100% found this document useful (7 votes)
46K views4 pagesSpring Constant Experiment
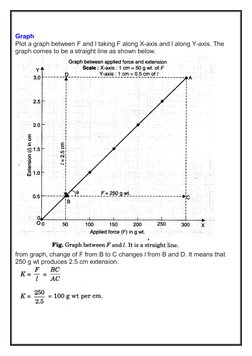
To determine the force constant of a helical spring, weights were added to extend the spring and measurements were recorded. A graph of force versus extension produced a straight line, and the slope equaled the force constant. The experiment found the force constant of the spring to be 100 g per cm.
Uploaded by
RacCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (7 votes)
46K views4 pagesSpring Constant Experiment
To determine the force constant of a helical spring, weights were added to extend the spring and measurements were recorded. A graph of force versus extension produced a straight line, and the slope equaled the force constant. The experiment found the force constant of the spring to be 100 g per cm.
Uploaded by
RacCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
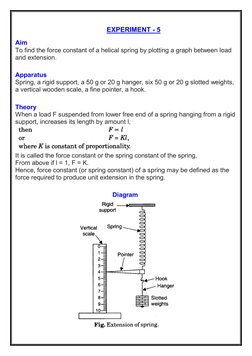
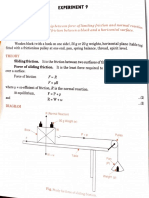
- Experiment Aim: Describes the objective of the experiment, focusing on finding the force constant of a helical spring by plotting a graph between load and extension.
- Theory: Explains the theoretical background of the experiment, including the concept of proportionality and calculating the spring constant.
- Apparatus: Lists the equipment and materials needed to perform the experiment, including spring, weights, scale, and others.
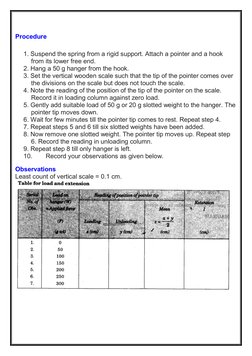
- Procedure: Outlines the step-by-step experimental procedure for measuring and recording the effect on the spring under varying loads.
- Observations: Describes the observations made during the experiment, emphasizing data on load and extension.
- Graph: Details the method of plotting a graph between force and extension to visually determine the spring constant.
- Result: Presents the calculated force constant of the spring based on experimental data and graph analysis.
- Sources of Error: Identifies potential sources of error in the experiment that could impact data accuracy.
- Precautions: Provides precautionary measures to ensure accurate results and maintain the integrity of the experiment.