Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics - Chapter-13
Uploaded by
TANJILUR RAHMAN 19090110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Dynamics -Chapter-13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesDynamics - Chapter-13
Uploaded by
TANJILUR RAHMAN 1909011Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ENGINEERING DYNAMICS
Prepared by Masum
Chapter-13: Kinematics of Particles (Energy and Momentum Methods)
Sample Problems: 13.1- to 13.17
(Book: Vector Mechanics for Engineers Dynamics <eighth edition > by P. Beer & Johnston)
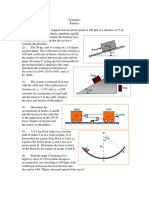
1. The 7-kg block A is released from rest
in the position shown. Neglecting the
effect of friction and the masses of the
pulleys, determine the velocity of the
block after it has moved 0.6 m up the
incline.
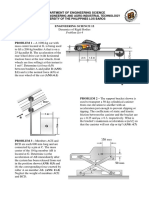
2. An 8-kg plunger is released from rest in
the position shown and is stopped by
two nested springs; the constant of the
outer spring is k1 = 3 kN/m and the
constant of the inner spring is k2 = 10
kN/m. If the maximum deflection of the
outer spring is observed to be 150 mm,
determine the height h from which the
plunger was released.
3. A bag is gently pushed off the top of a
wall at A and swings in a vertical plane
at the end of a rope of length l
Determine the angle θ for which the
rope will break, knowing that it can
withstand a maximum tension equal to
twice the weight of the bag
4. A spring is used to stop a 200-lb
package which is moving down a 20°
incline. The spring has a constant k =
125 lb/in. and is held by cables so that
it is initially compressed 6 in. Knowing
that the velocity of the package is 8 ft/s
when it is 25 ft from the spring and
neglecting friction, determine the
maximum additional deformation of the
spring in bringing the package to rest
ENGINEERING DYNAMICS
Prepared by Masum
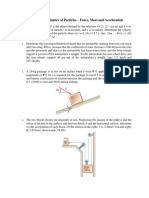
5. A satellite describes an elliptic orbit of
minimum altitude 376 mi above the
surface of the earth. The semi major and
semi minor axes are 10840 mi and 8670
mi, respectively. Knowing that the
speed of the satellite at point C is 2.97
mi/s, determine (a) the speed at point A,
the perigee, (b) the
speed at point B, the apogee
6. An experimental space probe is
launched from the earth and enters a
highly eccentric elliptic orbit as it
reaches point A. Knowing that its
velocity there is observed to be Va =
30,000 km/h at an angle of 60° with the
vertical, determine the minimum
altitude of the orbit
7. A 20-kg block is at rest on an incline
when a constant horizontal force P is
applied to it. The static and kinetic
coefficients of friction between the
block and the incline are 0.4 and 0.3,
respectively. Knowing that the speed of
the block is 15 m/s after 6 s, determine
the magnitude of P.
ENGINEERING DYNAMICS
Prepared by Masum
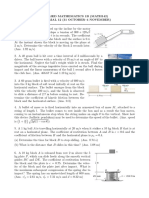
8. A 1-oz bullet is fired into an 8-lb
wooden block and becomes embedded
in it. Knowing that the block and bullet
then move up the smooth incline for 1.2
s before they come to a stop, determine
(a) the magnitude of the initial velocity
of the bullet, (b) the magnitude of the
impulse of the force exerted by the
bullet on the block
9. A 1.1-kg ball A is falling vertically with
a velocity of magnitude VA = 2.5 m/s
when it is hit as shown by a 0.7-kg ball
B which has a velocity of magnitude VB
= 2 m/s. Knowing that the coefficient of
restitution between the two balls is e =
0.75 and assuming no friction,
determine the velocity
of each ball immediately after impact
10. A girl throws a ball at an inclined wall
from a height of 3 ft, hitting the wall at
A with a horizontal velocity V0 of
magnitude 25 ft/s. Knowing that the
coefficient of restitution between the
ball and the wall is 0.9 and neglecting
friction, determine the distance d from
the foot of the wall to the point B where
the ball will hit the ground after
bouncing off the wall.
You might also like
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Document5 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Dynamics WorksheetDocument3 pagesDynamics Worksheetgirma workuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 WEDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Document5 pagesTutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Romharsh OliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 8Document3 pagesTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- MAK 217 2. ÖdevDocument2 pagesMAK 217 2. ÖdevBünyamin TatarNo ratings yet
- Probset - Mech 2 - DynamicsDocument5 pagesProbset - Mech 2 - DynamicsHeart VenturanzaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsDocument9 pagesTutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics (Kinetics)Document2 pagesDynamics (Kinetics)HeliosNo ratings yet
- 2-ENGINEERING-MECHANICS ProblemsDocument2 pages2-ENGINEERING-MECHANICS ProblemsJeoh SilangNo ratings yet
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsDocument7 pagesCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial TwoDocument5 pagesTutorial TwoParas gurungNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosDocument7 pagesTrabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosFabricio Espinoza GamarraNo ratings yet
- Quiz Spring SpecialDocument2 pagesQuiz Spring SpecialLugabalugaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Good Questions 1.: Z Q P y P R X R QDocument4 pagesMechanics Good Questions 1.: Z Q P y P R X R QrajdeepNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0910 Spring Set2Document3 pagesAssignment 0910 Spring Set2Sarp Yiğit ŞirinNo ratings yet
- Physics problems on velocity, motion, springs, collisions and projectilesDocument13 pagesPhysics problems on velocity, motion, springs, collisions and projectilessairin parkNo ratings yet
- DinmjgDocument10 pagesDinmjghaker linkisNo ratings yet
- Problem and Solution: Work and Kinetic EnergyDocument12 pagesProblem and Solution: Work and Kinetic EnergyJane100% (1)
- Phys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationDocument4 pagesPhys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationEngelbert Bicoy AntodNo ratings yet
- Arihant AIEEE PhysicsDocument3 pagesArihant AIEEE PhysicsraajeevmsNo ratings yet
- 8 CE199L-1 Physics2Document3 pages8 CE199L-1 Physics2IwaNo ratings yet
- Tut 12 (2016)Document2 pagesTut 12 (2016)Tendai M Mudziiri ShumbaNo ratings yet
- Es 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Document4 pagesEs 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Jerard BalalaNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Review Problems NewDocument6 pagesCh8 Review Problems NewVic VanceNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Solutions PDFDocument20 pagesTutorial 9 Solutions PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics ReviewerDocument4 pagesMechanics Reviewercobalt boronNo ratings yet
- CE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseDocument2 pagesCE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseSean TraverNo ratings yet
- Work Energy-6Document2 pagesWork Energy-6Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- Problem Set#8 PDFDocument29 pagesProblem Set#8 PDFMark Genesis VelonzaNo ratings yet
- Review Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2Document2 pagesReview Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2RamonNo ratings yet
- Particle Kinetics ProblemsDocument12 pagesParticle Kinetics ProblemsAeon ReignNo ratings yet
- Assignment2ed PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment2ed PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Summer 2016Document9 pagesDynamics Summer 2016islamatta91No ratings yet
- Review Notes7 Physics PDFDocument2 pagesReview Notes7 Physics PDFReynee Shaira Lamprea MatulacNo ratings yet
- Applied Dynamics QuestionsDocument5 pagesApplied Dynamics QuestionsKritamMaharjanNo ratings yet
- Examples MomentumDocument9 pagesExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Newton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) RectilinearDocument9 pagesNewton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) Rectilineardaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- Assign 3 - Ans Fall 2014Document2 pagesAssign 3 - Ans Fall 2014Mostafa Samir MorsiNo ratings yet
- DMCM 2713 Revision Questions (Chapter 4: Kinetics of A Particle: Impulse and Momentum)Document4 pagesDMCM 2713 Revision Questions (Chapter 4: Kinetics of A Particle: Impulse and Momentum)zul hilmiNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Document5 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- PP Otational Ynamics: B A C BDocument6 pagesPP Otational Ynamics: B A C BAbhinav ranaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 Div1A2A2B3BDocument2 pagesTutorial 7 Div1A2A2B3BAnimesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Practice Test FinalDocument23 pagesPractice Test FinalAllison TielkingNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 Motion MIDocument3 pagesTutorial 8 Motion MIPAWAN SHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document11 pagesChapter 10kiaunaNo ratings yet
- Practice-Problems-11_Dynamics-Part-2Document1 pagePractice-Problems-11_Dynamics-Part-2Jayve BasconNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument14 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- PHY11 Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesPHY11 Finals ReviewerAylaNo ratings yet
- Prblem Set 4 2S AY 2018-2019Document3 pagesPrblem Set 4 2S AY 2018-2019Allein Loisse EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet On DynamicsDocument6 pagesWork Sheet On DynamicstorsrinivasanNo ratings yet
- (Physics) AnswersDocument15 pages(Physics) AnswersLoraine Rose EstivaNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument17 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesAP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple Choicedipankar65No ratings yet
- FHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 6 SDocument4 pagesFHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 6 SSteve ThawNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Cambridge OLDocument14 pagesWork, Energy and Power Cambridge OLSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - FinalsDocument3 pagesProblem Set - FinalsJason TylerNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Business Research Study Material - Calicut UniversityDocument50 pagesBusiness Research Study Material - Calicut UniversityDr Linda Mary SimonNo ratings yet
- PHY3201Document3 pagesPHY3201Ting Woei LuenNo ratings yet
- Robbins OB15GE Inppt16Document31 pagesRobbins OB15GE Inppt16Nida IsrarNo ratings yet
- Analie T. Caro: Personal ParticularsDocument4 pagesAnalie T. Caro: Personal ParticularsAnalie Tañamor CaroNo ratings yet
- Excel Case Study 1 - DA - Questions With Key AnswersDocument56 pagesExcel Case Study 1 - DA - Questions With Key AnswersVipin AntilNo ratings yet
- Complete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedDocument82 pagesComplete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed Rajput75% (28)
- Illuminism - The Occult Force Behind Globalization - by Wes PenreDocument98 pagesIlluminism - The Occult Force Behind Globalization - by Wes Penrebreiard100% (1)
- Aci 306.1Document5 pagesAci 306.1safak kahramanNo ratings yet
- 05-Program Design and AnalysisDocument78 pages05-Program Design and AnalysisTarq AbdullahNo ratings yet
- D820-93 (2009) Standard Test Methods For ChemicalDocument10 pagesD820-93 (2009) Standard Test Methods For Chemicalobis8053No ratings yet
- Three Phase Traffic Theory PDFDocument11 pagesThree Phase Traffic Theory PDFKocic GradnjaNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate Prospectus 2021: World ChangersDocument35 pagesPostgraduate Prospectus 2021: World ChangersSKNo ratings yet
- Yu Gi Oh Card DetailDocument112 pagesYu Gi Oh Card DetailLandel SmithNo ratings yet
- BSM and NSM Best Practice 66Document67 pagesBSM and NSM Best Practice 66Freelancer83No ratings yet
- Electrode ChemDocument17 pagesElectrode Chemapi-372366467% (3)
- WRITTEN ASSIGNMENT Unit 2 - The Peer Assessment Strategy - 1Document2 pagesWRITTEN ASSIGNMENT Unit 2 - The Peer Assessment Strategy - 1asdsafsvvsgNo ratings yet
- Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDocument17 pagesDisaccharides and PolysaccharidesAarthi shreeNo ratings yet
- Module 24 - EditedDocument18 pagesModule 24 - EditedGabriel Cabansag50% (2)
- Information Pack: Creative Media EducationDocument26 pagesInformation Pack: Creative Media EducationDaniel VladimirovNo ratings yet
- Connected Topological Spaces: Definition 3.1.1Document22 pagesConnected Topological Spaces: Definition 3.1.1WilmerAlexanderVivasNogueraNo ratings yet
- The Law of DemandDocument13 pagesThe Law of DemandAngelique MancillaNo ratings yet
- PDMS JauharManualDocument13 pagesPDMS JauharManualarifhisam100% (2)
- Karl-Fischer TitrationDocument19 pagesKarl-Fischer TitrationSomnath BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SPEC 2 - Module 1Document21 pagesSPEC 2 - Module 1Margie Anne ClaudNo ratings yet
- February 2023Document2 pagesFebruary 2023rohitchanakya76No ratings yet
- Cook's Illustrated 090Document36 pagesCook's Illustrated 090vicky610100% (3)
- Section10 - POST-DRILLING ACTIVITIESDocument16 pagesSection10 - POST-DRILLING ACTIVITIESMohamed ElshoraNo ratings yet
- The Man Who Married A Hen, Stories of A Zambian SchoolboyDocument78 pagesThe Man Who Married A Hen, Stories of A Zambian SchoolboyGerard StoutNo ratings yet
- Jenkins Lab Guide: 172-172, 5th Floor Old Mahabalipuram Road (Above Axis Bank-PTC Bus Stop) Thuraipakkam Chennai 600097Document45 pagesJenkins Lab Guide: 172-172, 5th Floor Old Mahabalipuram Road (Above Axis Bank-PTC Bus Stop) Thuraipakkam Chennai 600097thecoinmaniac hodlNo ratings yet
- 2022 Consumer Trends ReportDocument29 pages2022 Consumer Trends Reportadelin litan100% (1)