add 5.0 g / a little magnesium powder and stir. 1
5. Measure the highest temperature, T2
To calculate: 1
Temp rise = T2 – T1 = T 1
H= 50 x c x T = P
Heat of displacement = P / mol
n= 1 Max
8
Precaution: Stir
Measure the highest reading
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
SULIT 15 4541/2
12 (a) 1. K : Analgesics 1
2. L : Antibiotic 1
3. M : Psychothearapeutic 1
4. Ramli = Paracetamol 1
5. Hamid = Penicillin 1
6. Amins’ daughter = Antidepressen 1 6
(b) (i) 1. Plastic B 1
2. Improper disposal cause blockage of drainage /flash flood 1
3. Burning of plastic release poisonous / toxic / acidic gas 1
4. Reduce, reused and recycle // burn in incinerator 1 4
(ii) 1. Substance P : H2SO4 // sulpuric acid 1
2. Substance Q : NH3 // ammonia 1
3. Fertilizer R = (NH4)2SO4 1
4. Fertilizer S = NH4NO3 1
5. Correct formula of reactants 1
6. Correct formula of products 1 6
H2SO4 + NH3 (NH4)2SO4 //
HNO3 + NH3 NH4NO3
1. Percent of N2 fertilizer R 1
x 100 = 21.2 % 1
2. Percent of N2 fertilizer S
x 100 = 35%
3. Fertilizer S 1
4. Percentage of nitrogen by mass fertilizer S is higher. 1 4
TOTAL 20
END OF MARKING SCHEME
4541/2 ® ZAR19@PPDB [Lihat halaman sebelah
KIMIA-Kertas 2- Esei SULIT
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Innocent Words That Make Her HornyDocument14 pagesInnocent Words That Make Her HornyH69% (13)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Installation of Submarine PE PipesDocument84 pagesInstallation of Submarine PE Pipeswaseemiqbal133100% (2)
- Shelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesShelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions Manualjuanlucerofdqegwntai100% (10)
- Cummins: ISX15 CM2250Document17 pagesCummins: ISX15 CM2250haroun100% (4)
- Plan J Kimia F4Document22 pagesPlan J Kimia F4Zaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Maktab Rendah Sains Mara Peperiksaan Sijil Pendidikan MRSM 2015Document28 pagesMaktab Rendah Sains Mara Peperiksaan Sijil Pendidikan MRSM 2015Zaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Plan-J: Chemistry Form 5Document12 pagesPlan-J: Chemistry Form 5Zaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Plan J Kimia F4Document22 pagesPlan J Kimia F4Zaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Trialkedah2015 Kimia PDFDocument85 pagesTrialkedah2015 Kimia PDFZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Laws of ChessDocument25 pagesLaws of Chesstaher adelNo ratings yet
- DADAH3Document3 pagesDADAH3Zaza MawarNo ratings yet
- 02 Structure of Atom K1 - Final BIDocument21 pages02 Structure of Atom K1 - Final BIZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Trial 2014 Chem p2 MsDocument11 pagesTrial 2014 Chem p2 MsZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ibnu Sina Manufactured Substance in IndustryDocument3 pagesSoalan Ibnu Sina Manufactured Substance in IndustryZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- LTLNS: R"Uif::Il:LthDocument1 pageLTLNS: R"Uif::Il:LthZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Informative Periodic Table of ElementDocument10 pagesInformative Periodic Table of ElementZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Kajian KimiaDocument25 pagesKajian KimiaZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Cara Menulis Inferens (Kelantan 2012)Document3 pagesCara Menulis Inferens (Kelantan 2012)Everest Lim Yong KeanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 F5 Microorganisms and Their Effect On Living ThingsDocument38 pagesChapter 1 F5 Microorganisms and Their Effect On Living ThingsZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Practical Student's ModuleDocument13 pagesPractical Student's ModuleHasbullah Md SukurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 F5 Preservation and Conservation of The EnvironmentDocument158 pagesChapter 3 F5 Preservation and Conservation of The EnvironmentZaza Mawar100% (1)
- Write The Charge For The Cation and Anion BelowDocument1 pageWrite The Charge For The Cation and Anion BelowZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Formation of Ionic BondDocument14 pagesFormation of Ionic BondZaza MawarNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorDocument1 pageAction Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Democracy or Aristocracy?: Yasir MasoodDocument4 pagesDemocracy or Aristocracy?: Yasir MasoodAjmal KhanNo ratings yet
- 03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaDocument48 pages03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaSudarshan GadalkarNo ratings yet
- Academic Performance of Senior High School Students 4Ps Beneficiaries in VNHSDocument19 pagesAcademic Performance of Senior High School Students 4Ps Beneficiaries in VNHSkathlen mae marollanoNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Compressor Models: P105WJD, P130DWJD, P160DWJD, P175DWJDDocument70 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual Compressor Models: P105WJD, P130DWJD, P160DWJD, P175DWJDManuel ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Ass AsDocument23 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Nascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Document35 pagesNascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Prasoon SimsonNo ratings yet
- 3-A Y 3-B Brenda Franco DíazDocument4 pages3-A Y 3-B Brenda Franco DíazBRENDA FRANCO DIAZNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Strategic Management BarbosaDocument11 pagesSustainable Strategic Management BarbosapurwawardhaniNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsDocument7 pagesHalf Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsSusanket DuttaNo ratings yet
- X Lube Bushes PDFDocument8 pagesX Lube Bushes PDFDavid TurnerNo ratings yet
- Amerex Ansul Badger Ul Catalogo Por PartesDocument37 pagesAmerex Ansul Badger Ul Catalogo Por PartesPuma De La Torre ExtintoresNo ratings yet
- Turner Et Al. 1991 ASUDS SystemDocument10 pagesTurner Et Al. 1991 ASUDS SystemRocio HerreraNo ratings yet
- Handout Waste Catch BasinDocument2 pagesHandout Waste Catch BasinJonniel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Alds 2202Document13 pagesWeek 3 Alds 2202lauren michaelsNo ratings yet
- C103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratoriesDocument19 pagesC103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratorieshuidhyiuodghNo ratings yet
- Bassoon (FAGOT) : See AlsoDocument36 pagesBassoon (FAGOT) : See Alsocarlos tarancón0% (1)
- Eng03 Module Co4Document14 pagesEng03 Module Co4Karl Gabriel ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cornish BoilerDocument3 pagesCornish BoilerDeepak KV ReddyNo ratings yet
- Calendar of Activities A.Y. 2015-2016: 12 Independence Day (Regular Holiday)Document3 pagesCalendar of Activities A.Y. 2015-2016: 12 Independence Day (Regular Holiday)Beny TawanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial MotivationDocument18 pagesEntrepreneurial MotivationRagavendra RagsNo ratings yet
- Dress Code19sepDocument36 pagesDress Code19sepapi-100323454No ratings yet
- 한국항만 (영문)Document38 pages한국항만 (영문)hiyeonNo ratings yet
- Full Download University Physics With Modern Physics 14th Edition Young Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument13 pagesFull Download University Physics With Modern Physics 14th Edition Young Test Bank PDF Full Chapterpoetrycloudyzjm12q100% (19)
- The Teacher Research Movement: A Decade Later: Cite This PaperDocument13 pagesThe Teacher Research Movement: A Decade Later: Cite This PaperAlexandre NecromanteionNo ratings yet