Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Work Energy-6
Uploaded by
Zahida Parnis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Work Energy-6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesWork Energy-6
Uploaded by
Zahida ParnisCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Tutorial 6
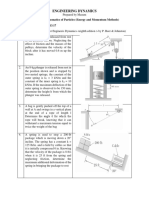
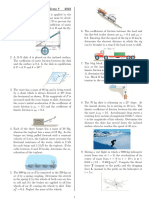
The motor lifts the 50-kg crate with an acceleration of 6 m/s2.
Determine the components of force reaction and the couple
moment at the fixed support A.
If the supplied force F = 150 N, determine the velocity
of the 50-kg block A when it has risen 3 m, starting from rest.
Block A and B each have a mass m. Determine the
largest horizontal force P which can be applied to
B so that it will not slide on A. Also, what is the
corresponding acceleration? The coefficient of static friction between
A and B is s. Neglect any friction between A and the horizontal
surface.
When the driver applies the brakes of a light truck traveling
40 km/h, it skids 3 m before stopping. How far will the truck
skid if it is traveling 80 km/h when the brakes are applied?
The force F, acting in a constant direction on the 20-kg
block, has a magnitude which varies with the position s of
the block. Determine how far the block must slide before
its velocity becomes 15 m/s. When s = 0 the block is
moving to the right at v = 6 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic
friction between the block and surface is k = 0.3.
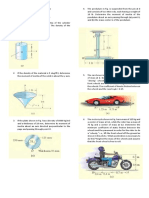
If the cord is subjected to a constant force of F=300 N, and
the 15-kg smooth collar starts from rest at A. Determine the
velocity of the collar when it reaches point B. Neglect the
size of the pulley.
The 8-kg block is moving with an initial speed of 5 m/s.
If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block
and plane is k = 0.25, determine the compression in the
spring when the block momentarily stops.
The collar has a mass of 20 kg and slides along the
smooth rod. Two springs are attached to it and the
ends of the rod as shown. If each spring has an
uncompressed length of 1 m and the collar has a speed
of 2 m/s when s = 0, determine the maximum
compression of each spring due to the back-and-forth
(oscillating) motion of the collar.
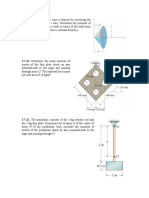
Marbles having a mass of 5 g are dropped from rest at A
through the smooth glass tube and accumulate in the can at C.
Determine the placement R of the can from the end of the tube
and the speed at which the marbles fall into the can. Neglect
the size of the can.
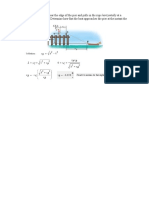
If the 60-kg skier passes point A with a speed of 5 m/s,
determine his speed when he reaches point B. Also find the
normal force exerted on him by the slope at this point. Neglect
friction.
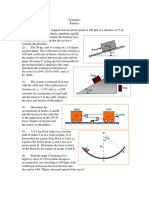
If the 75-kg crate starts from rest at A, determine its
speed when it reaches point B. The cable is subjected to a
constant force of F = 300 N. Neglect friction and the size
of the pulley.
You might also like
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Tutorial 7 8Document3 pagesTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0910 Spring Set2Document3 pagesAssignment 0910 Spring Set2Sarp Yiğit ŞirinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5-1Document1 pageTutorial 5-1Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- Force and acceleration problem setDocument2 pagesForce and acceleration problem setBenedick Jayson P. Marti100% (1)
- Particle Kinetics ProblemsDocument12 pagesParticle Kinetics ProblemsAeon ReignNo ratings yet
- Newton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) RectilinearDocument9 pagesNewton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) Rectilineardaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarDocument12 pagesF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarAndre BocoNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosDocument7 pagesTrabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosFabricio Espinoza GamarraNo ratings yet
- Dynamics WorksheetDocument3 pagesDynamics Worksheetgirma workuNo ratings yet
- CE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseDocument2 pagesCE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseSean TraverNo ratings yet
- Opción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDocument11 pagesOpción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDiego Naspud UrgilesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Solutions PDFDocument20 pagesTutorial 9 Solutions PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Chapter-13Document3 pagesDynamics - Chapter-13TANJILUR RAHMAN 1909011No ratings yet
- Planar Kinetics of Rigid Body Work, Energy, Impulse & Momentum TutorialDocument6 pagesPlanar Kinetics of Rigid Body Work, Energy, Impulse & Momentum TutorialChin Tiong LeeNo ratings yet
- CH 17Document7 pagesCH 17Amer JumahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 WEDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Document5 pagesTutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Romharsh OliNo ratings yet
- Final 08 Engg SolDocument6 pagesFinal 08 Engg SolyanelaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics problems solved step-by-stepDocument6 pagesMechanics problems solved step-by-stepAndrea 75No ratings yet
- 2 Unit DynamicsDocument5 pages2 Unit DynamicsmanojNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2MarlNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4 - QuestionDocument5 pagesTutorial Chapter 4 - QuestionNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Sol Final Exam JanDocument5 pagesSol Final Exam JanPablo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document2 pagesAssignment 6Sean TraverNo ratings yet
- Sheet 7 - Work and Energy-10807Document9 pagesSheet 7 - Work and Energy-10807Bahaa RaghebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Worksheet (F Ma)Document3 pagesChapter 3 Worksheet (F Ma)Obsinet ObsinetNo ratings yet
- Review Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2Document2 pagesReview Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2RamonNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Particles Work and Energy ClassworkDocument2 pagesKinetics of Particles Work and Energy ClassworkHarvey BautistaNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Document5 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document19 pagesTutorial 3Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- Dynamics (Kinetics)Document2 pagesDynamics (Kinetics)HeliosNo ratings yet
- MAK 217 2. ÖdevDocument2 pagesMAK 217 2. ÖdevBünyamin TatarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 KINETICS OF RIGID BODIES 2DDocument45 pagesCHAPTER 4 KINETICS OF RIGID BODIES 2D2021839932No ratings yet
- Trabajo Fisica IDocument5 pagesTrabajo Fisica IMVAZ233No ratings yet
- MEC107 Tutorial Sheet 6 Problems on Forces, Friction, Work, Energy and Moment of InertiaDocument2 pagesMEC107 Tutorial Sheet 6 Problems on Forces, Friction, Work, Energy and Moment of Inertiasiddharth yadavNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering Dynamics ReviewDocument2 pagesStructural Engineering Dynamics ReviewVincent NavaNo ratings yet
- The tow truck with attached 1200Document18 pagesThe tow truck with attached 1200david caraballoNo ratings yet
- Unit V - Unid End Questions - EMDocument6 pagesUnit V - Unid End Questions - EMNaresh JonnaNo ratings yet
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsDocument7 pagesCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 PDFDocument16 pagesTutorial 8 PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- PP Otational Ynamics: B A C BDocument6 pagesPP Otational Ynamics: B A C BAbhinav ranaNo ratings yet
- Es221 Chapter ExamDocument1 pageEs221 Chapter ExamNini JimbuuNo ratings yet
- Problem Set2 PDFDocument1 pageProblem Set2 PDFMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet On DynamicsDocument6 pagesWork Sheet On DynamicstorsrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Addpro 7Document1 pageAddpro 7Mary Izere MutabaziNo ratings yet
- Assignment2ed PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment2ed PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Ch17 DynamicsDocument2 pagesCh17 DynamicsAaron WoodNo ratings yet
- HW05 Solution METUDocument3 pagesHW05 Solution METUFatih BodrumNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Document5 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument2 pagesProblem SetBen Matthew Alferez CoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Quiz - Impulse, Momentum & CollisionsDocument1 pageDynamics Quiz - Impulse, Momentum & CollisionsNathanielle AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Board Work DynamicsDocument1 pageQuiz - Board Work DynamicsNathanielle AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Flip Problem SetDocument4 pagesFlip Problem SetNikhole JaneNo ratings yet
- Physics problems on velocity, motion, springs, collisions and projectilesDocument13 pagesPhysics problems on velocity, motion, springs, collisions and projectilessairin parkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsDocument9 pagesTutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Phys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationDocument4 pagesPhys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationEngelbert Bicoy AntodNo ratings yet
- 8 CE199L-1 Physics2Document3 pages8 CE199L-1 Physics2IwaNo ratings yet
- Forces and accelerations on connected bodiesDocument4 pagesForces and accelerations on connected bodiesSyed ShaulNo ratings yet
- SOR1211 Probability - Solutions To Exercises in Notes - Chapter 2Document15 pagesSOR1211 Probability - Solutions To Exercises in Notes - Chapter 2Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- SOR1211 Probability - Jan 2021Document5 pagesSOR1211 Probability - Jan 2021Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- 2.0 - Fluid BasicsDocument20 pages2.0 - Fluid Basicsjaden.borg.22No ratings yet
- Mme 2203Document4 pagesMme 2203Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- Work Energy-5Document4 pagesWork Energy-5Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- FIFE Symat 70G PDFDocument25 pagesFIFE Symat 70G PDFmartian18298706100% (1)
- HW 6 - Phys - AnswersDocument17 pagesHW 6 - Phys - AnswersJohn GamboaNo ratings yet
- PS Statics 1Document9 pagesPS Statics 1Kenny SiludNo ratings yet
- Design Notes - Calculations Tutorials: IndexDocument6 pagesDesign Notes - Calculations Tutorials: IndexrobsNo ratings yet
- General Awareness & General Science Capsule SummaryDocument159 pagesGeneral Awareness & General Science Capsule SummarySonu Dedha GurjarNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument43 pagesFinal ReportAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Hysteretic Energy DissipationDocument22 pagesHysteretic Energy Dissipationdharma raj upadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Selection Factors for Construction EquipmentDocument23 pagesSelection Factors for Construction Equipmentsachin100% (1)
- Astm d4812Document11 pagesAstm d4812qwerty0987No ratings yet
- FRICTION ON INCLINED PLANES AND LADDERSDocument15 pagesFRICTION ON INCLINED PLANES AND LADDERSdivyannshNo ratings yet
- Hopper Design PDFDocument31 pagesHopper Design PDFMuhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Pemex PoroFlexDocument34 pagesPemex PoroFlexvictorNo ratings yet
- Surface Modification and MechanismDocument922 pagesSurface Modification and MechanismG_Garlic100% (3)
- RE WALL Design As Per Irc 102Document16 pagesRE WALL Design As Per Irc 102Naresh Sharma100% (2)
- Advanced Structural Dynamic: Subject of PresentationDocument27 pagesAdvanced Structural Dynamic: Subject of PresentationSaurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Rock Stabilisation Methods.Document58 pagesChapter 8 Rock Stabilisation Methods.Koh Jia JieNo ratings yet
- Clay Reinforcement Using Geogrid Embedded in Thin Layers of Sand PDFDocument12 pagesClay Reinforcement Using Geogrid Embedded in Thin Layers of Sand PDFThãshñêëShävNo ratings yet
- PKP ED NOTE Module1 FinalDocument66 pagesPKP ED NOTE Module1 FinalSamarjit SenNo ratings yet
- THK Linear GuidewaysDocument24 pagesTHK Linear GuidewaysAvish ShahNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test Procedure and CorrectionsDocument45 pagesStandard Penetration Test Procedure and CorrectionsVivek DhutNo ratings yet
- Chgairflowlab JOSHI CAREYDocument20 pagesChgairflowlab JOSHI CAREYelsmuchoNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment ASPDocument104 pagesSelf Assessment ASPTarek San100% (1)
- Physical Sciences Winter Classes Manual June 2023Document99 pagesPhysical Sciences Winter Classes Manual June 2023Magadani FhatuNo ratings yet
- Natural Science: Part 1-Content UpdateDocument23 pagesNatural Science: Part 1-Content UpdateNina claire BustamanteNo ratings yet
- TGN 1 25 Introduction To FatigueDocument2 pagesTGN 1 25 Introduction To FatigueMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- L3-Structural SteelDocument58 pagesL3-Structural SteelTjia Tjie100% (1)
- A Comparative Analysis of The Coefficient of Static Friction of A Running Shoe and A Skateboard ShoeDocument5 pagesA Comparative Analysis of The Coefficient of Static Friction of A Running Shoe and A Skateboard ShoeRyan HolinsheadNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 2 Measuring Density and Viscosities of Different FluidsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity 2 Measuring Density and Viscosities of Different FluidsJohn Patrick Sanay NunezNo ratings yet
- The Newton's Second LawDocument7 pagesThe Newton's Second LawАйзада СатбергеноваNo ratings yet
- PPR Pipe Installation & Technical DetailsDocument29 pagesPPR Pipe Installation & Technical DetailsRAJESHNo ratings yet