Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week1 Ict
Uploaded by
Jhervhee A. Arapan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views11 pagesWeek1
Original Title
Week1 ict
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWeek1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views11 pagesWeek1 Ict
Uploaded by
Jhervhee A. ArapanWeek1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Harmful Light
Protect your eyes from the harmful light that may be in te fiber-optic
strands. The light is a color that humans cannot see. It can damage your eyes
before you can feel it When you use a magnifier to inspect fiber-optic cable
and connectors, the light emitted trom the fiber could be directed into yaur
eyes. When working with fiber, be sure to disconnect the light source. Lise
special detectors to help you toll ifa fiber is energized.
Caution:
Obtain proper training before you atlempt to aut, strip, or splice
fiber-optic cable. An experienced technician should supervise you until
you bacome adequately skilled.
Networking Devices, Media and Connector
To make data transmission more extensible and efficient than a simple
peer-to-peer network, network designers use specialized network dewcos
such as hubs, switches, routers, and wireless access points to send data
between devices You have already discussed in your Grade 9 CHS dass the
diferent devices used in networking and which prowdes you the knowedge
on the common networking cables that ane essential in putting up anetwork.
Common Network Cables
Until recently, cables were the only medium used to connect devices
on networks. A wide variety of networking cables are available. Coaxial and
twisted-palr cables use copper to transmit data. Fiber-optic cables use giass
of plastic to transmit data. These cables differ in bandwidth, size, and cost
You need to know what type of cable to use based on the job requirements.
You also need tobe able to troubleshoot and repair problems along the way.
< CHS 10,pd# =
Twisted Pair
Twisted parr is a type of copper cabling hat is used for telephone
communications and mast Ethemet networks. A pair of wites forms a circuit
‘hat ransmits data. The pair is twisted ta provide protectien against crosstak,
‘he noise generated by adjacent pairs of wires in the cable. Pairs of copper
wires are encased in color-coded plastic insulation and aro twisted together.
‘An auter jacket protects the bundles of twisted pairs.
‘Souroa: www lanshaek com
Figure 39, UTP and STP Gable
When electricity flows through a copper wire a magnetic fleld is
created araund the wire. Acircuit has two wires, and in a circuit, the two wires
have oppositely-charged magnetic fidds. When the two wires of the circuit
are next to each other, the magnetic fields cancel each other out. This is
called the cancellation effect Without the cancellation effect, your network
communications become slaw because of the interference caused by the
magnetic fields.
“The to basic types of twisted pair cables are as follows!
‘© Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)is the cable that has two or tour pairs
of wires. This type of cable ralies solely on the cancellation effect
Produced by the twisted-wre pairs that limits signal degradation
caused by oleciromagnetic interface (EMI) and rado frequency
interference (FFI). UTP is the mest commonly used cabling in
etworks. UTP cables have a range of 228 feet (100 m).
With shielded twisted pair (STP) each pair of wire is wrapped in
metallic foll to better shield the wres from noise. Four pairs of wires
are then wrapped in an overall metallic braid or foil, STP reduces
ectrical noise from within the cable, It also recuoos EM! and FFI trom
a6
Ad closed by Google
Stop seeing this ad
qutside the cable. Alhough STP prevents interference better than
UTP, STP is more expensive because of the extra shielding. It is also
more difficult to install because of the thickness In addition, the
metallic shielding must be grounded at bofh ends. If it is improperly
grounded, the shield acts like an antenna, picking up unwanted
signals.
Category Rating
UTP comes in several categories that are based on two factors:
4
5
= The number of wires in the cable
= The number of twists in those wires
. Category 3 is the wiring used for telephone systems and Ethemet
LAN at 10 Mega byte per second (Mbps).
Category 3 has four pairs of wires.
Category 5 and Category 5e have four pairs of wires with a
transmission rate of 100 Mbps.
Category 5 and Category 5e is the most common network cables
used.
Category Se has more twists per foot than Category 5 wring.
These extra twists further prevent interference from outside sources
and from the other wires within the cable.
Some Category 6 cables use a plastic divider to separate the pairs of
Wires, which prevents interference. The pairs also have more twists than
Category 5e cable.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxid cable is a copper-cored cable surrounded by a heavy
shielding. Coaxial cable is used to connect the computers to the rest of the
network.
Source: www. phoneam.com
Higure 40. Goaxial Wable
Coaxial cable uses “British Naval Connectors (BNC/J' or "Bayonet Neil-
‘Concalmar? connectors, at the ends of the cables to make the connection.
Several types of coaxial cable axist:
* Thicknai (108 ASE5) is a coaxial cable used in networks operating at
10 Mbps, with a maximum length of 500 moters.
« Thinnet (TOBASE2) is a coaxial cable used in networks operating at
10 Mbps, with a maximum length of 185 meters.
* FG-$9 is most commonly used for cable television in the U.S,
* AG-6 is higher-quality cable han AG-59, wih more bandwidth and
less susceptibility to interference.
Fiber -Optic Cable
An optical fiber is a glass or plastic conductor that transmits
Information using light Fiber eptic cable has one or more optical fibers
enclosed In a sheath or jacket Because It is made of glass, fiber-optic cable
Is not affected by EMI or FF. All signals are converted to light pulses to enter
the cable and are converted back into electrical signals when they leave it
This means that fiber-optic cable can deliver signals thal are clearer, and can
go farther, without compromising the clarity of signals.
Figure 41, Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber-optic cable can reach distances of several miles or kilometers
bafore the signal needs to be regenerated. Fiber-optic cable usually is more
expensive to usa than coppar cable, and the connectors ara more costly and
harder to assembie, Common connectors for fiber-optic networks are SC, ST,
and LC. These three types of fiber-optic connectors are half-duplex, which
allows data to flow In only one direction. Therefore, two cables are needed.
These are the two types of glass fiber-optic cable:
« Mulfmode's the cable that has a ticker core than single-mode cable.
| is easier to make can use simpler light sources such as Light
Emitting Diodes (LEDs), and works well over distances of a few
kilometers or less.
« Single-mode is the cable that has a very thin core. ft is harder to
make, uses lasers as alight source, and can transmit signals dozens
of kilometers with ease.
Creating Ethernet Cable
Ethernet cabling has been the standard in networking instalation for
years. It is the fastest way of connecting PC toa peer or to your router or a
central switch. This section of the module will bring you back to the
Procedures in creating an Ethernet cable specifically straight-through and
qoss-over. Try to recall the procedures as you go on with the lesson.
Fabricating an Ethernet Cross-over and Straight+through Cable
han Ethernet networking environment = like in a home or an office
with multiple PCs that are wired — the computers need to be connected to a
central router to allow data transfer. The router takes all the bits being sent
qui by the computers and relays them onto the other devices on he network.
The svaight-trough Ethernet cable is used in local area network
connect a PC to a network hub and router. This is the standard cable used for
almost all purposes.
A cross-over cable, on the other hand, can be used to connect two
network devioas directly, without the need for a router in the middie. it simply
reverses some of the pins so that the aufput on one computer is being sent to
‘the input of another.
Bear in mind thai safety precautions must always be applied and
observed during the fabrication of the said cables. Also, mawrials.and tools to
be used must always be complete and functional to save time, money and
effort,
The following items are the materials and tools used fo making
Ethernet cables:
v Ethernet Cable Category 5e or CatSe- standard wire for cabling:
R45 crimpable connectors for Cathe;
R45 Crimping tool;
Wire cutter, stripper or pliers; and
Ethernet cable tester.
saan8
Straight- Through
Figure 42. Cross-Over and Straight- Through Color Codng
The picture below will serve as your guide in making the two important
Ethernet cables.
1. Cut into the plastic sheath 1 Inch fram the end of the cut cable. Tha
crimping tool has a razor blacie that will do the trick with practica.
Figure 43. Step 1
2 Unwind and pair the similar colors.
3 Finch the wires between your fingers and straighten them out as
‘shown. The color onder is important to do this correct y.
Figure 45. Stap 3
4 Use wire cutter to make a straight cut across the wires 1/2 Inch from
‘he cutsleeve to the and of the wires.
§& Push the wires into the connector. Each wire fits Into a slotin the FUdS
connector. Note the position of the blue plastic shielding Also note
how the wires go all the way to the and.
Figure 46. Step 5
& Take Wew from the top. Make sure the wres are all the way In. There
should be no short wires.
Figure 47. Stap 6
7. Crimping the Cable - carefully place the connector into the Ethernet
Grimper and cinch down om the handles tightly, The copper splicing
fabs on the connector will piarca into each of the eight wires. Thera is
also a locking tab that holds the blue plastic sleeve in place for a tight
compression fit. When you remove the cable from the crimper, thatand
is ready to use.
Figure 48, Step 7
& For a standard "Straight-Through” cable, repeat all steps and wre
color order on the other end of cable. For a cross-over cable - the other
end wil have a different color order as shown by the crossover picture
mn page 64,
& Make sure to test the cables bebre Installing them. An Inexpensive
Ethernet cable tester does this quite wall,
Figure 49. Sep 9
Giss-Cross Puzde
Directions: Complete the criss-cross puzzle and familianize yoursell of the
cables belng described. Write your answer in a dean sheet af paper.
CABLES
: ial TTT]
Across
1. each pair of wires is wapped in metallic foil
43. one or more optical fibers enclosed in a sheath or jacket
4 used to connect two devicas directly
& cable that has two or four pairs of wires
7. the standard cable usad for almost all purposes
Down
1. cable that has a very thin core
2 cable that has a thicker core
4 used for telephone communications and Ethernet networks
4 copper-cored cable
Now that you are equipped with the knowledge on the different cables
weed in networking, you also need to know that fiber technologes and
connectors have changed through the years. In thesa videos, you will leann
about the different fiber connectors, copper connectors and their
characteristics. To watch the video presentations just type in the following
URAL:
1) http: weww professormesser.com/n 10-005/copper- connectors!
2)http sew. profess ormess er. com/n10-O00S/capper- connectors!
| hope you leamed a lot from the video presentations. After
‘watching tha videos, answer the following guide questions and submit
it to your teacher. Writa your answer in a clean sheat of paper. Good
Luek!
Here are the questions:
1. What ara the different types of fiber connectors? Cite their
advantages and disadvantages.
2 Ust down the different types of connectors,
Whatare the characteristics of UTP, STP and coaxial cable?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- TLE ICT Straight Through Cable LessonDocument6 pagesTLE ICT Straight Through Cable LessonJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- What is Science? Defining ScienceDocument8 pagesWhat is Science? Defining ScienceAdam ChabchoubNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Seat PlanDocument1 pageSeat PlanJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Fish Processing Learning ModuleDocument190 pagesK To 12 Fish Processing Learning ModuleSan Vicente Integrated80% (15)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Provincial Consolidated Monitoring ReportDocument1 pageProvincial Consolidated Monitoring ReportJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- BibliographyDocument3 pagesBibliographyJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Plumbing10 PDFDocument11 pagesPlumbing10 PDFPatrick PhoenixNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Mark Conrad DuzonDocument2 pagesMark Conrad DuzonJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Bam BamDocument4 pagesBam BamJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- M3 U3 Bill of MaterialsDocument14 pagesM3 U3 Bill of MaterialsPotchinoParuntongNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Home Networking 101 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesHome Networking 101 Lesson PlanJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Number 1 Single Acting SolisDocument3 pagesNumber 1 Single Acting SolisJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Madre de Cacao Is Nitrogen-Fixing Tree That Can Grow From 10 To 12 Meters High. ... inDocument4 pagesMadre de Cacao Is Nitrogen-Fixing Tree That Can Grow From 10 To 12 Meters High. ... inJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Retail Supply Chain Service Levels: The Role of Inventory StorageDocument18 pagesRetail Supply Chain Service Levels: The Role of Inventory StorageJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Bam BamDocument4 pagesBam BamJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Information and Communications Technology: Teachers GuideDocument2 pagesInformation and Communications Technology: Teachers GuideLevi Lico PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Meaningful vocabulary wordsDocument10 pagesMeaningful vocabulary wordsJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Home EcoDocument2 pagesHome EcoJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Tarp ApelDocument30 pagesTarp ApelJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Healthy Choices in The School CafeteriaDocument44 pagesMarketing Healthy Choices in The School CafeteriaJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Improving Handwashing in School CanteensDocument10 pagesImproving Handwashing in School CanteensJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Agricultural Economics ExplainedDocument7 pagesAgricultural Economics ExplainedJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Field Notes Zumba - 0Document3 pagesField Notes Zumba - 0Jhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- How To Enter Your Internship in Hawks Hunt-1Document2 pagesHow To Enter Your Internship in Hawks Hunt-1Jhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Agricultural Economics ExplainedDocument7 pagesAgricultural Economics ExplainedJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- LSPU Provides Quality Education Through Responsive InstructionDocument4 pagesLSPU Provides Quality Education Through Responsive InstructionJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Inquiries, Investigation and ImmersionDocument4 pagesInquiries, Investigation and ImmersionJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Transmitted Diseases ReportDocument15 pagesTransmitted Diseases ReportJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
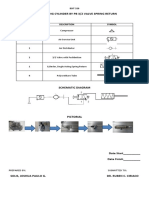
- Electro-Pneumatics & Principle of Operation: Prepared By: Kim Syro S. BorgoniaDocument16 pagesElectro-Pneumatics & Principle of Operation: Prepared By: Kim Syro S. BorgoniaJhervhee A. ArapanNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)