0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views2 pagesSpring Constant Measurement in Helical Springs
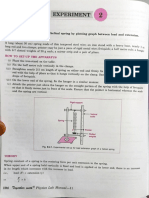
This document describes an experiment to determine the spring constants of a helical spring under both tension and compression. When a tensile or compressive load is applied to a spring, its elongation or shortening is directly proportional to the load based on Hooke's law. The experiment involves gradually applying known loads and measuring the corresponding displacements of the spring in both loading and unloading stages under tension and compression. The spring constants are then calculated from the slope of the load-displacement graphs.
Uploaded by
LaasyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views2 pagesSpring Constant Measurement in Helical Springs
This document describes an experiment to determine the spring constants of a helical spring under both tension and compression. When a tensile or compressive load is applied to a spring, its elongation or shortening is directly proportional to the load based on Hooke's law. The experiment involves gradually applying known loads and measuring the corresponding displacements of the spring in both loading and unloading stages under tension and compression. The spring constants are then calculated from the slope of the load-displacement graphs.
Uploaded by
LaasyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd